Where Did Humans First Appear?

- Early humans are thought to have evolved between 6 and 2 million years ago in eastern and southern Africa.
- Humans did not walk into the Americas until about 13,000 years ago, and are thought to have crossed a land bridge between Asia and North America.
- Evolution shows we share a common ancestor with chimpanzees and gorillas that lived millions of years ago.
Where do we come from? Many different groups of people have their own theories about the origins of humans. Science shows that human evolution goes back for millions of years on Earth. The very first humans are thought to have evolved in Africa. There are fossils of early humans showing we lived between 6 and 2 million years ago that have been found on this continent, and researchers think that hominids, or human-like beings, diverged from other primates during this time in eastern and southern Africa.
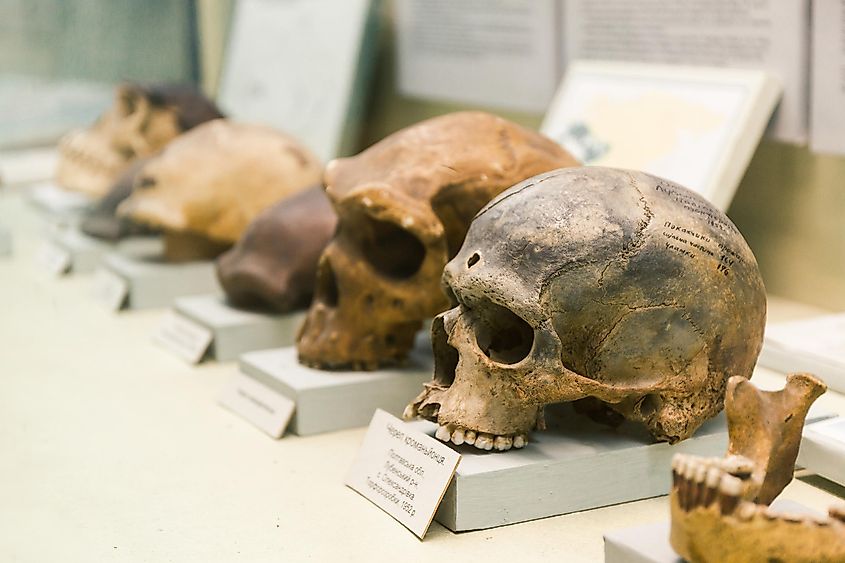
Many scientists now believe there were somewhere between 15 and 20 different species of early humans alive on the planet.
Did we evolve in seclusion? Hardly. We are primates, and we share a common ancestor with chimpanzees and gorillas; this ancestor was alive between 8 and 6 million years ago. Some scientists think that hominids who lived in the trees of Africa could have been pushed to leave the trees as the climate dried up, and shrank the forests while expanding the African savannah. This would have required early hominids to come down from the trees and to walk upright, or become “bipedal,” in order to find enough food to survive.
The Great Migration
It was not soon after walking on land that early humans left Africa, however. Only after we had been living for a long time on the continent did we finally decide to begin to move around the Earth. Scholars do not really know exactly why humans began to move from their original home, but it is believed that things like drought could have pushed early humans out of Africa in order to survive.
Timelines are certain but also vague. Homo sapiens (which is us, the first known modern humans) evolved on Earth somewhere between 300,000 and 200,000 years ago. We then waited until about 100,000 to 70,000 years ago to walk out of Africa into Asia and later Europe, where Neanderthals lived and eventually became extinct. Homo sapiens are thought to have reached Australia by canoe between 65,000 and 35,000 years ago. It is hypothesized that we then walked over a land bridge connecting Asia and North America about 13,000 years ago, and from there, migrated south.

As humans evolved to live in different environments and harnessed the power of fire, our brains also evolved. We learned to use language, develop weapons for hunting and defence, and to work together for an easier and better future. Eventually, many of us shifted from being hunter-gatherers and living a nomadic lifestyle, to living in settlements for longer periods of time, and turning to agriculture for survival.
We are now able to communicate around the world by video and voice and to share information in ways that would have stunned our ancestors. It is rather amazing what humans are able to achieve as we evolve.
What will the future look like? That seems to be up to us, and a larger power, if you believe in one, as well as the singular drive of evolution.