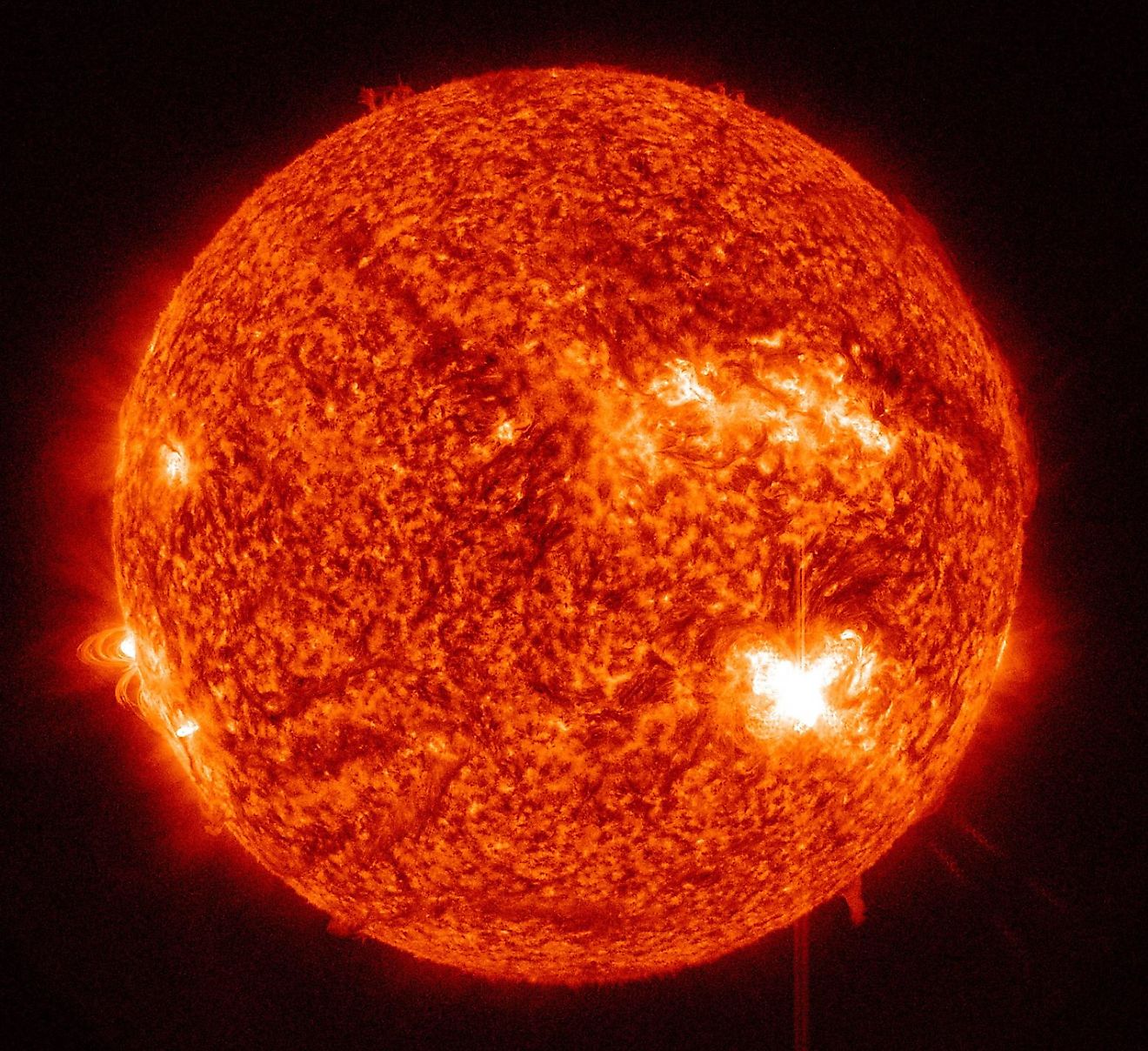
How Are Stellar Life Cycles Determined?
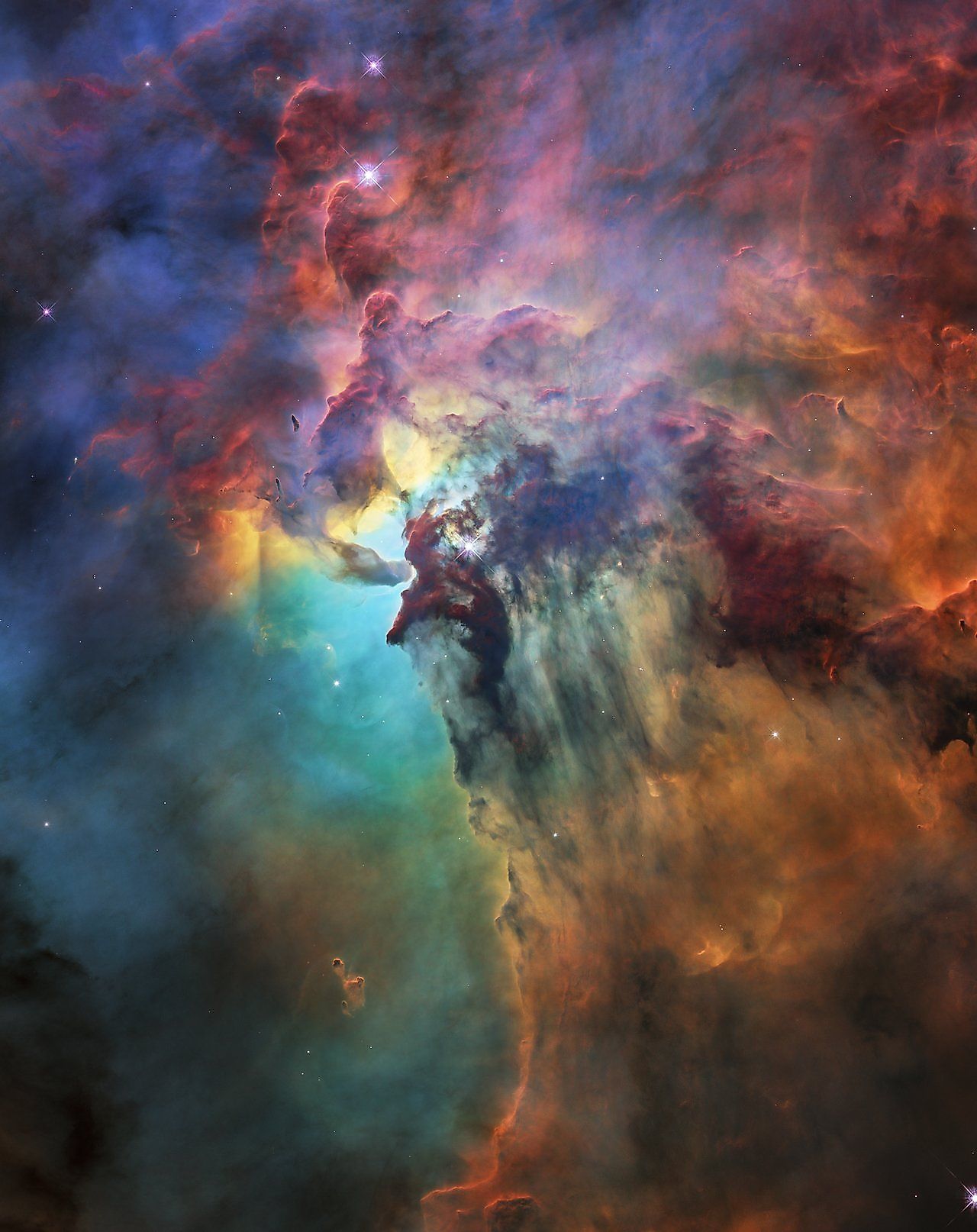
The science of astronomy generally deals with events that take many millions to billions of years to unfold. One such event is the lifecycle of a star. Stars can live anywhere from a few million years to over a trillion years. Relative to the life of even the shortest lived stars, we humans are gone in the blink of an eye. How then do astronomers study the lifecycle of a star? We can never hope to live for billions of years, and so how do they research stellar lifecycles?
Observing Multiple Stars
To overcome the vast amounts of time required to observe a star from formation to death, astronomers have come up with a very clever solution. Rather than observe one star, astronomers can observe a large number of stars that are nearly identical to one other that also happen to exist at different stages of their lifecycle. To get an idea of how this works, imagine you are a biologist tasked with studying the lifecycle of the African Elephant. The catch is that you only have one day to do your research. African Elephants have a lifespan of about 70 years, and so given only one day of research, you could not research their lifecycle by observing only one elephant. Rather, you could observe multiple elephants of varying ages. By observing elephants at varying stages of their life, you could get a fairly good idea of their lifecycle in a relatively short period of time. Astronomers do something similar when it comes to stars. Astronomers observe stars at every stage of their life, from formation to death. Since some stars are nearly identical to one another, astronomers can paint an accurate picture for how different stars evolve over time.
Interestingly, there is one type of star that this method does not actually work for. The smallest stars, called red dwarfs, have lifespans that are estimated to be upwards of one trillion years. Since the universe is 13.8 billion years old, no red dwarf star has yet reached the later stages of their life. Every red dwarf star in the universe is still young, and so astronomers have no way of studying how these stars will evolve throughout their lifecycle. However, based on their mass, astronomers have a pretty good idea how they will likely develop. Every other type of star in the universe has a lifespan lower than the age of the universe, and so astronomers are able to understand how they evolve over time. Unfortunately, red dwarf stars have lifespans that are so long, we will never be able to observe their full lifecycle, even by observing different ones of varying ages.