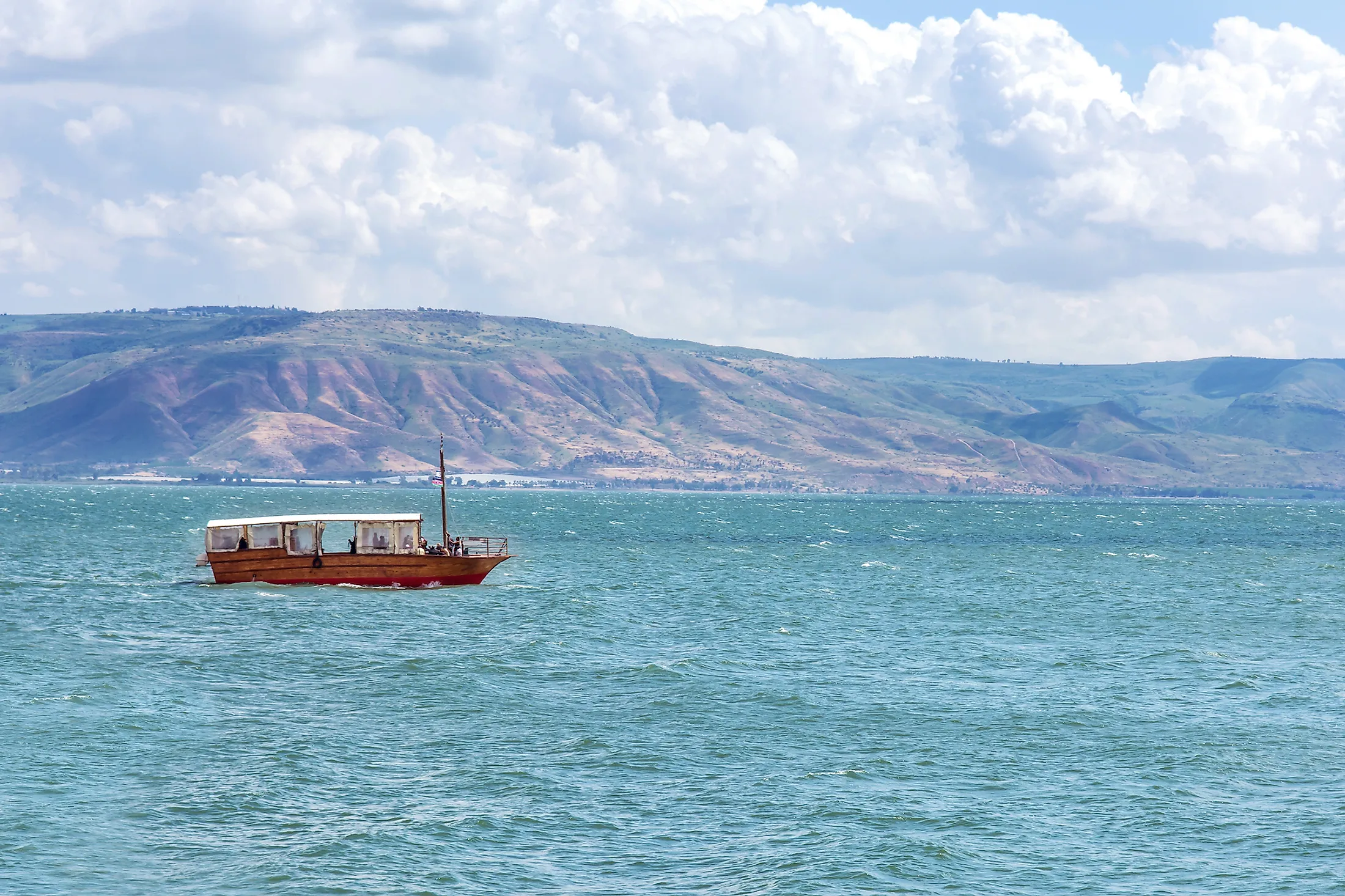
Sea Of Galilee
Also referred to as Lake Tiberias, the Sea of Galilee is a large freshwater lake situated in the northeastern part of Israel. The Sea of Galilee is considered the lowest freshwater lake on the planet and the world’s second-lowest lake after the Dead Sea. Throughout its history, the Sea of Galilee has been referred to by various names such as the Sea of Kinneret, Lake of Gennesaret, Sea of Ginosar, Sea of Tiberias, Lake of Tiberias, Bahr Tubariya, etc.
About The Sea of Galilee
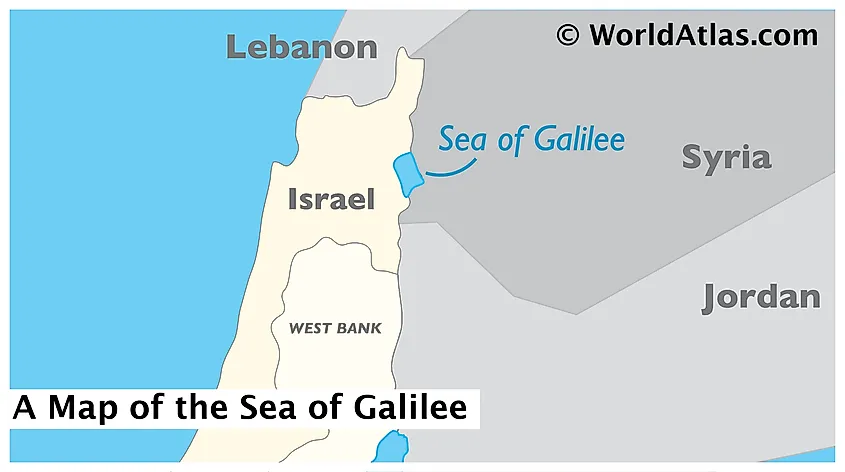
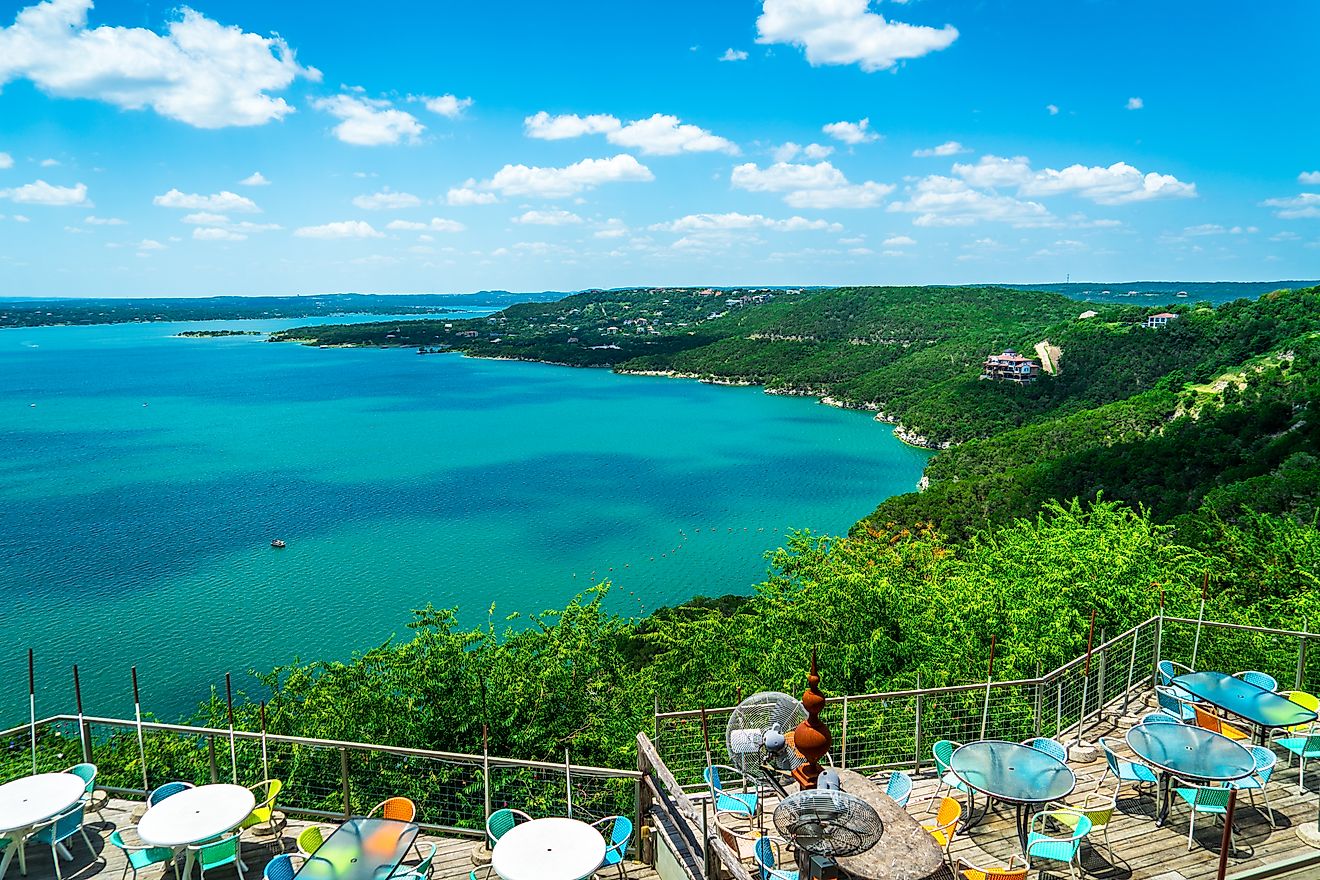
Covering an area of 166 sq. km, the Sea of Galilee is a large freshwater lake located in the Jordan Rift Valley between the Galilee region and Golan Heights in the northeastern part of Israel, close to its borders with Jordan and Syria. The Sea of Galilee is a pear-shaped monomictic lake with a length of 21km, a maximum width of 13km, and a circumference of 53km. Being the planet’s lowest freshwater lake, the surface elevation of the Sea of Galilee varies between 215m and 209m below sea level. The lake reaches an average depth of 25.6m and a maximum depth of 43m. The Sea of Galilee holds a water volume of about four cubic kilometers and has a residence time of 5 years. The National Water Carrier of Israel transfers water from the Sea of Galilee in the north to the highly populated centers of the country in the south. At present, the Sea of Galilee supplies about 10% of the total drinking water needs of the country.
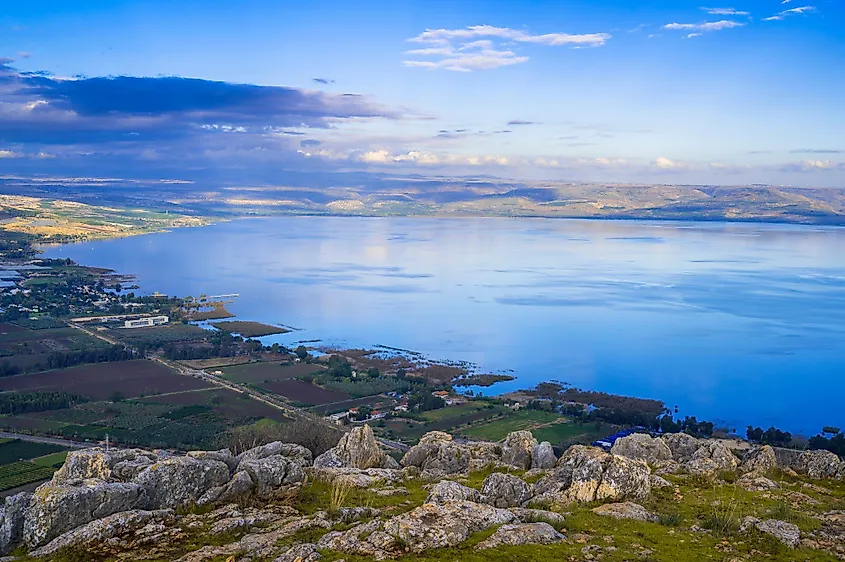

The Sea of Galilee is primarily fed by the Jordan River and partly by underground springs. Besides being its inlet, the Jordan River also serves as the outlet and exits out of the lake at the Degania Dam. In addition to this, the lake also loses water by evaporation. Geological studies have revealed that the Jordan Valley was formed due to the separation of the African and the Arabian tectonic plates. Therefore, the Sea of Galilee area is subjected to many earthquakes and has also witnessed intense volcanic activities.
Ecology Of The Sea of Galilee
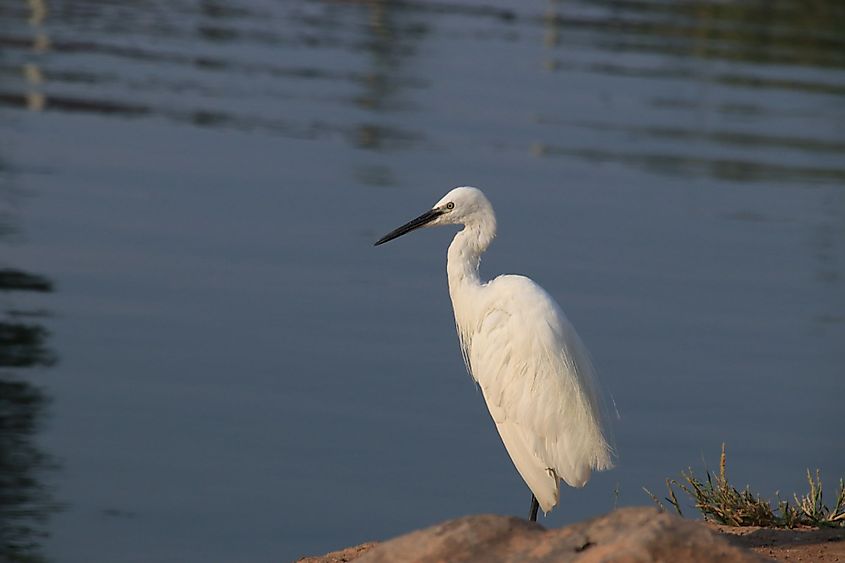

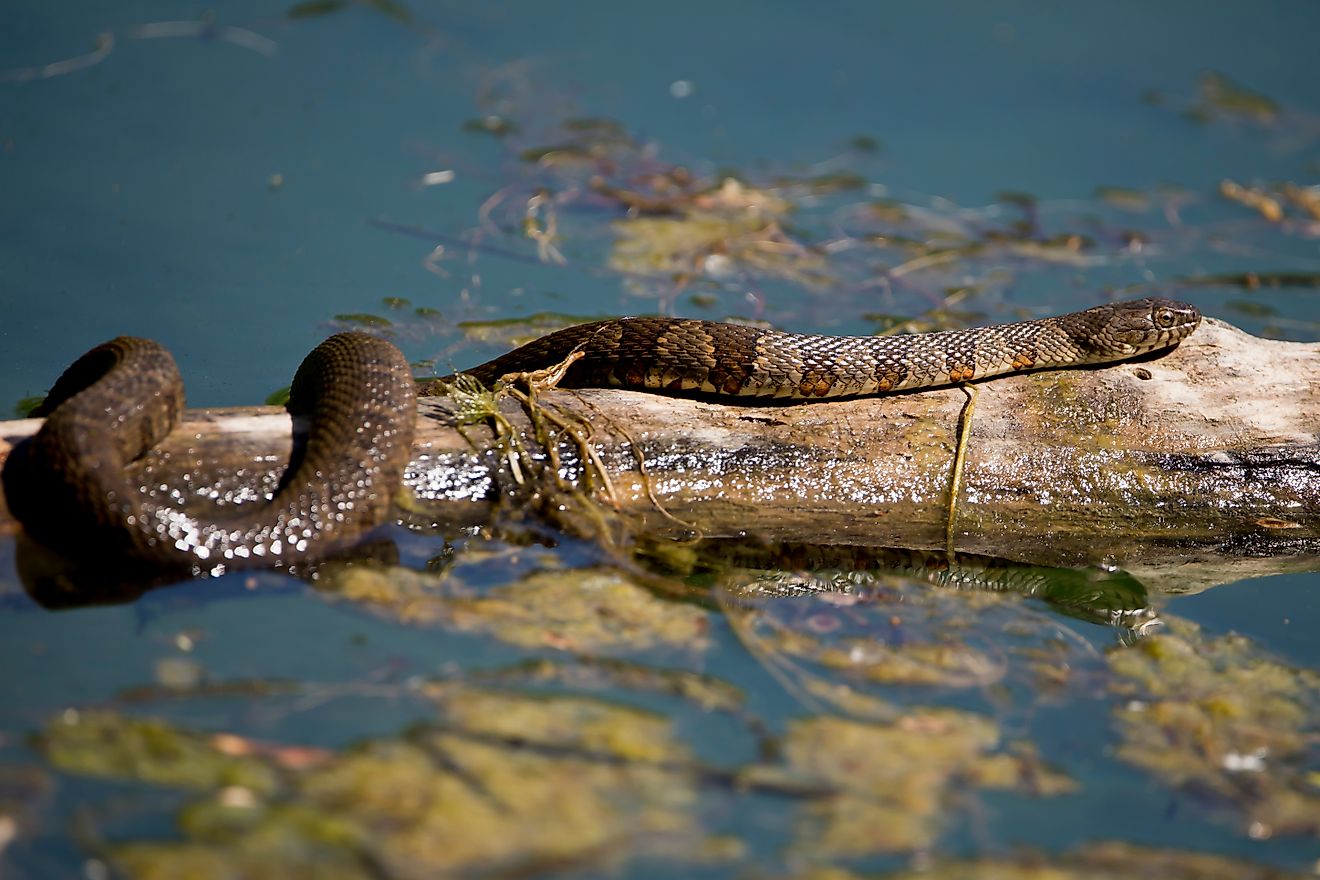
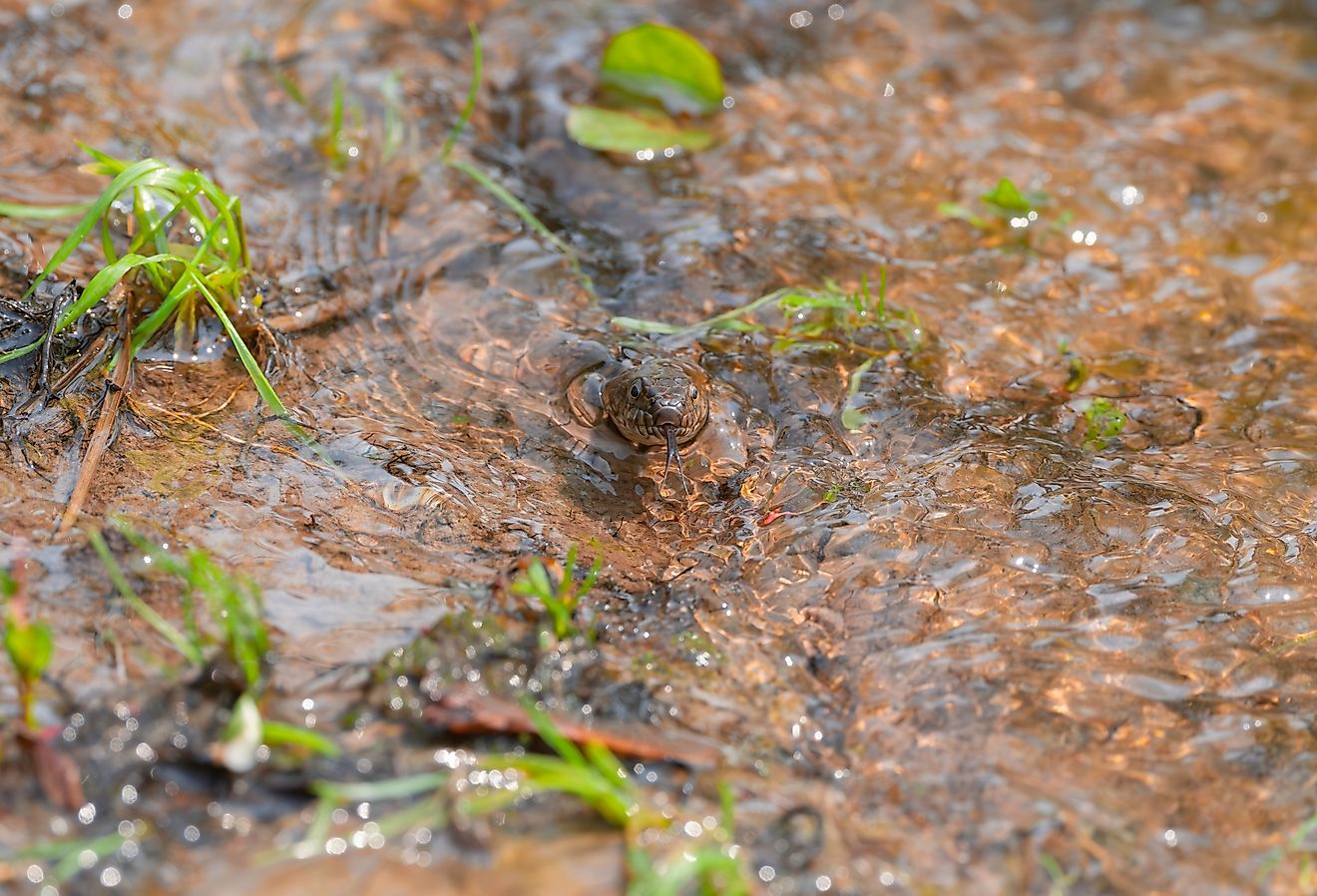
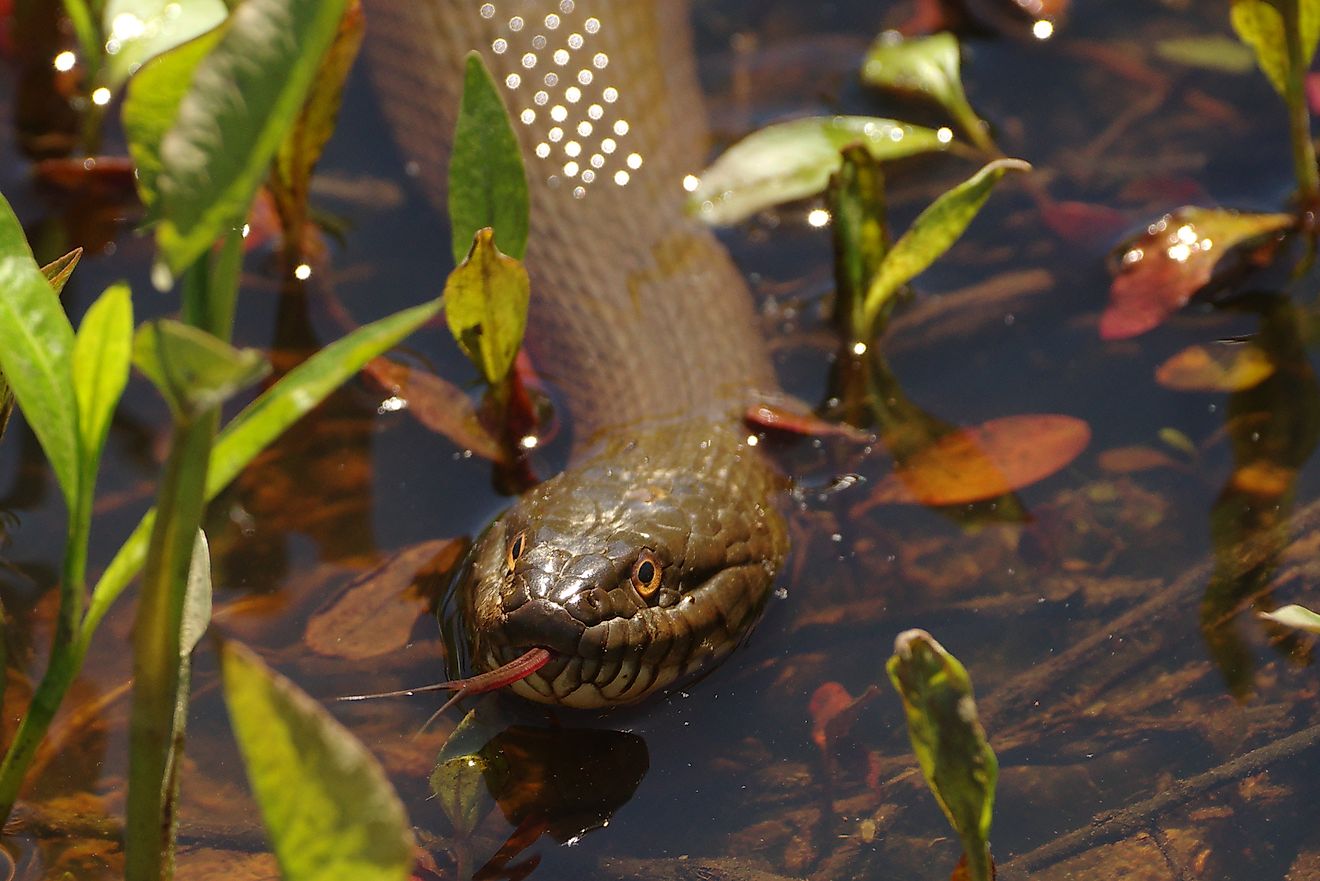
The waters of the Sea of Galilee support a variety of flora and fauna. The local flora found along most of the lake’s shoreline include various reeds and phytoplankton. Some of the notable fauna found in the lake include zooplankton and fishes like the Kinneret bleak, tilapia, catfish, the long jaw tristramella, the short jaw tristramella, etc. The tilapia species found in the lake include the Galilean tilapia, the blue tilapia, and the redbelly tilapia. The Sea of Galilee and its surroundings have been designated as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International. The freshwater lake supports many avian species like marbled teals, grey herons, great cormorants, great crested grebes, great white egrets, black-headed gulls, griffon vultures, and black francolins.
Tourism
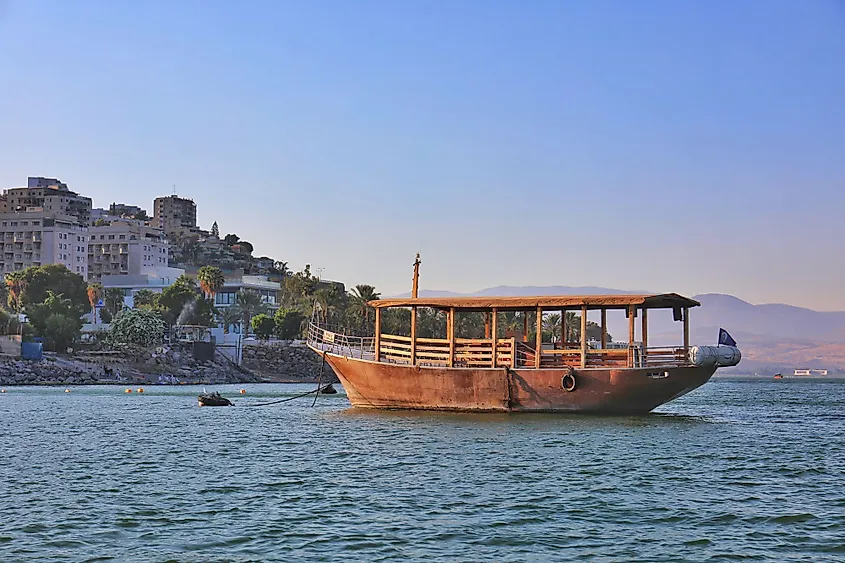

The Sea of Galilee is a popular tourist attraction that draws many local and international tourists. The Sea of Galilee is a popular attraction for the Christian pilgrims who visit the region to see where Jesus Christ performed miracles as per the New Testament. In April 2011, a 64km long hiking trail in the Galilee region referred to as the “Jesus Trail” was constructed by the Government of Israel for the Christian pilgrims. The hiking trail includes a network of roads, bicycle paths, and footpaths that connects the holy sites associated with the lives of Jesus Christ and his disciples. The hiking trail ends at the ancient fishing village of Capernaum on the northern shores of the Sea of Galilee, where Jesus Christ is believed to have delivered his “Sermon on the Mount.” Every year in September, the Kinneret Crossing, one of Israel’s most well-known open water swim races, is held, which attracts a lot of swimmers to participate in the racing events. Tourists also enjoy raft building on Lavnun Beach. The other economic activities that take place in the lake and its surrounding fertile areas include commercial fishing and the cultivation of grapes, dates, bananas, olives, and mangoes.
Brief History Of The Sea of Galilee
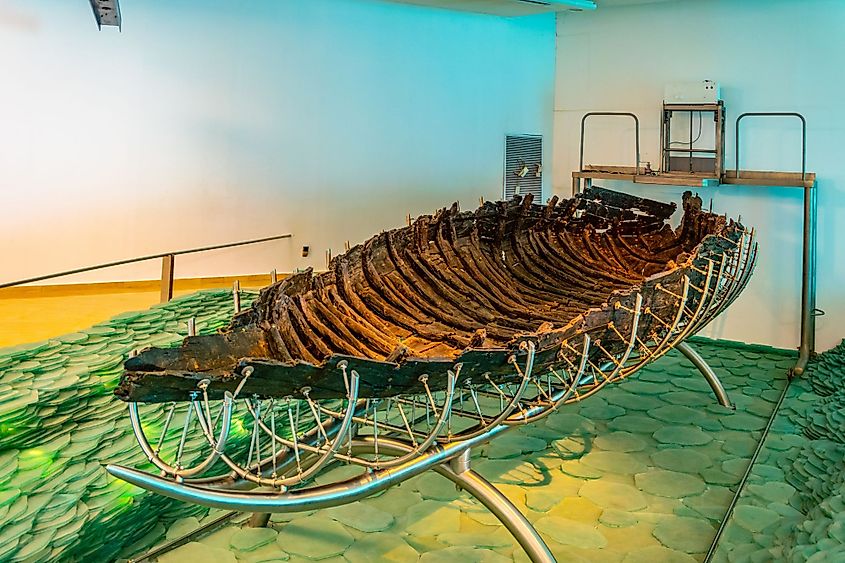

The pleasant climatic conditions, abundant water supply, and the surrounding fertile plains have supported several people in the region throughout history. Located about 3km east of the lake at Nahal Ein Gev, one of the world's first permanent human settlements dating about 400,000 to 500,000 years ago has been found. An ancient fishing boat dating from the 1st century AD referred to as "Jesus Boat" was discovered by archaeologists on the northwestern shores of the lake in 1986. As per the New Testament, many miracles of Jesus Christ are said to have taken place on the lake's shores. The area started attracting a lot of Christian pilgrims during the rule of the Byzantine Empire. However, the area's importance declined after it was occupied by the Umayyad Caliphate and other Islamic Empires. In 1908, the Kinneret Farm was established by the Jewish pioneers close to the Sea of Galilee. In 1967, a dispute over the rights to use the waters from the Sea of Galilee led to the Six-Day War between Israel and the coalition of Arab states. During the war, the Golan Heights was captured by Israel from Syria. As per the terms of the Israel-Jordan peace treaty signed on October 26, 1994, Israel annually supplies about 50 million cubic meters of water to Jordan from the Sea of Galilee. At present, the Government of Israel has taken serious efforts for water conservation, reclamation, and desalinization of saline water bodies in the country.