What Are Grasslands?
- Grasslands are vast areas covered mostly by grass and grass-like plants.These areas don’t receive enough rainfall to grow trees or support a forest, but they don’t get too little either to become a desert.
- In the US they’re called prairies, in Australia, they’re called rangelands, while in South America they’re called pampas, llanos, and cerrados.
- There are two main types of grasslands: tropical or savanna and temperate grasslands.
What Are Grasslands?
Grasslands are vast areas covered mostly by grass and grass-like plants. They have many different names. In the US they’re called prairies, in Australia, they’re called rangelands, while in South America they’re called pampas, llanos, and cerrados. These areas don’t receive enough rainfall to grow trees or support a forest, but they don’t get too little either to become a desert. Grasslands are somewhere in between these two ecosystems. They receive just enough rain to support an abundance of grass and in some areas, a few trees spaced far apart from each other and clusters of shrubs as well. Grasslands support grazing animals or those that mainly feed on the grass to survive like zebra, antelope, and bison.
There are two main types of grasslands: tropical or savanna and temperate grasslands.
Tropical Grasslands
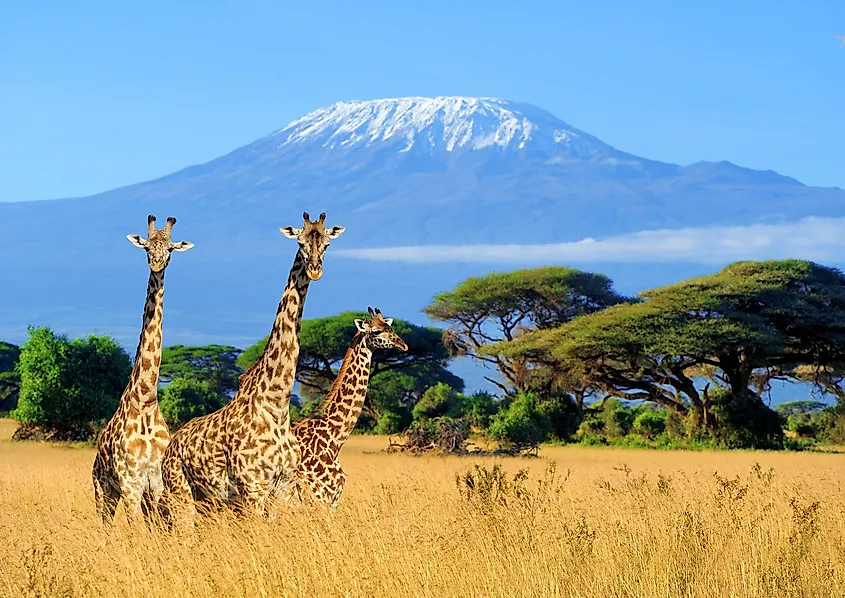

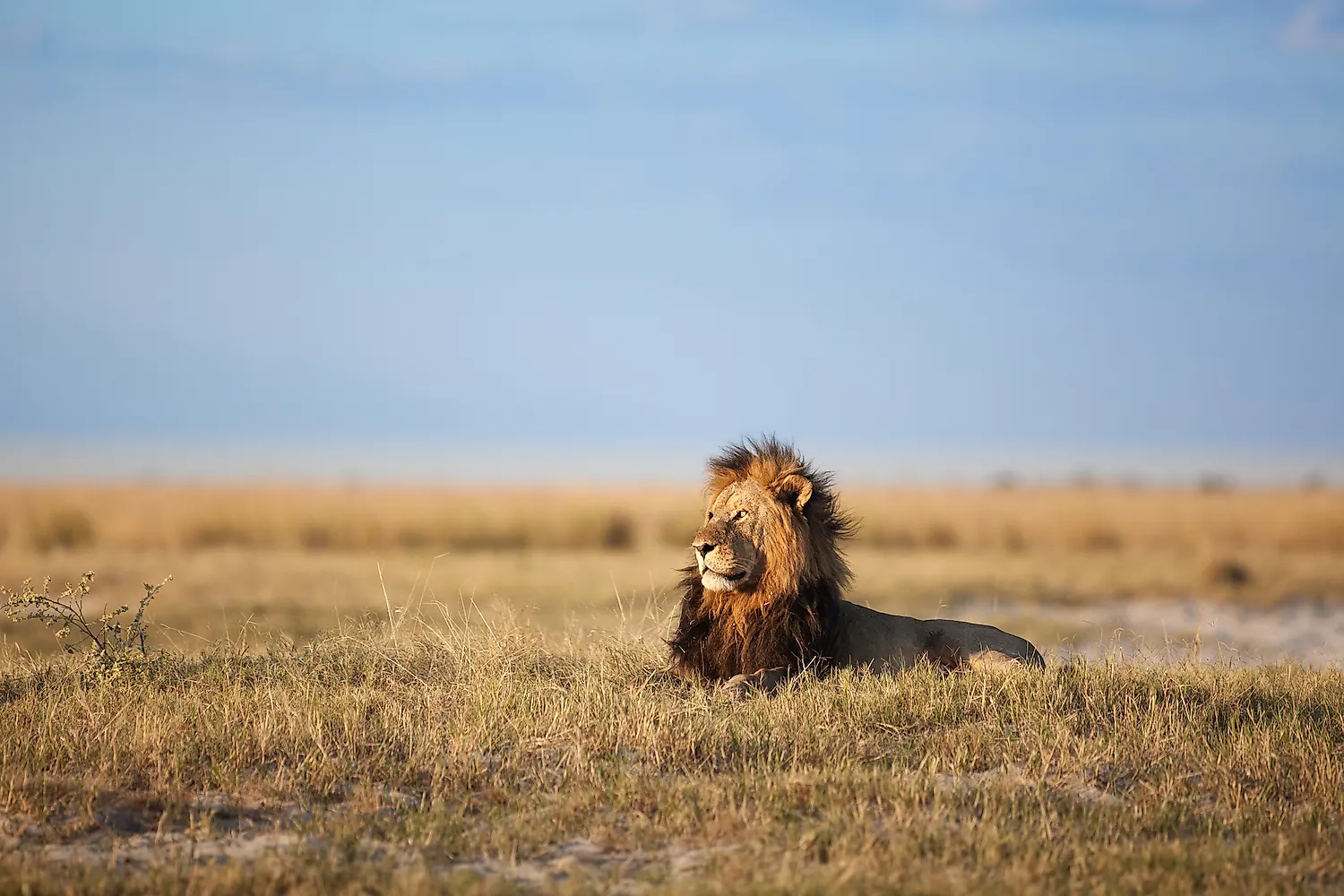
Tropical grasslands are grasslands with scattered trees and some shrubs. Trees often grow away from each other, and in between these widely spaced trees are shrubs that grow in small clumps. These grasslands, also called savannas, are mostly found all over Africa, in Australia, South America, and India. According to information from the University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP), savannas are always found in warm or hot climates where the annual rainfall is from about 50.8 to 127 cm (20-50 inches) per year. Rainfall occurs within a six-to-eight-month period followed by a very long period of drought.
These tropical grasslands are home to a wide variety of animals and support a thriving ecosystem. Many medium-sized to large herbivores thrive in grasslands since there is plenty of grass to eat. There are also a lot of carnivores that roam these areas that feed on these grazing animals. Some of those that live in many well-known savannas include zebras, gazelles, wildebeests, antelopes, elephants, impalas, lions, cheetahs, and wild dogs among many others. There are also a variety of birds that roam grasslands to feed on insects that live on grass and shrubs.
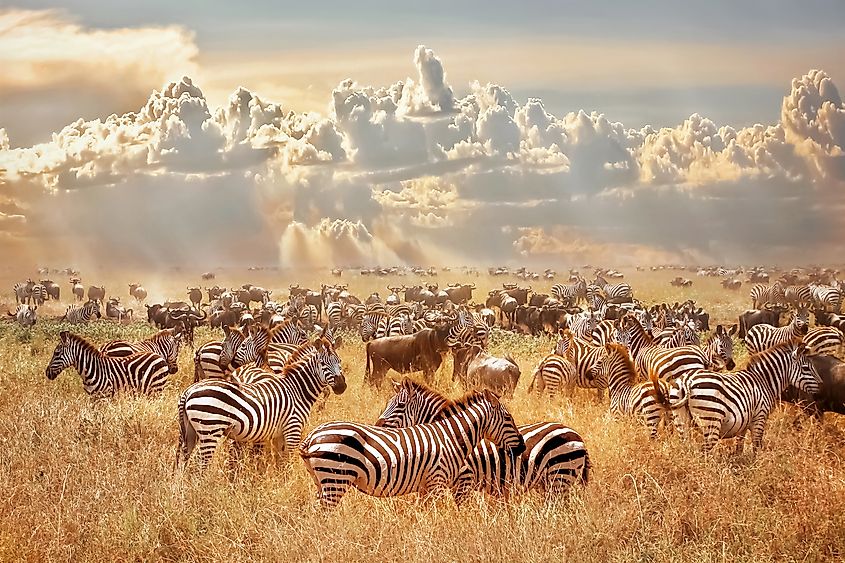

The largest savannas are found in Africa. It covers more than 50% of the entire continent. Many species of flora and fauna are found here. Tourists from all over the world visit Africa to see the beautiful animals in their savannas. African safari tours allow visitors to observe animals in their natural habitat and in some cases even take photos from afar. Some lodges also allow tourists to camp out for a night or two in the middle of a grassland.
Temperate Grasslands
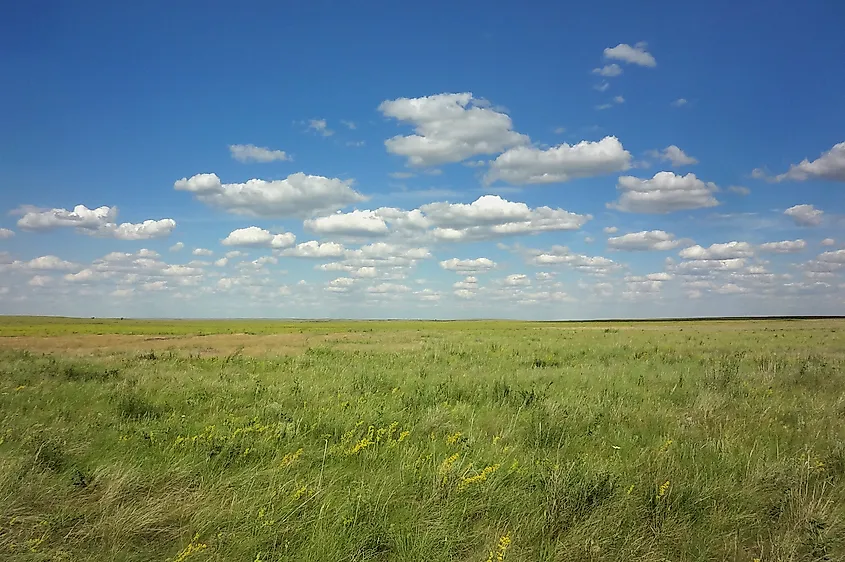

Temperate grasslands are typically found in areas above the equator. These are wide plains that are often drier than savannas with temperatures that are a lot colder. They are flat, treeless, covered with grass, and have rich soil. This is why many temperate grasslands have been turned into farms or grazing lands for cattle.
Temperate grasslands include the Eurasian steppes in Ukraine and some parts of Russia, Argentine pampas as well as all the prairies found throughout North America and the great plains of Canada. According to UCMP temperate grasslands have hot summers and cold winters with moderate rainfall.“The temperature range in temperate grasslands is very large over the course of the year. Summer temperatures can be well over 38° C (100 degrees Fahrenheit), while winter temperatures can be as low as -40° C (-40 degrees Fahrenheit).”
The soil in temperate grasslands are dark and covered with a very fertile and nutrient-rich layer that supports different species of grass including blue grama, purple needlegrass, and buffalo grass, as well as some flowers such as, goldenrods, blazing stars, wild indigos, coneflowers, sunflowers, clovers, and asters. The species depends on the area’s amount of rainfall, temperature, and overall climate.
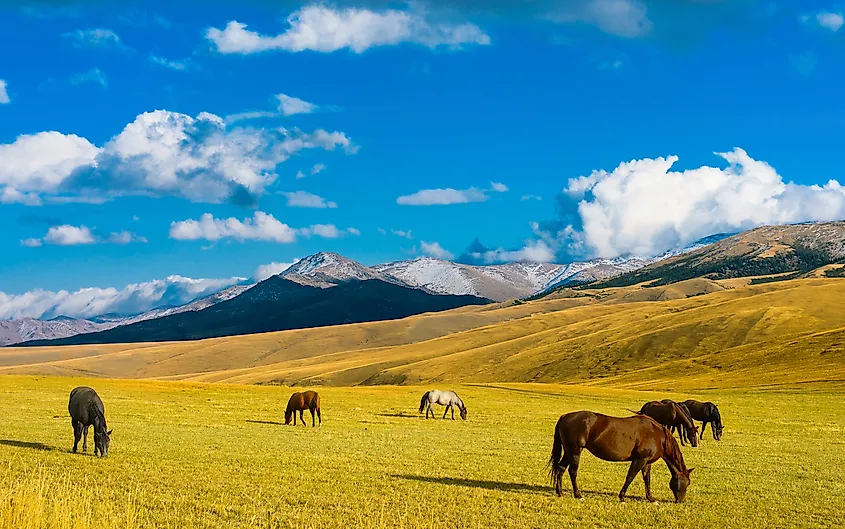

Numerous animals thrive in temperate grasslands according to the UCMP. These include “gazelles, zebras, rhinoceroses, wild horses, lions, wolves, prairie dogs, jackrabbits, deer, mice, coyotes, foxes, skunks, badgers, blackbirds, grouses, meadowlarks, quails, sparrows, hawks, owls, snakes, grasshoppers, leafhoppers, and spiders.”