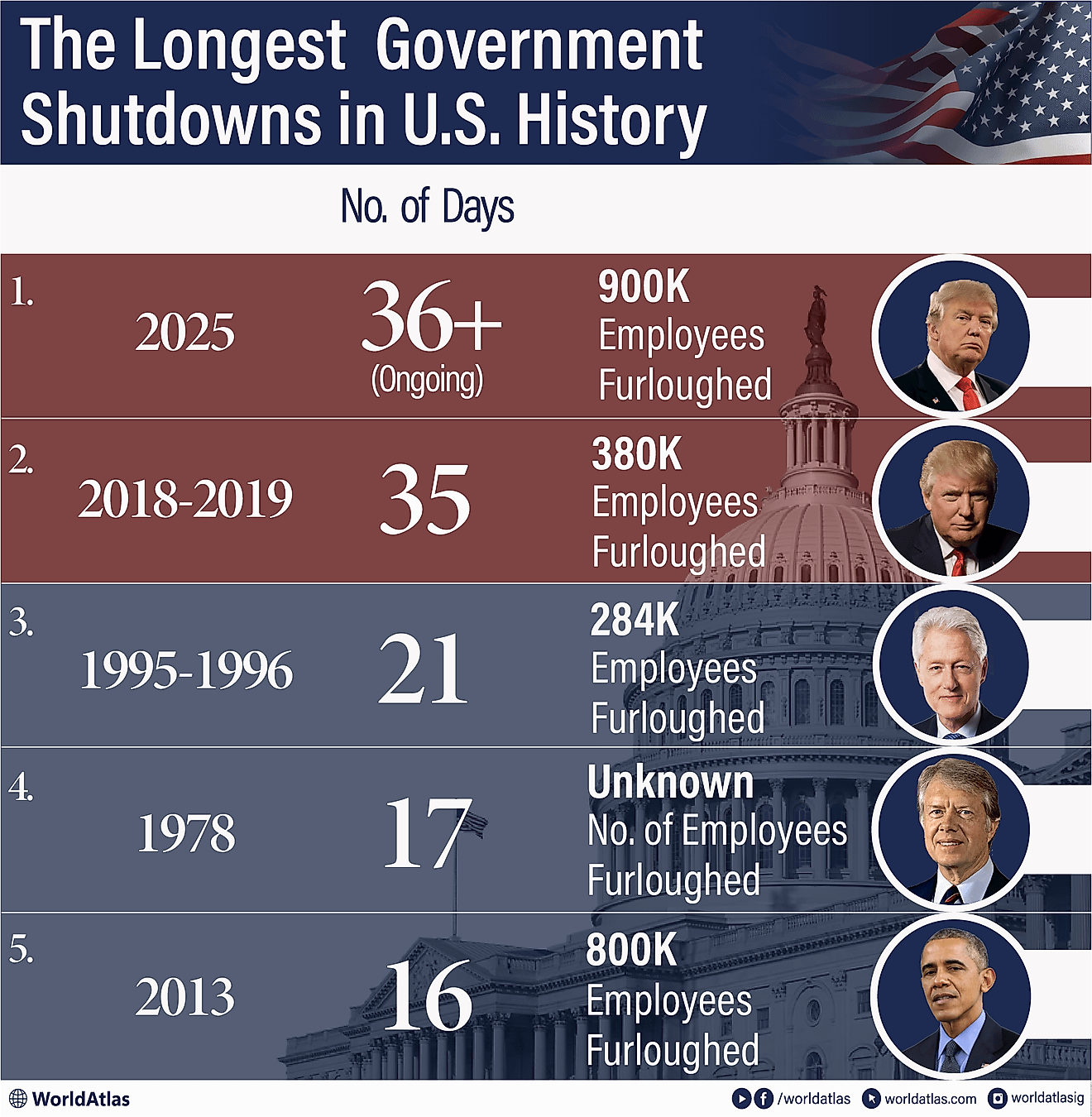
What Type Of Government Does The Central African Republic Have?

The Central African Republic is a semi-presidential republic, which attained independence from the French in 1960. The president of the Republic serves as the chief of state with the prime minister taking the role of the head of government. The Republic has gone through several transitions in its forms of government, which have evolved through a democratic process and military coups. Since its independence, presidents have established themselves as the overall authorities in the country. Attempts to establish democracy saw the ushering of a multi-party state in 1993 and a succession of coups to remove autocratic regimes. A transitional government was established in 2013 under the interim president Catherine Samba-Panza. The current form of government is established under the new constitution of 2015 establishing Faustin-Archange Touadera as the president and Simplice Sarandji as the prime minister. The country is a unitary state.
The Executive Branch Of The Government Of The Central African Republic
The head of government is the prime minister and is the supreme executive body in the Republic. The executive consists of the president the cabinet (which is made up of the prime minister and the council of ministers).It is the president of the republic who appoints the cabinet to serve for a term of six years. The citizens of the republic elect the president through popular vote and have a tenure of a five-year term. The council of ministers is responsible for initiating laws and overseeing the various operations of the government, and it is the president who chairs the council of ministers
The Legislative Branch Of The Government Of The Central African Republic
With the new constitution, the Central African Republic has a bicameral parliament with two chambers of the lower house or the national assembly and the upper house or the Senate, and the legislative power is shared between the parliament and the government. The legislature holds its meetings in Bangui, the capital city. The national assembly is made up of 131 members who are elected from their respective constituencies through a runoff system, when necessary they serve for five years. The parliament passes laws and nominates the prime minister.
The Judicial Branch Of The Government Of The Central African Republic
The Central African Republic has a civil law system that draws from the French system. The judiciary is the legal government body, which is made up of the Supreme Court, the constitutional court, the high courts, and magistrate courts. The highest court in the land is the Supreme Court and presided by the judges who are selected by the president for seven-year non-renewable terms. While the judiciary is supposed to uphold the sanctity of the law of the republic, outside parties sometimes influence its decisions mainly due to understaffing and under financing.
Elections In The Central African Republic
The Republic held its first general elections under the new constitution on December 30, 2015. The elections to determine the president and members of the national assembly ended in an annulment of the national assembly election results with no president. Since no presidential candidate achieved above 50% of the votes, a runoff was held in March 2016. The Transitional Constitutional Court, established under the transitional government, had the mandate of approving or annulling the election results as well as calling for runoffs. National Assembly elections were held in February 2016. The next general elections for the presidential and national assembly seats will be held in 2021. All citizens of the Republic who are above the age of 18 are eligible to participate in elections. The National Election Authority is the body responsible for overseeing the election process.