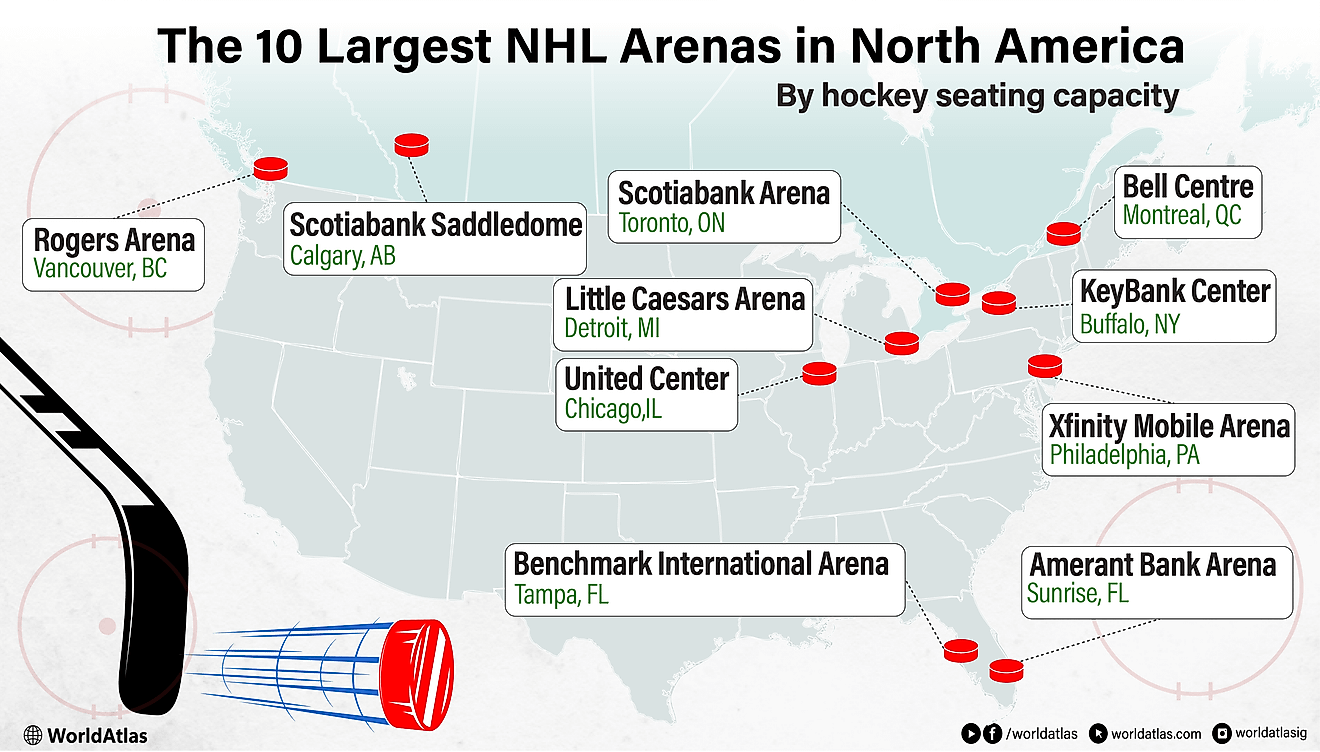
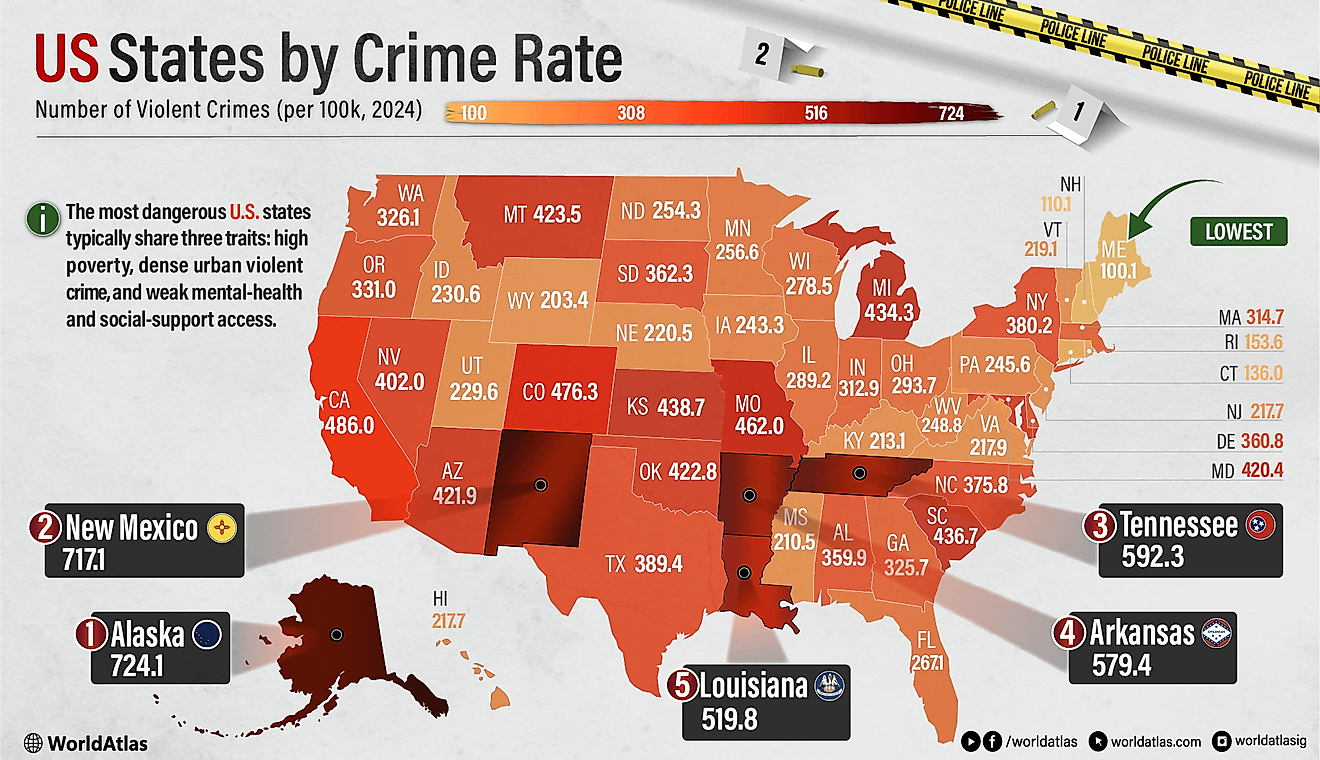
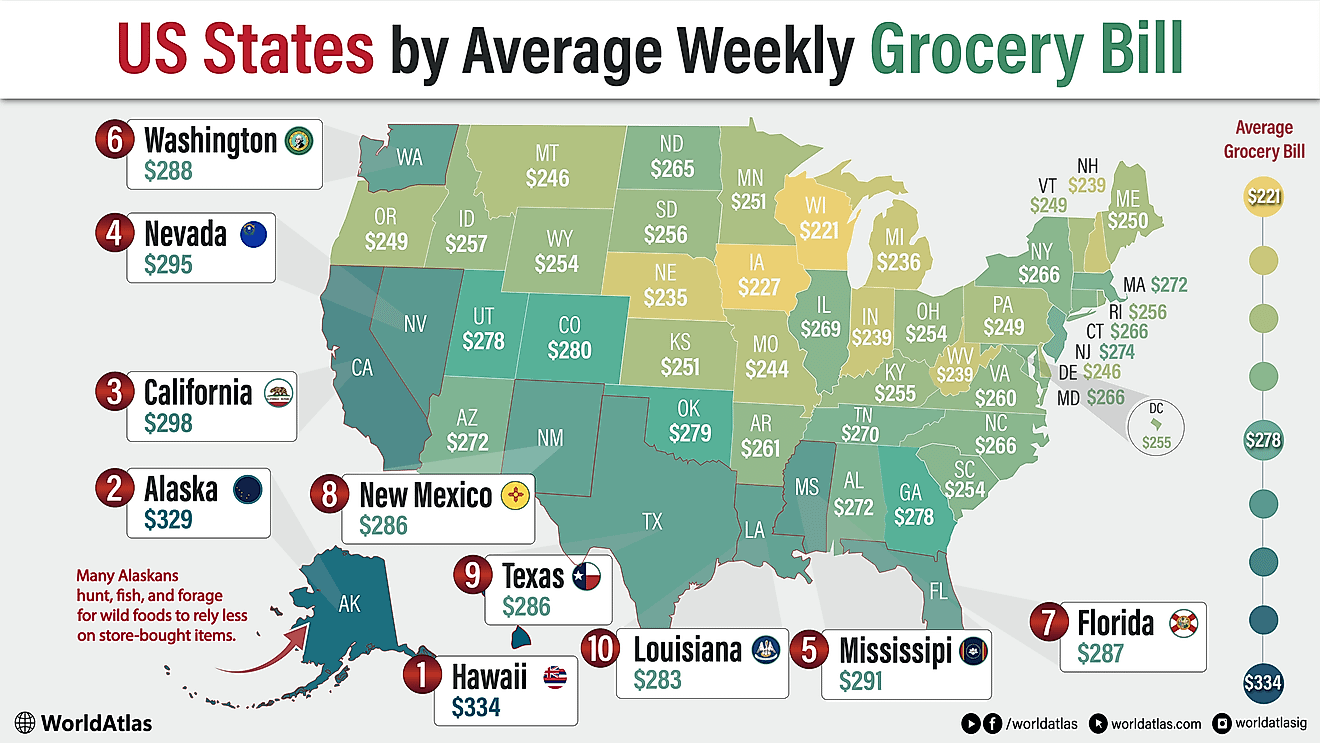
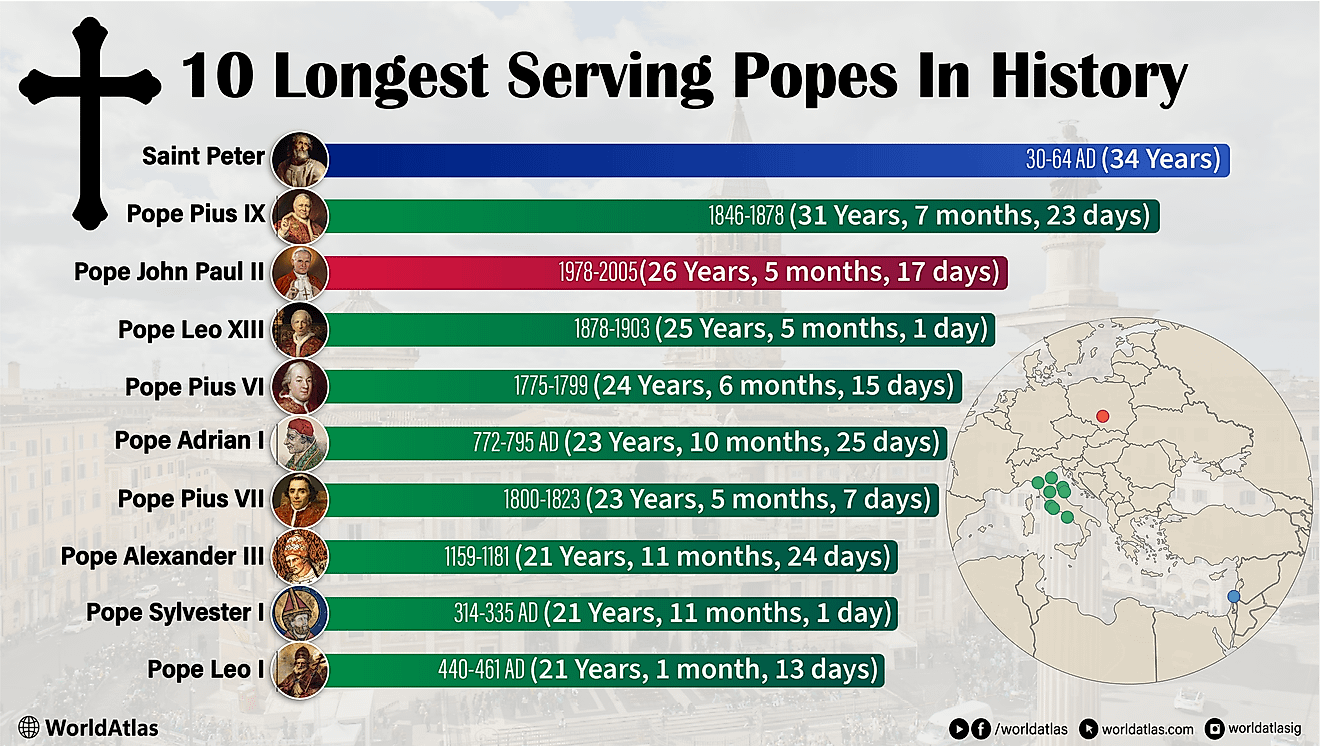
What Languages Are Spoken in Tanzania?

Tanzania is an East African country and Swahili is the nation's official language. English is widely spoken, and other languages spoken in the country are the native tongues of various ethnic groups. The ethnic languages are mainly of Bantu and Nilotic origin. These languages have various levels of growth, and 58 of 126 are considered to be in vigorous use, 18 are developing, some are dying, and three languages have become extinct. Most of Tanzania's population is fluent in their mother tongue and one other language, mainly Kiswahili. The general population has considerable knowledge of English, but their fluency in Swahili is more noticeable.
The Official Language of Tanzania
Swahili
Swahili is the official and most commonly used language in Tanzania. Swahili is a Bantu language that developed from interactions between Arab traders and the Bantu communities of the coastal region of East Africa. Besides its widespread use in Tanzania, Swahili is also spoken in neighboring countries of the East African community. Swahili has a native speaker base of about 20 million people. Swahili was first written in the Arabic script during its earlier period and later adopted the Latin system. The Christian missionaries introduced the Latin system of writing during their Christian works, including translations of the Bible. As the national language of Tanzania, Swahili brings a sense of identity and belonging to Tanzanians. The language is used in all spheres of life, including music, education, politics, legal affairs, technology, business, media, and film production.
Most Spoken Foreign Language of Tanzania
English
English was the language commonly used in the country during Tanzania's British colonial era. The language has been used alongside Swahili since independence as a medium of instruction in schools. However, during the presidency of Jakaya Kikwete, an overhaul of the educational system resulted in the abandonment of English as a teaching subject in schools.
Ethnic Languages Spoken in Tanzania
Tanzania is an ethnically diverse region with more than 100 ethnic communities. These communities fall into two broad classifications of either Bantu or Nilotes. Some of the Nilotic languages spoken in Tanzania include Maasai, which is shared among the Maasai group found in both Kenya and Tanzania. Other Nilotic languages include Datooga, Ngasa, Ogiek, Kisankasa, and Pare. Bantu languages spoken in the country include Bemba, Safwa, Digo, Hehe, Makonde, Nyamwezi, Yao, and Luguru, among others. Minority ethnic languages including those of the Afro-Asiatic family, such as Iraqw, Gorowa, Arabic, Burunge, and Khoisan languages like Hadza and Sandawe. Hadza and Sandawe are click dialects of Khoisan origin, used primarily by hunter-gatherer communities. Indo-European languages in Tanzania include Hindustani, Portuguese, French, and Gujarati.
Tanzanian Sign Language
Several sign languages are used by more than 280,000 members of the Tanzanian deaf community. Users are scattered but are more likely to be found in urban areas. Various forms of sign languages have been used both in education and in communication since 1963. While most schools for the deaf use sign language, others teach lip-reading. A standardized Tanzanian Sign Language was suggested in 1984, but has never been officially introduced.