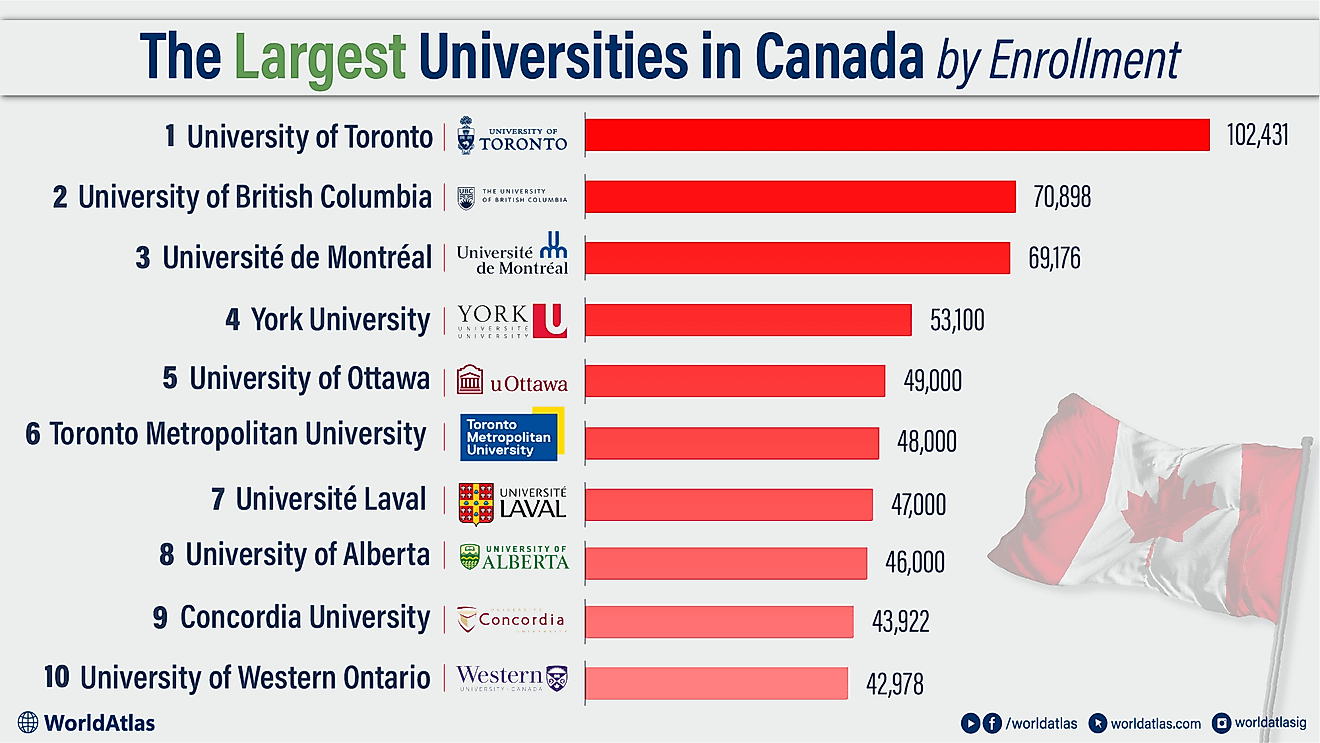
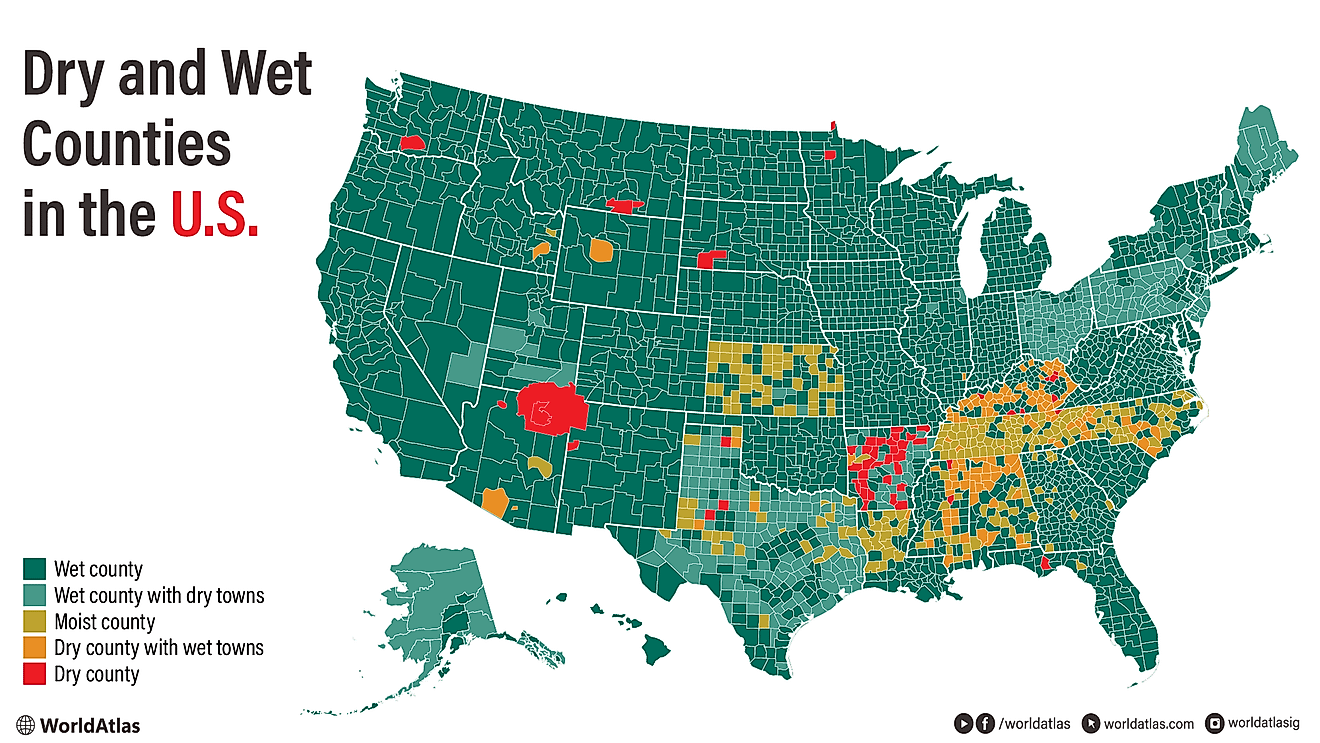
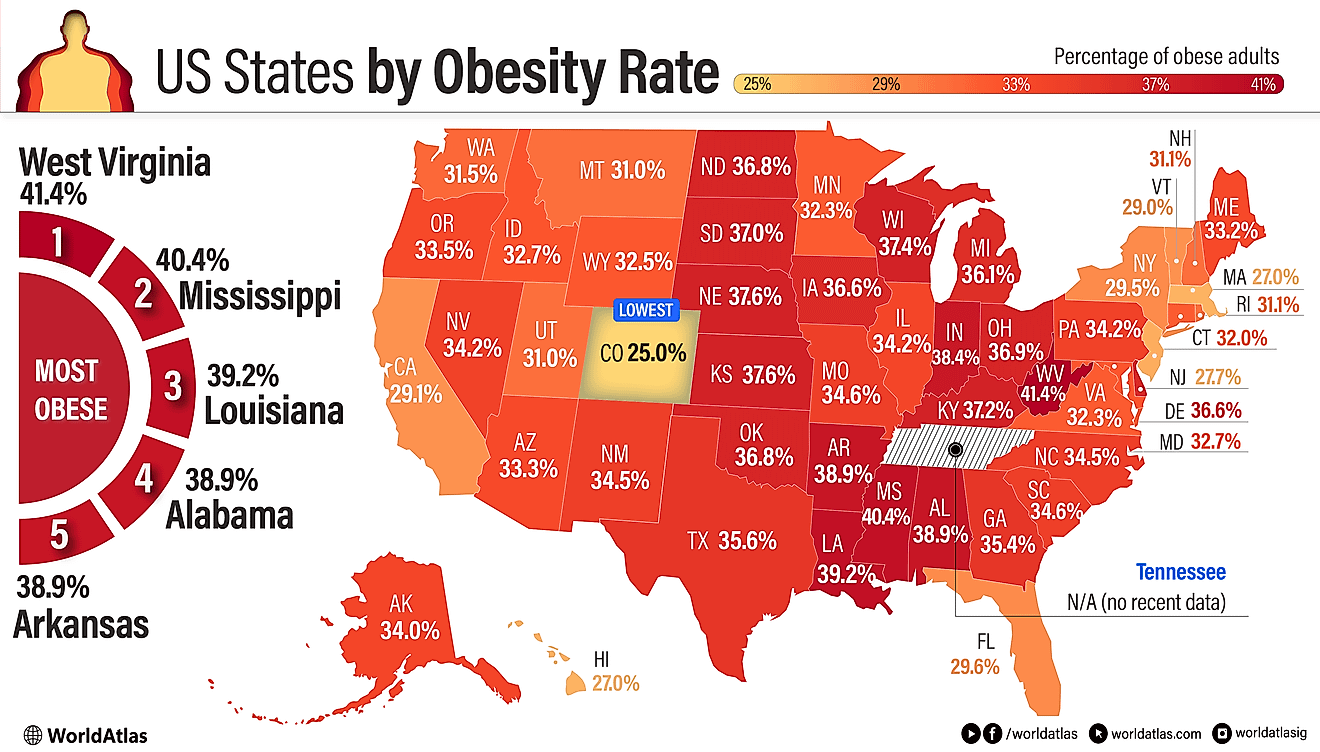
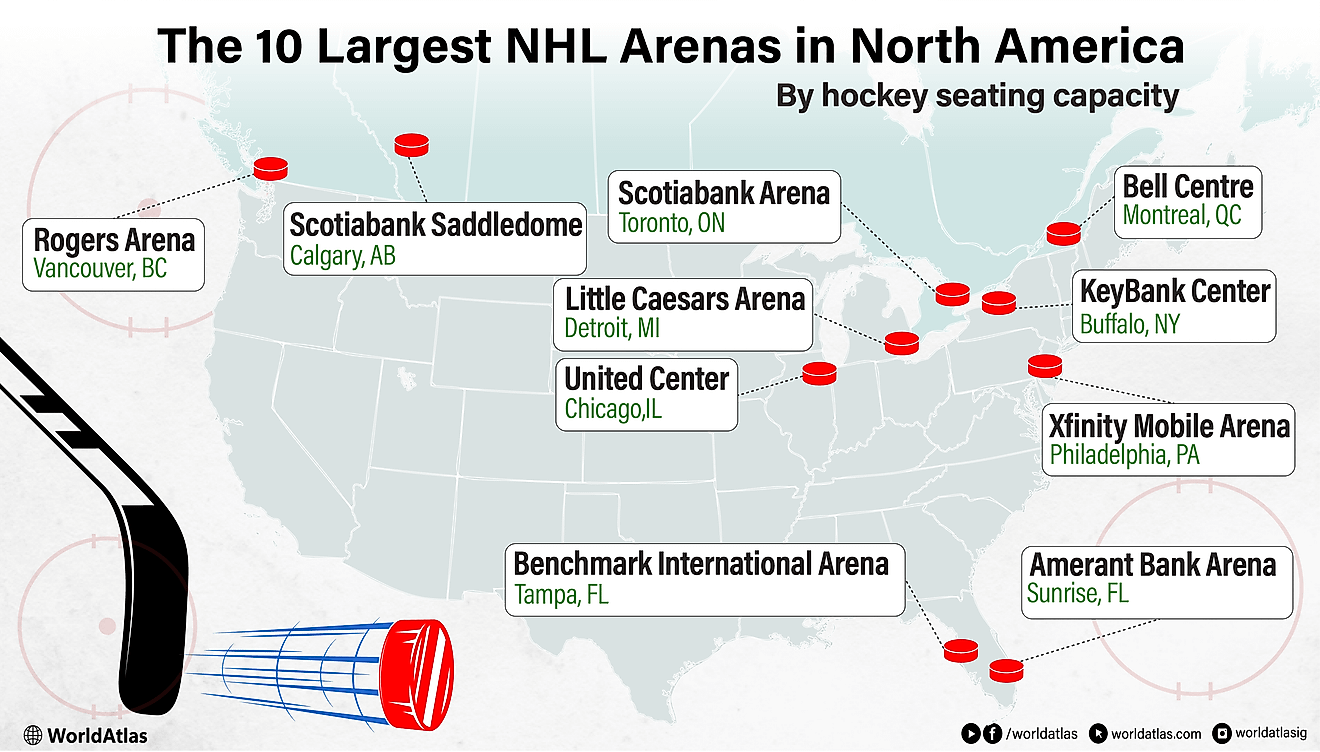
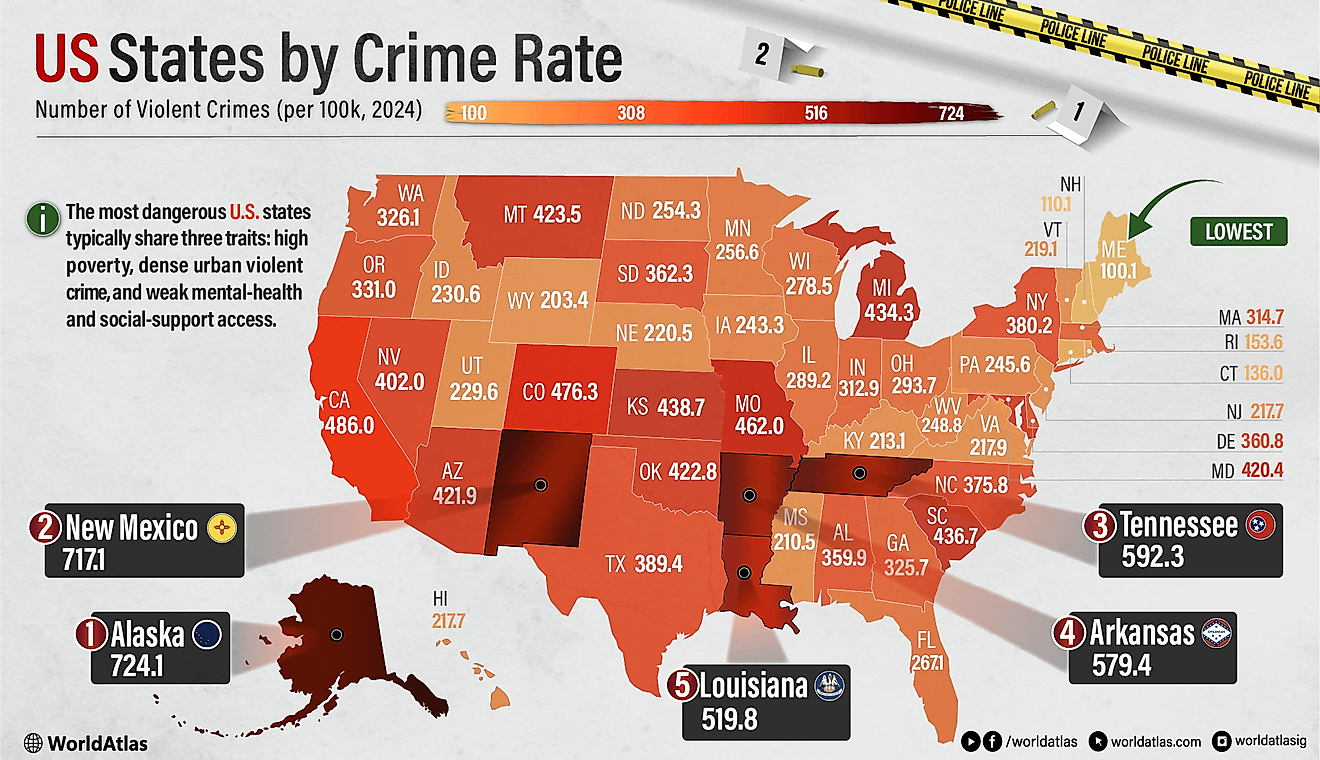
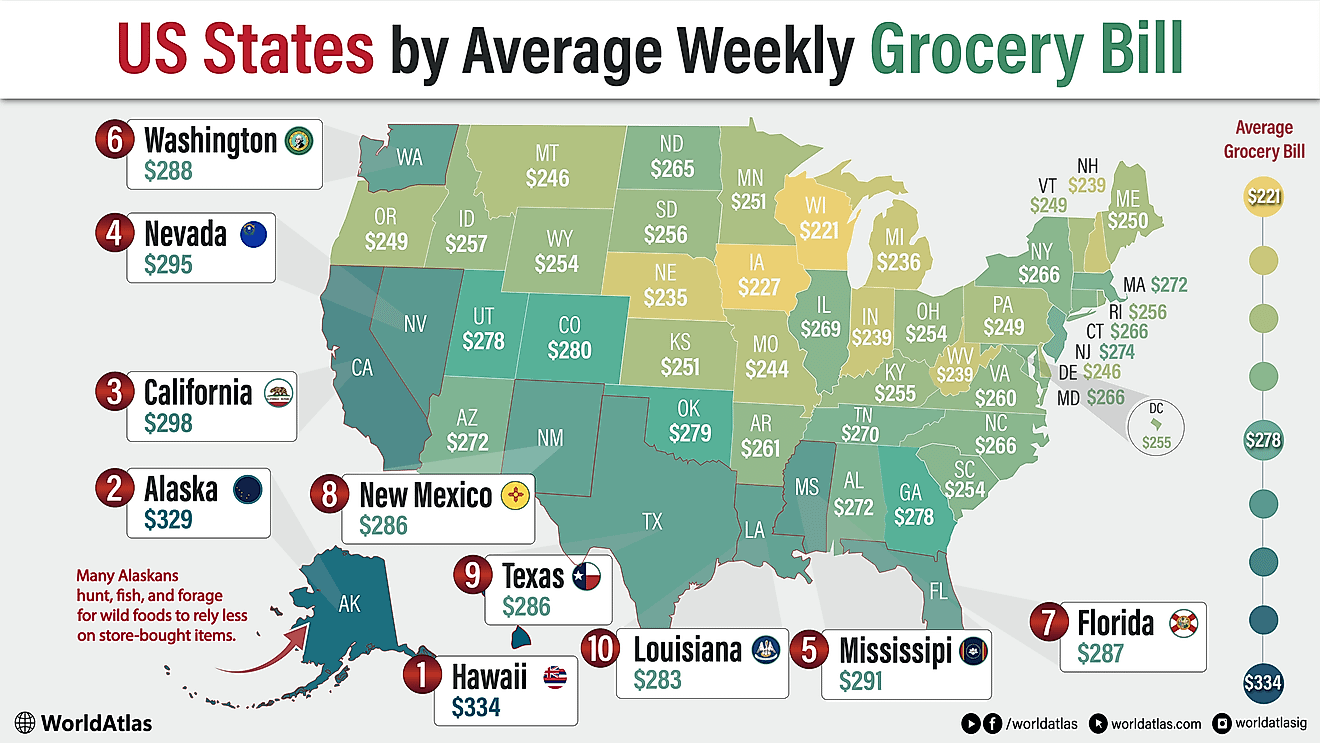
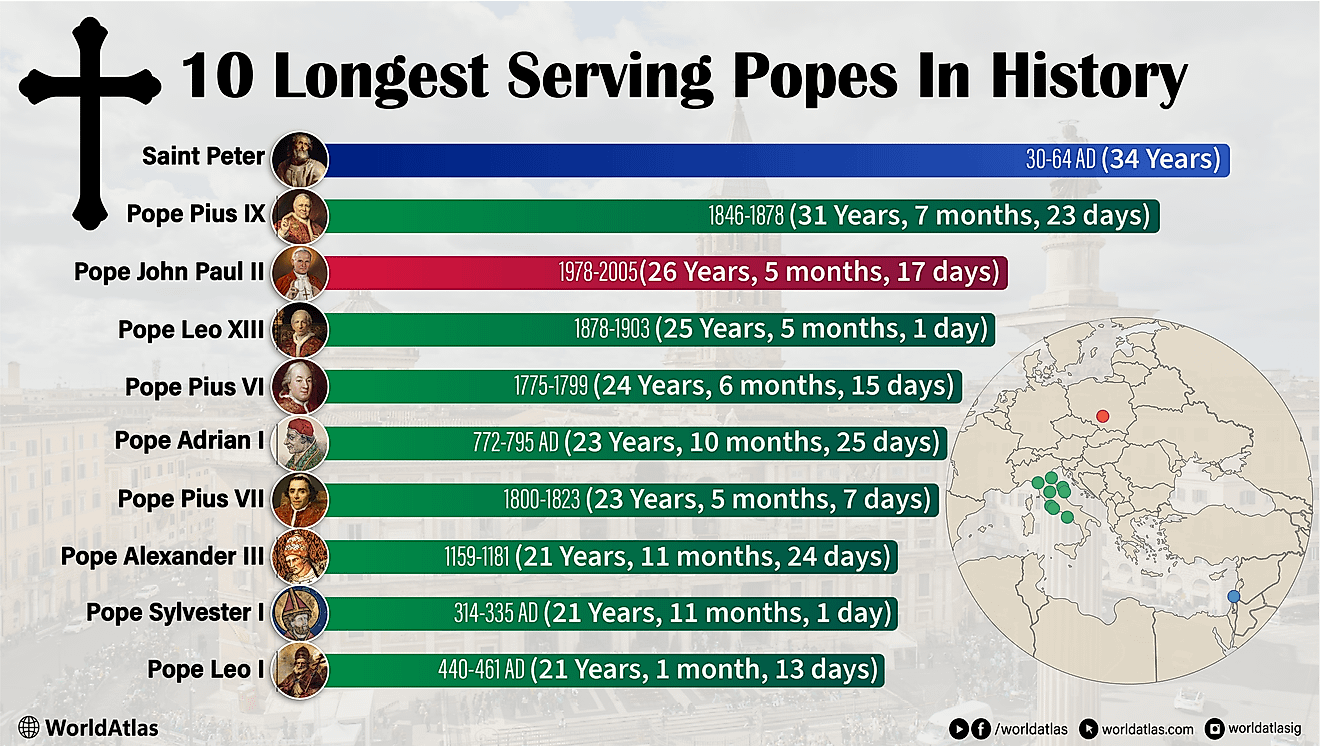
What is a Community?
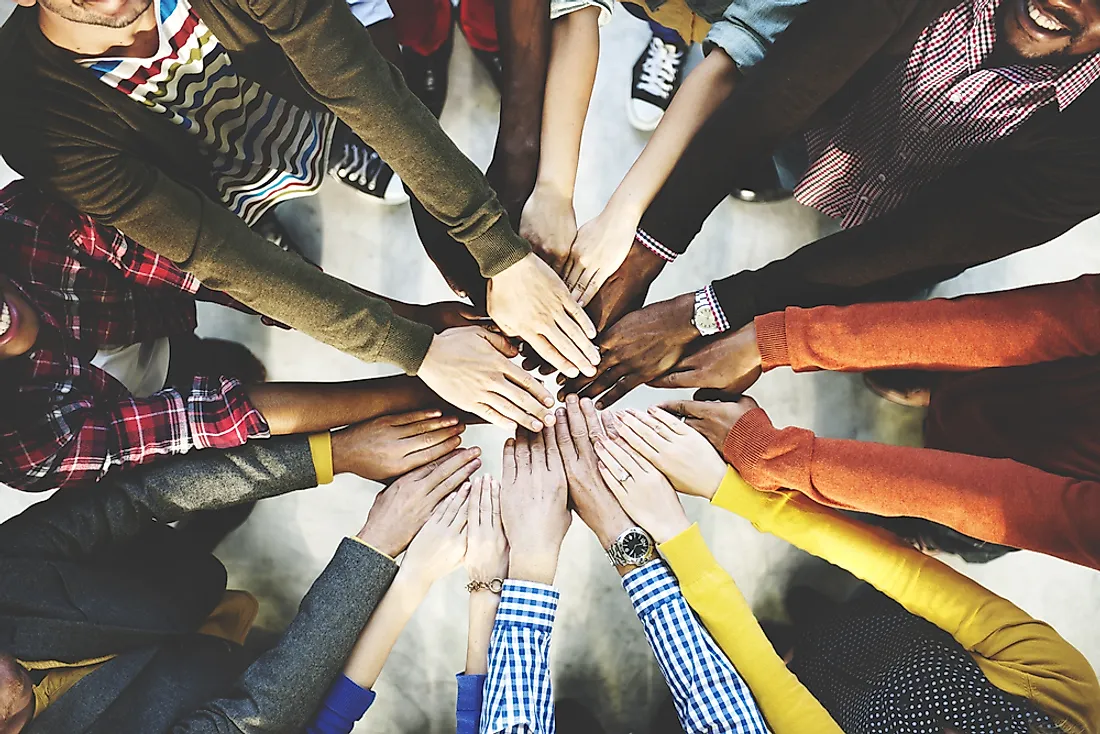

A community is comprised of a group of people residing or working together in an area. People belonging to a particular community may attend the same educational institutions, share activities, and purchase commodities from the same stores. Although people involved in bigger communities might not visit the same place all the time, they might believe in or like similar things. There is also cooperation in communities as the people offer assistance to one another. The term community is based on the Old French comuneté which derives from Latin communitas.
Description
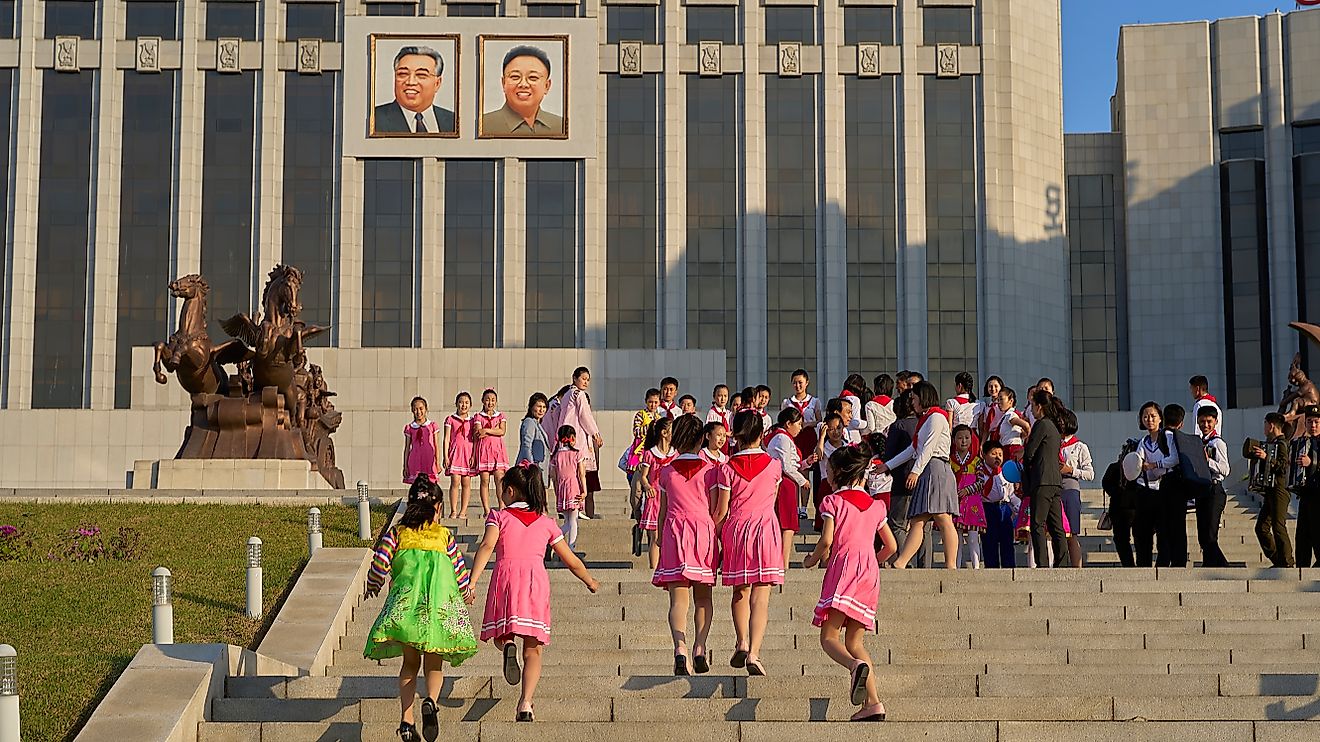
A community brings together people who have certain aspects in common including values, norms, and religion. Communities can either share a physical space contained in a particular geographical territory such as a neighborhood, village, or nation or a virtual space via communication platforms. Long-lasting relations formed outside genealogical roots create a sense of community too. People recognize such ties as integral to their practice, identity, and responsibilities in such social institutions as society, home, government, and family. Most communities are normally small in terms of personal social ties although they can be large group affiliations including international and virtual communities.
Characteristics
Communities are recognized by many different elements. A community revolves around people, and it is built upon a set of relationships among individuals and feelings. Participants of a community have a sense of safety, trust, and belonging. People participate in different communities based on their gender, age, neighborhood, country, faith, hobbies, politics, ethnicity, sexual orientation, and race. Communities also have formal and informal institutions. Institutions like schools, law enforcement, religious organizations, and government fulfill some of the needs of the communities. Credit and saving organizations, councils of elders, and gardening clubs are some of the informal institutions. Participants in a community have similarities in customs, language, culture, and traditions. Communities are nested within other communities. A neighborhood, for example, may have other communities revolving around ethnicities, race, age, and economic interests. Communities are also organized differently for example immigrants to a new destination may form a community.
Types
Different types of communities have been identified. Geographic communities refer to those communities sharing physical space and participants thus relate to each other because of proximity and not intent. The people in such communities have to have a sense of belonging and share at least several values for them to be working community. Communities of interests arise where participants willingly choose to be involved in a community revolving around common interests and concerns. Virtual communities involve people linking through communication media. Participants in online communities interact via computer networks, and they discuss similar concerns for periods long enough to create webs of personal relationships.
Community Development
Community development is primarily associated with community work, and it may include stakeholders, government agencies, foundations, NGOs, and universities. These organizations implement programs intended to advance the social standing of local, regional, and even national communities. Community organizing or building refers to more grassroots efforts which empower people and groups alike to bring about change in their societies by equipping them with specific skills. Such skills enable people to build political power by the creation of large social groups with a common agenda.