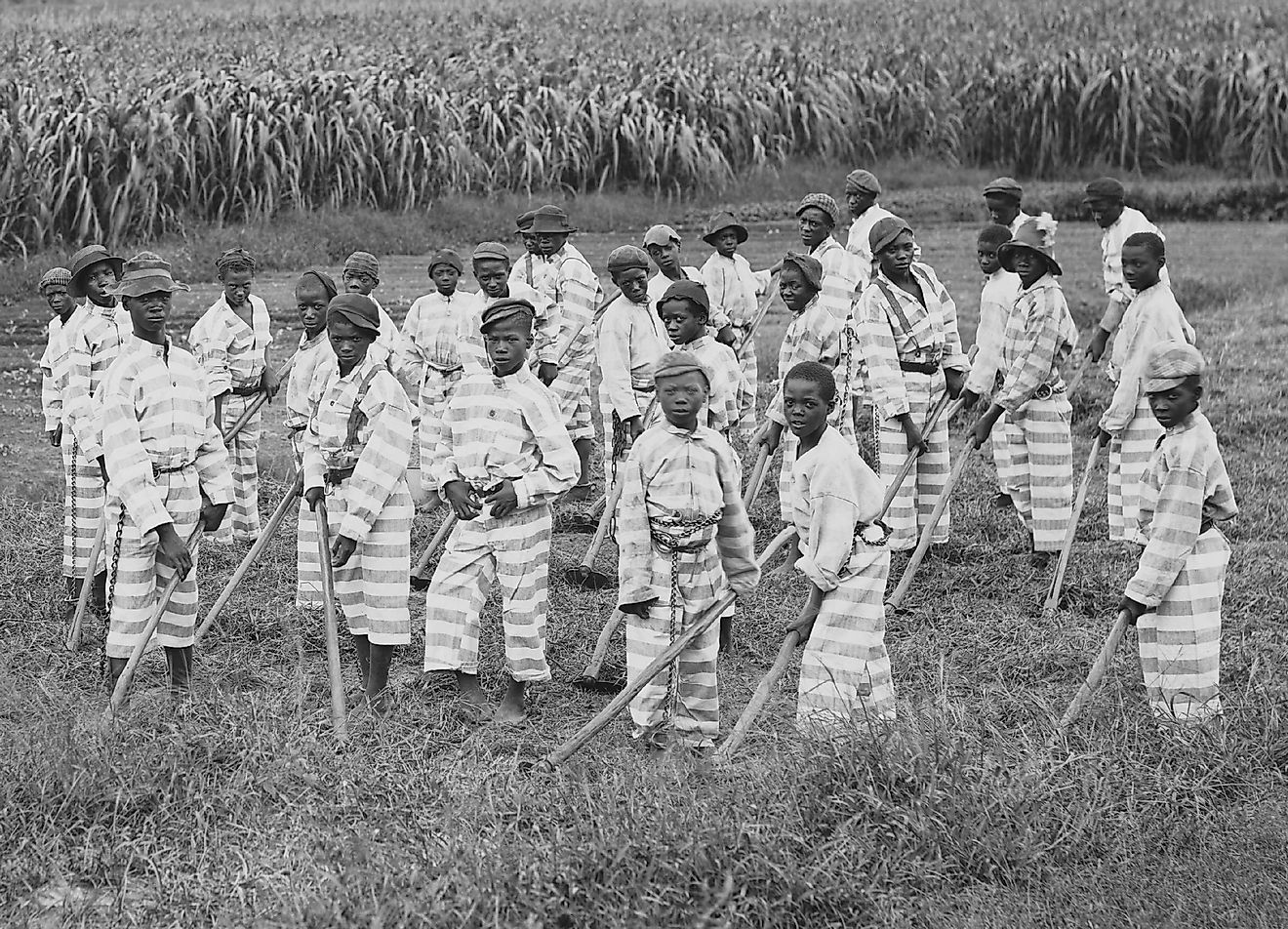
What Type Of Government Does Iraq Have?

Iraq’s federal government features the executive, judicial, and legislative branches in addition to many independent commissions. The country uses the Constitution approved in 2005 which established it as an Islamic, democratic, federal parliamentary republic.
The Executive Branch Of The Government Of Iraq
Executive responsibilities in Iraq are executed by the President and the Council of Ministers. The President requires a two-thirds majority from the Council of Representatives and can serve for a maximum of two four-year terms. The president of Iraq ratifies laws and treaties approved by the Council of Representatives and also grants pardons to convicts upon advice from the Prime Minister. The President further safeguards the nation’s unity, independence, and sovereignty as well as the security of Iraq’s territories. The Council of Ministers is made up of the Prime Minister who serves as the head of the government and his cabinet. The Prime Minister is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president directs the State policy and can dismiss the Ministers with the consent of the Council of Representatives. The Cabinet manages their respective ministries; appoints high-ranking officials such as the Director of the National Intelligence Service, ambassadors, undersecretaries, Division Commander and heads of security agencies; drafts the budget; and proposes laws.
The Executive Branch Of The Government Of Iraq
Legislative duties in Iraq are carried out by the Council of Representatives and the Federation Council. Iraq’s Constitution stipulates that the members of the Council of Representatives should be at a ratio of one to 100,000 Iraqi citizens. The council members are elected by the Iraqi population for four-year terms. The Council of Representatives is mandated to elect the country’s President and approve the appointment of top officials made by the Cabinet and the Higher Judicial Council. Representatives from regions and governorates will sit in the Federation Council.
The Judicial Branch Of The Government Of Iraq
The Iraqi federal judiciary system features various bodies and numerous courts regulated by law. The Higher Judicial Council is at the top of this judicial hierarchy. It oversees the activities of the federal judiciary and judicial committees. In addition to drafting the budget of the Judiciary, the Higher Judicial Council nominates such officials as the Chief Public Prosecutor and members of the Court of Cassation. The Supreme Court is legally authorized to interpret the Iraqi Constitution and also decide on the constitutionality of regulations and laws. The primary criminal court in the nation is the Central Criminal Court.
Federalism In Iraq
Iraq was first defined as a federal nation in 2003 by the short-lived Transitional Administrative Law. Article 118 of the country’s Constitution stated that no new region should be formed before the National Assembly has approved a law which provides the framework for creating a new region. A law was subsequently adopted in 2006 after an agreement was made with the Iraqi Accord Front. The agreement involved the creation of the constitutional review committee and the postponement of the law’s implementation for 18 months.
Independent Commissions And Institutions
The Council of Representatives monitors the various independent commissions namely the Commission on Integrity, the Independent High Commission for Human Rights, and the Independent High Electoral Commission. Iraq also has several administratively and financially independent bodies such as the Endowment Commission, the Board of Supreme Audit as well as the Central Bank of Iraq. Matters of the federal public service are handled by the Federal Public Service Council.