The Marginal Seas Of The Arctic Ocean
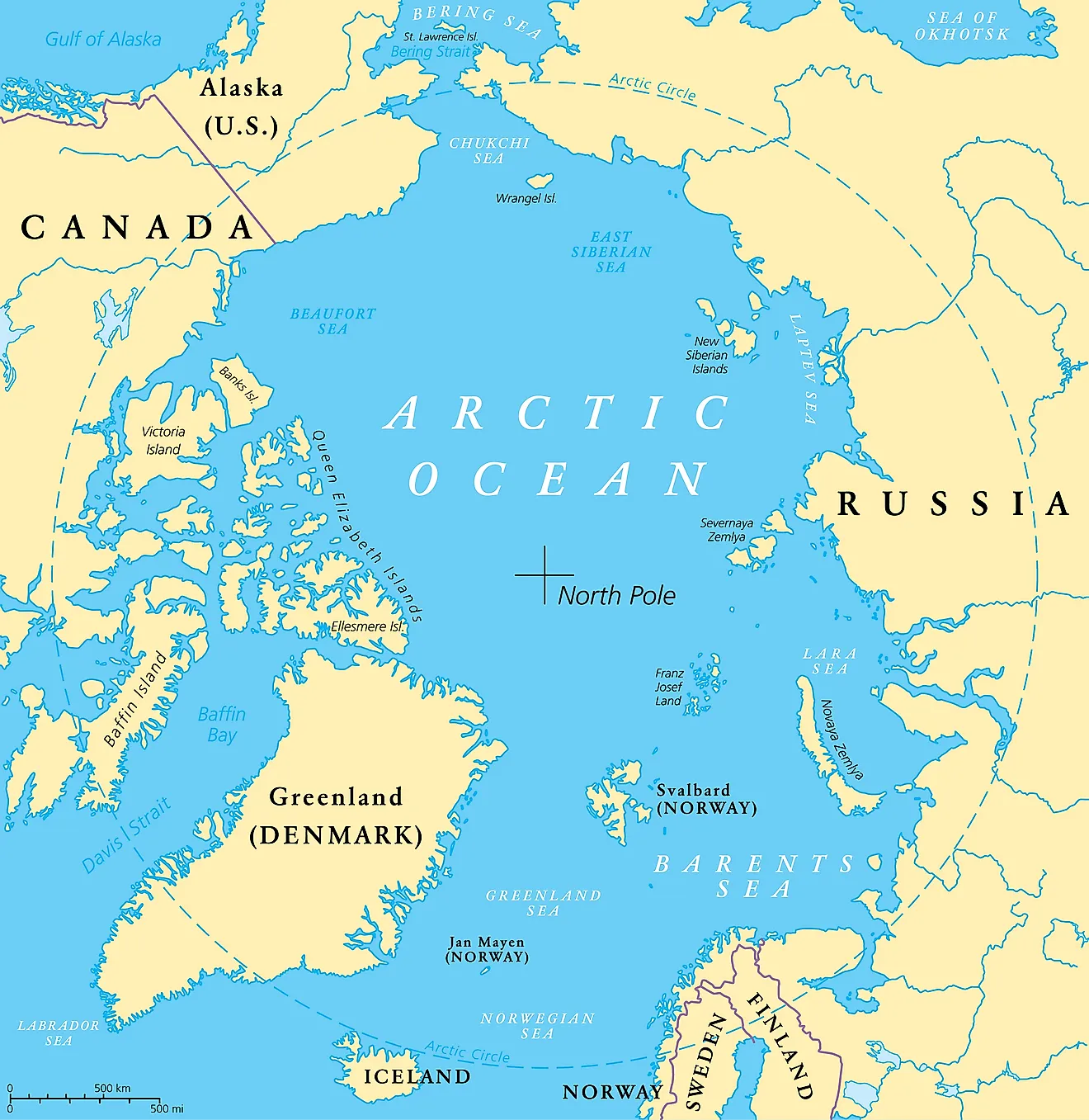
The Arctic Ocean is one of the world's five oceans. It is the northernmost, shallowest, and smallest of these oceans. Although the IHO recognizes it as an ocean, a section of the oceanographers labels it as the Arctic Sea. Large parts of the Arctic Ocean remain seasonally or permanently covered by ice. This ocean also has the lowest salinity of the world’s oceans due to the low evaporation rates. The ocean also receives large volumes of freshwater from a large number of rivers draining into it.
The Arctic Ocean features many marginal seas, bays, gulfs, straits, and other water bodies. Some of the most important of these water bodies are described below:
- Chukchi Sea
- East Siberian Sea
- Laptev Sea
- Kara Sea
- Barents Sea
- Queen Victoria Sea
- Wandel Sea
- Greenland Sea
- Lincoln Sea
- The Northwest Passages
- Prince Gustav Adolf Sea
- Amundsen Gulf
- Hudson Strait
- Hudson Bay
- James Bay
- Beaufort Sea
- Norwegian Sea
Chukchi Sea
The Chukchi Sea covers an area of 620,000 square km between Alaska’s Point Barrow to the east and the Long Strait off the coast of the Wrangel Island to the west. The sea is connected to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean via the Bering Strait at its southernmost end.
East Siberian Sea
Another marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, the East Siberian Sea is one of the least studies water bodies in the area. The sea is located between the Arctic Cape and the Siberian coast to the north and south, respectively. The sea’s limits to the west are defined by the presence of the New Siberian Islands while the Wrangel Island and Cape Billings lie to the east of the sea. The East Siberian Sea experiences extremely harsh climate. The sea is relatively quite shallow with depths not exceeding 50 m. The sea has very little species diversity as the low temperatures, poor salinity, and low nutrient levels do not provide ideal living conditions for most species
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea is surrounded on three sides by land. The northern Siberian coast lies to the south of this sea. The western boundary is formed by the Severnaya Zemlya and the Taimyr Peninsula. The New Siberian Islands border the sea to the east. The Laptev Sea extends into the rest of the Arctic Ocean in the north. The East Siberian Sea and the Kara Sea lie to the east and west of the Laptev Sea. Like the East Siberian Sea, this sea also has a harsh climate and a scarcity of flora and fauna. The Laptev Sea occupies an area of 700,000 square km and has a maximum depth of 11,106 ft.
Kara Sea
Named after the Kara River, the Kara Sea is located to the north of Siberia between the Barents Sea and the Laptev Sea. The Novaya Zemlya and the Kara Strait separates the Kara Sea from the former while the archipelago of Severnaya Zemlya separates it from the latter. The sea covers an area of around 880,000 square km. It has an average depth of 430 ft. The sea remains froze for about nine months in a year. It receives fresh water from several large rivers like the Ob, Yenisei, and others.
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea is off the northern coasts of Russia and Norway and is relatively shallower than the other parts of the Arctic Ocean. The sea serves as an important site for the exploration of hydrocarbon resources. It is also a productive fishing area. The Barents Sea has a surface area of 1,400,000 square km and an average depth of 750 ft. The Pechora Sea and the White Sea are both parts of the Barents Sea. The former is in the southeastern part of the Barents Sea while the latter is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea.
Queen Victoria Sea
The Queen Victoria Sea stretches from Svalbard archipelago’s northeast to the Franz Josef Land’s northwest. The sea remains frozen most of the year. The Victoria Island and the Kvitøya island are located to the south of this sea.
Wandel Sea
Another marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, the Wandel Sea, stretches from Greenland’s northeast to Svalbard. Ice covers large areas of the sea for several months of the year while seas further north are frozen all year-round.
Greenland Sea
The Greenland Sea is located between Greenland to the west and the archipelago of Svalbard to the east. Iceland and the Norwegian Sea defines the southern limits of the sea while the Arctic Ocean and the Fram Strait lie to the north. There is debate as to whether the Greenland Sea is a part of the Arctic Ocean or the Atlantic Ocean. Most oceanographic studies, however, regard is as part of the Norwegian Sea. The Greenland Sea has a surface area of 1,205,000 square km and a maximum depth of 15,899 ft.
Lincoln Sea
The Lincoln Sea extends from Canada’s Cape Columbia in the west to Greenland’s Cape Morris Jesup in the east. Sea ice covers the Lincoln Sea all year-round. The sea has a surface area of 64,000 square km and a maximum depth of 980 ft. The only place permanently inhabited by humans on the coastline of the Lincoln Sea is Alert of Canada.
The Northwest Passages
The Northwest Passage refers to the sea route that leads to the Pacific Ocean from the Arctic Ocean via the waterways of the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The Prince Gustav Adolf Sea and the Amundsen Gulf are part of this passage.
Prince Gustav Adolf Sea
This marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean is located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The sea lies between the islands of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. To the north, the sea opens out into the Arctic Ocean while to the south, it is connected to the Maclean Strait and the Byam Martin Channel.
Amundsen Gulf
This is located in the Northwest Territories of Canada and is about 400 km long. The gulf lies at the western end of the Northwest Passages. It is rich in marine life like beluga whales, seals, and several species of Arctic fish, etc.
Hudson Strait
This strait connects the Hudson Bay to the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea and separates Canada’s Nunavik from the Baffin Island. The strait extends for a distance of 750 km and has a maximum width of 240 km.
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay is a massive body of water in northeastern Canada. The bay has an area of 1,230,000 square km and a maximum depth of 890 ft. By most definitions, the Hudson Bay is a part of the Arctic Ocean. The bay drains several Canadian provinces and American states.
James Bay
The James Bay is located to the south of the Hudson Bay in Canada. The bay is the site of large hydroelectric projects and recreational activities.
Beaufort Sea
A marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, the Beaufort Sea located to the west of the Arctic island of Canada and to the north of Alaska, Yukon, and the Northwest Territories. The Beaufort Sea remains frozen almost all year-round. One of the world’s largest colonies of beluga whales lives in this sea. The sea has a surface area of 178,000 square km and a maximum depth of 15,364 ft.
Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea is also a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Greenland Sea and the North Sea to Norway’s northwest. The sea is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge. The Norwegian Sea has an area of 1,383,000 square km and a maximum depth of 13,020 ft.