What Is A Vihara?
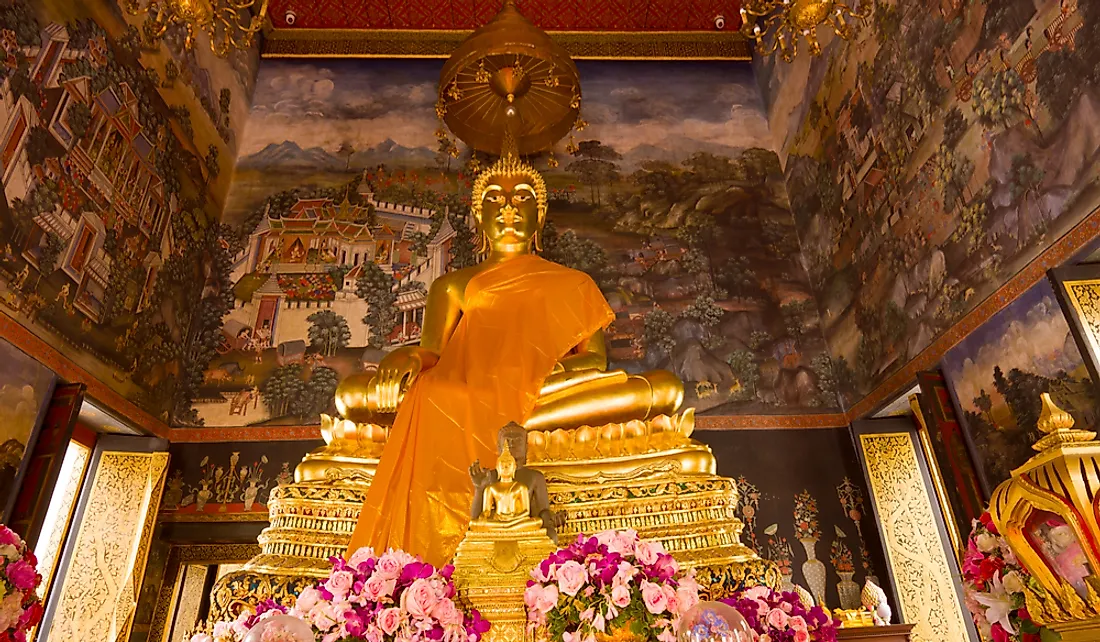

A vihara usually refers to a Buddhist monastery that is inhabited by Buddhist monks. However, the term can have different meanings. For instance, in other religious texts, such as Hindu, Ajivika, and Jain, a vihara refers to a temporary dwelling place for wandering monks seeking refuge or rest during the rainy season. Additionally, in Pali and Sanskrit, a vihara is a place for leisure and entertainment, while in Indian architecture viharas refer to central halls fitted with tiny cells that contain small beds carved from stone. Viharas are commonly found in Thailand because Buddhism is the country's predominant religion.
Origin of Viharas
During the reign of the Indian emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, "vihara yatras" were leisurely travels based around pleasure or hobbies, including hunting. However, after Ashoka converted to Buddhism, vihara yatras were replaced with "dharma yatras" that focused on religious purposes or pilgrames. Viharas were typically caves and involved cutting into the rock. They typically consisted of large halls and a series of small cells that contained a bed and pillow carved from stone. Viharas also usually contained monuments and symbols of Buddhist worship.
Significance of Viharas
The most significant part of a vihara is the shrine room, which is used for worship. Inside the shrine room, monks practice spiritual rituals to honor Buddha, and can give offerings such as flowers, water, incense, and candles. Most viharas also feature a hall for the ordination ceremony of new monks. In addition to serving as a religious place of worship, monks also use viharas as a place for study and learning. In fact, some viharas served as important Buddhist universities during the medieval era.
Practice of Meditation in Viharas
Buddhist monks observe two types of meditation: mindful and Metta reflections. The former practice is highly emphasized and entails devoting all of one’s thoughts in worship, whereas Metta meditation involves monks expressing love and kindness to one another. Buddhists typically practice meditation in a meditation hall.