What Is The Capital Of Tibet?

Where Is Tibet?
Tibet is an autonomous region within mainland China. The region is said to have the highest elevation on earth with an average altitude of 4,900 meters above sea level. The area is commonly referred to as ‘the roof of the earth’ due to its high elevation. It covers an area of 474,300 square miles. Tibet is situated on the Tibetan plateaus of Central Asia. It borders the Chinese Provinces of Yunnan, Sichuan, and Qinghai. India, Bhutan, and Nepal form the southern border of Tibet.
What Type Of Government Does Tibet Have?
Tibet is a province-level division of the Republic of China. The region enjoys autonomy from mainland China nonetheless. Tibet autonomous region was established in 1965 to replace Tibet area an administrative unit of the People’s Republic of China. The region is headed by a Chairman who has to be of Tibetan origin. The Chairman is under the rulership of a regional secretary of the Communist Party of China. The Chairman also works with a regional standing committee made of Tibetan and non-Tibetan members. Tibet is divided into seven prefectures and further sub-divided into 68 counties.
What Is The Capital Of Tibet?
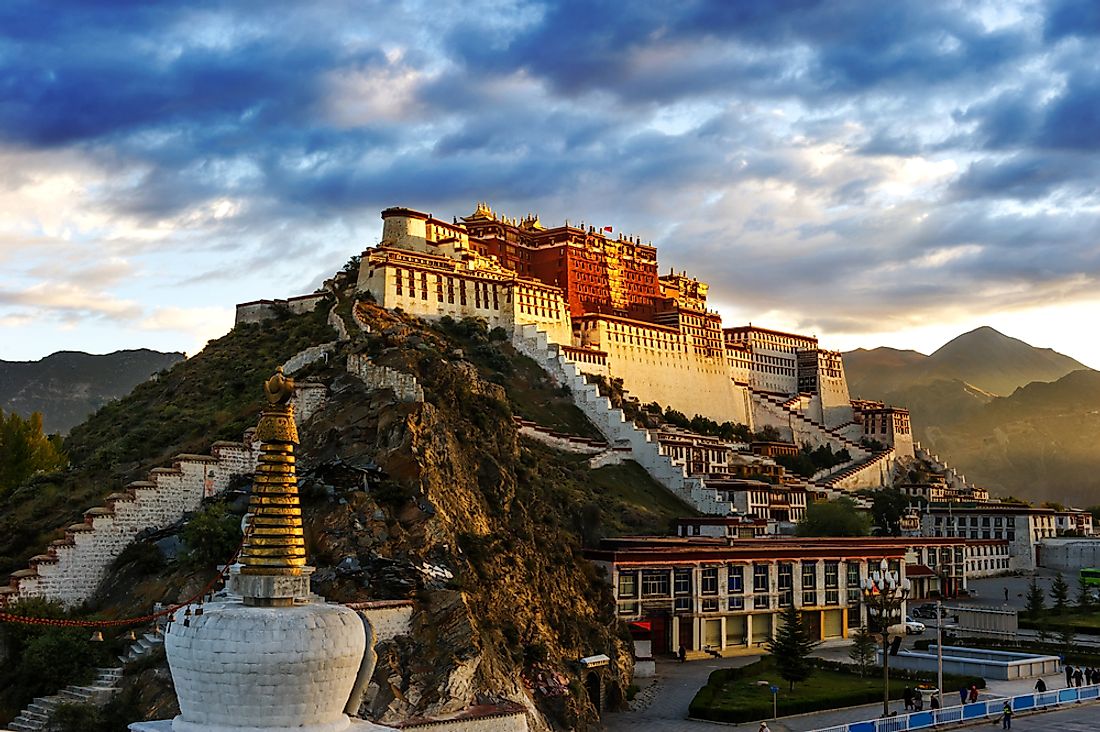
The capital city of Tibet is Lhasa. It is also an administrative and religious capital of the autonomous region of Tibet. The city has been in existence from as early as the 15th century when three famous monasteries were built in the area. At an elevation of 3,650 meters above sea level, the city is among the highest cities in the world. The city is a popular tourist destination.
Why Was Lhasa Chosen To Be The Capital Of Tibet?
Lhasa was established as the capital of Tibet in the 9th century. It became a prominent religious and political center mainly occupied by Buddhist monks and lay people. The city grew into a converging point of the historic trade routes from India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China. Lhasa turned into a cosmopolitan city with Chinese, Mongols, Nepalese, Armenians, and Indian traders occupying the city. Commodities such as gold, fur, saffron, tea, sugar, and medicinal plants were traded. In 1642, Lobsang Gyatso, the 5th Dalai Lama established Lhasa as a center of administration. Additionally, the Potala Palace, constructed in Lhasa as a winter residence for the Dalai Lama gave the city prominence. Other notable sites that gave significance to Lhasa are the Jokhang Temple and Norbulingka Palace.
Lhasa's Role As A Political And Religious Capital Of Tibet
The Jokhang Temple situated on Barkhor Square in Lhasa is viewed as the most sacred site for Tibetan Buddhists. The site is the spiritual center of Lhasa. The four-story temple is the famous site for tourists and Buddhist pilgrims who visit annually. Lhasa is an important political site in that it hosts two palaces for the Dalai Lama, a respected spiritual and political Tibetan leader. Until the 1950s, the Dalai Lama was the head of the Tibetan government. He exercised his leadership from Lhasa. Besides, Lhasa experienced political demonstrations against the Chinese government in the between 1987 and 1989.
Tibet is a region with a rich culture and history. Lhasa, its capital city, holds much of the cultural and historical significance. As a result, the city has three sites listed as UNESCO world heritage sites namely; the Jokhang Temple, the Potala Palace, and Norbulingka Palace.