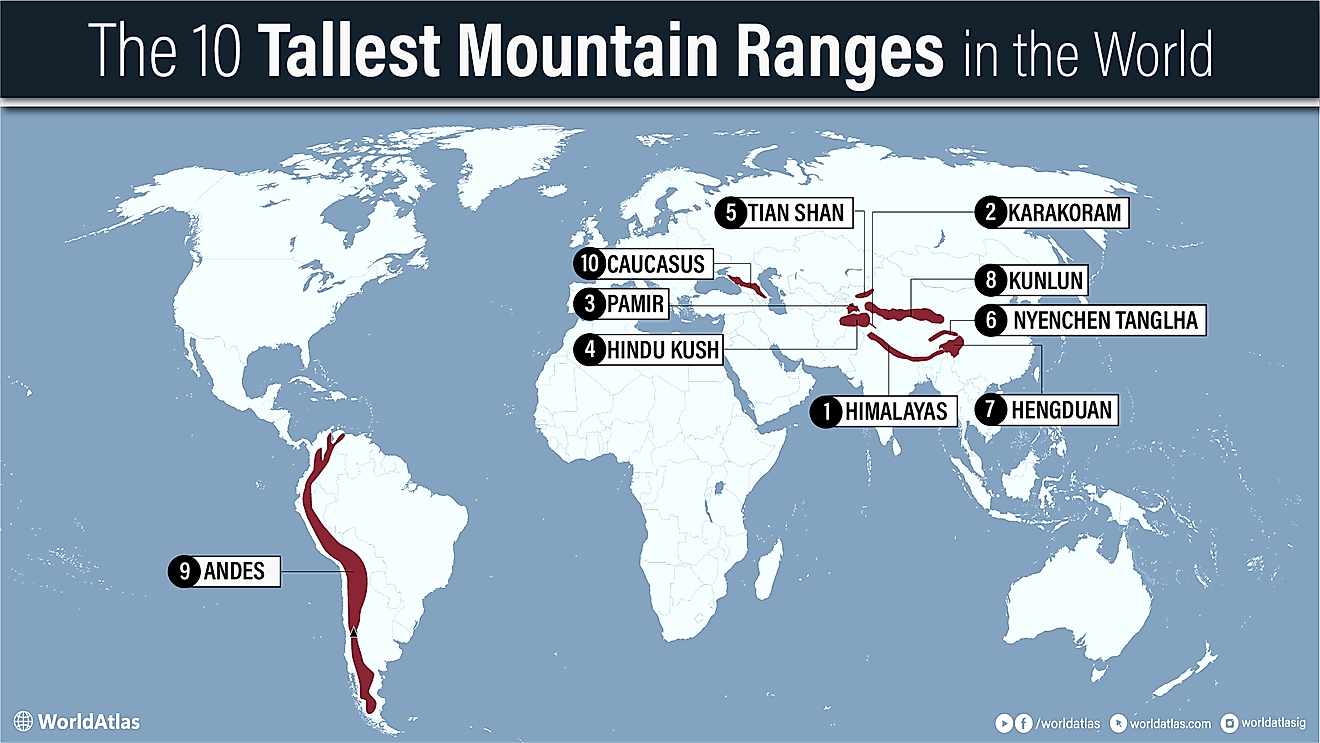
Mount Vinson
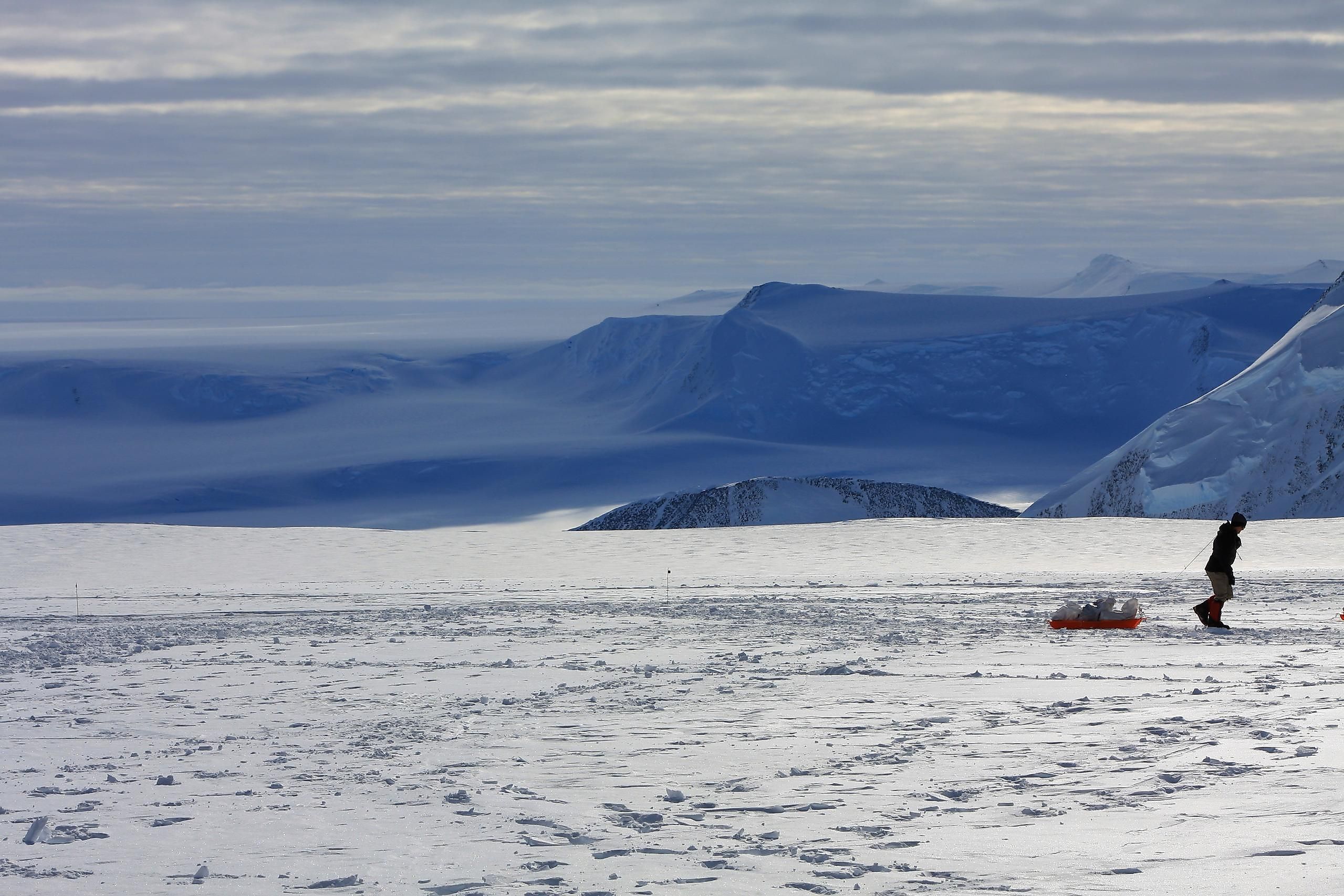
Located in the southern part of the main ridge of the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Mount Vinson is the highest peak in the continent of Antarctica. Along with the nearby five other tall mountains, Mount Vinson forms a part of a large mountain massif in Antarctica, known as the Vinson Massif. This 21km long and 13km wide mountain massif overlooks the Ronne Ice Shelf and is located about 1,200km from the South Pole.
Geography

Rising to an elevation of 4,892m, Mount Vinson is the most recently discovered and the most remote of the Seven Summits. Mount Vinson is situated in the northern part of the summit plateau of the Vinson Massif, and about 2km to the north of the Hollister Peak. The Vinson Massif is surrounded by the Branscomb Glacier and the Goodge Col in the northwest; the Nimitz Glacier in the southwest; the Gildea Glacier in the south; and the Dater Glacier and its tributary the Hinkley Glacier in the east. Geologically, the Vinson Massif has been formed by steeply inclined strata known as the Crashsite Group. The Crashsite Group is further subdivided into many subdivisions of which the Mount Wyatt Earp Formation makes up Mount Vinson and the crest of the Vinson Massif.
Mount Vinson, the highest mountain in Antarctica, attracts many mountaineers, geologists, and climbers, who wish to visit the mountain to study its climatology and the geological history of its formation. To date, more than 1,400 climbers have attempted to reach the summit of Mount Vinson. However, the extreme climatic conditions and remoteness have prevented human presence on the mountain, and have made Mount Vinson one of the world’s most pristine and unspoiled mountains.
Climate and Ecology
The high-pressure system of the polar ice caps mainly controls the climate of Mount Vinson. During the summer season when there are 24 hours of sunlight, the average temperature is about -30°C, while during winters, the average temperature falls as low as -90°C. The mountain region receives very low precipitation while high winds blow occasionally. Due to such extreme climatic conditions, no life forms have been found on Mount Vinson.
Brief History
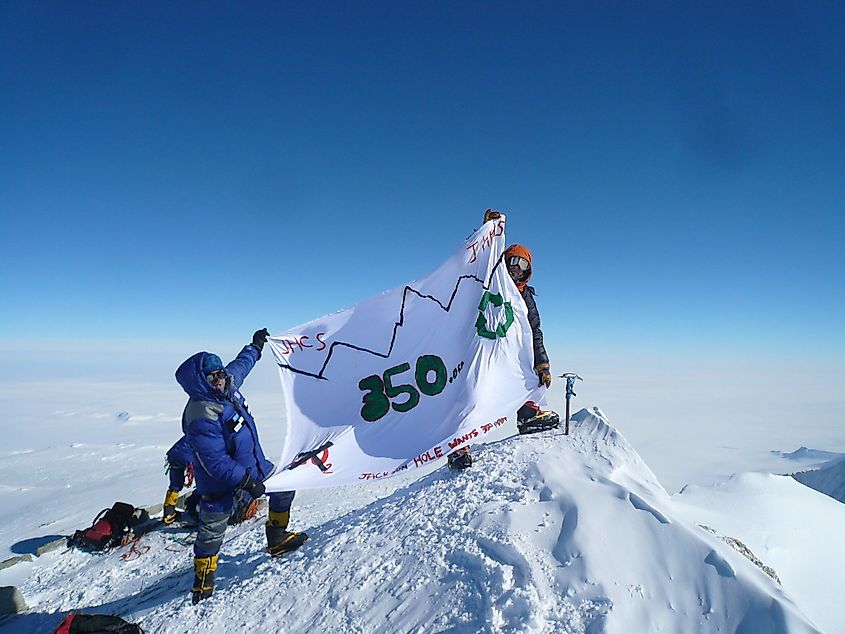

Mount Vinson is one of the most recently discovered mountain peaks in the world. Its existence was first reported in January 1958, by a US Navy aircraft from the Byrd Station. This high mountain peak was named in honor of the American politician Carl Vinson, who served as the US Representative from the State of Georgia and was one of the major supporters of the United States funding for the exploration of Antarctica. The mountain was first climbed in December 1966, by a US expedition team that was led by a well-known American mountain climber Nicholas Clinch and was officially known as the American Antarctic Mountaineering Expedition. This extremely well-planned expedition was a grand success, as all the members of the expedition team were able to successfully reach the summit. A GPS survey conducted in 2004 by the Omega Foundation Team had reported the current height of Mount Vinson to be 4,892m. On November 1, 2006, the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names, declared that Mount Vinson and the Vinson Massif were two separate entities.