Reasons Why The Earth's Magnetic Field Is Extremely Useful
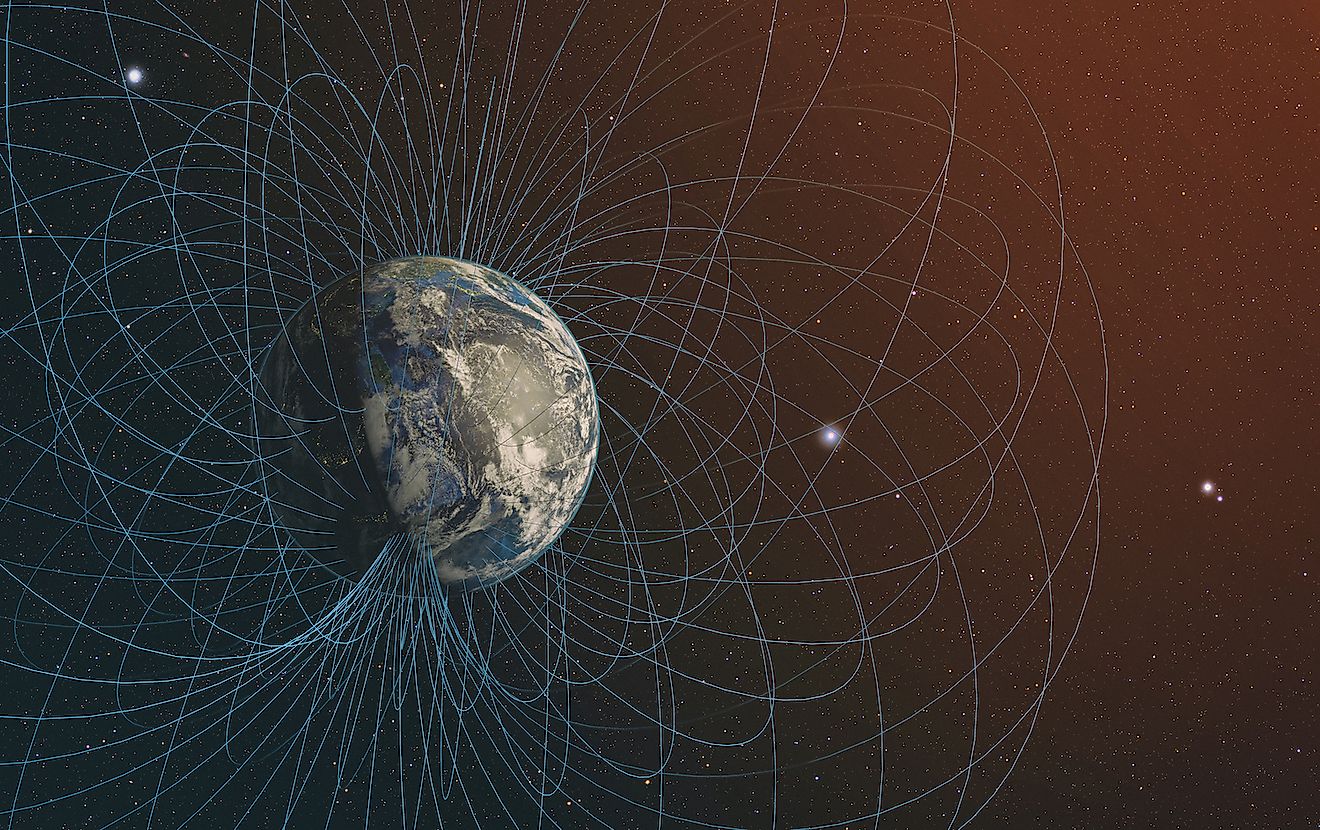
- The Earth's magnetic field protects our atmosphere from solar winds that can strip it bare, exposing us to too much ultraviolet light from the sun, and essentially killing our planet.
- Mars lost its magnetic field billions of years ago and this is said to have made it the barren planet we now know it as.
- Animals who migrate can see the Earth's magnetic field by detecting blue wavelengths. This allows them to know where they are going.
Earth’s magnetic field is an amazing tool of nature. According to Oxford Languages, magnetism is a physical phenomenon produced by the motion of electric charge that results in both attractive and repulsive forces between objects. Think of the magnets on the fridge in your kitchen and you get the picture. To add more description, Earth’s magnetic field forms a region around a moving electric charge inside which the force of magnetism is active.
The Earth’s magnetic field is mainly a dipolar geomagnetic field, which means it has two poles, the geomagnetic North and South poles, that exist on Earth’s surface. Our planet has an iron core that is part liquid and part solid. Scientists think that as things move around in this core, this is how Earth’s magnetic field is produced.
It may seem like this invisible field is something that simply makes the arrow hand on your compass twirl around but it actually forms many amazing functions for us.
Here are 8 things that this magnetic field does for us.
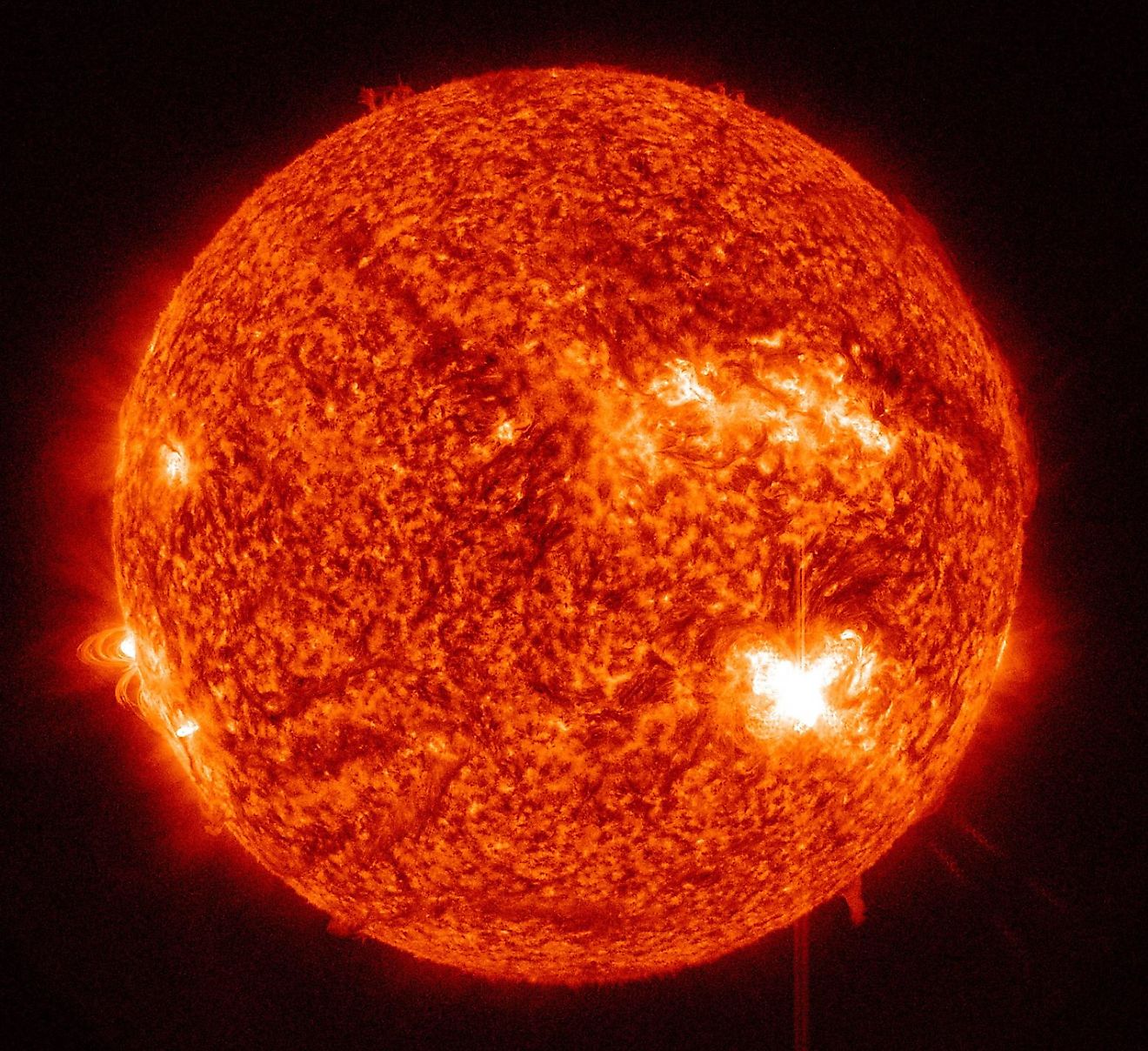
8. It protects us from solar winds.
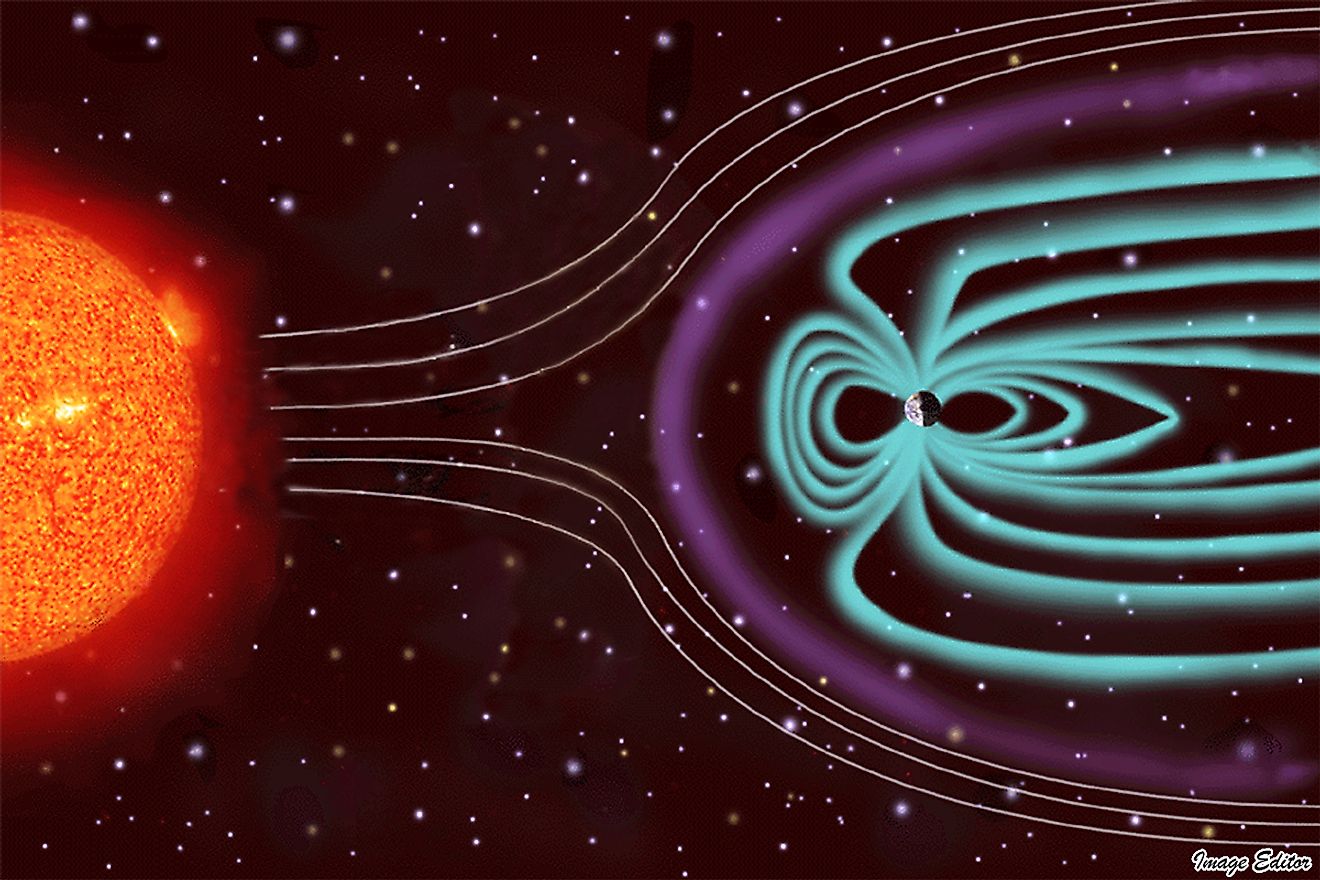

Earth’s geomagnetic field is largely responsible for keeping us alive. This force is responsible for protecting us from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. The field deflects much of the solar material coming off the sun towards us at about 1 million miles per hour. If we did not have a magnetosphere, the ongoing action of these solar particles would strip the protective layers of our atmosphere that keep us from being destroyed by the ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun. Mars, for example, is said to have lost its magnetosphere somewhere around 4.2 billion years ago. This destroyed Mars’ atmosphere, and has left it void of life as we know it.
7. It is used for navigation with a compass.
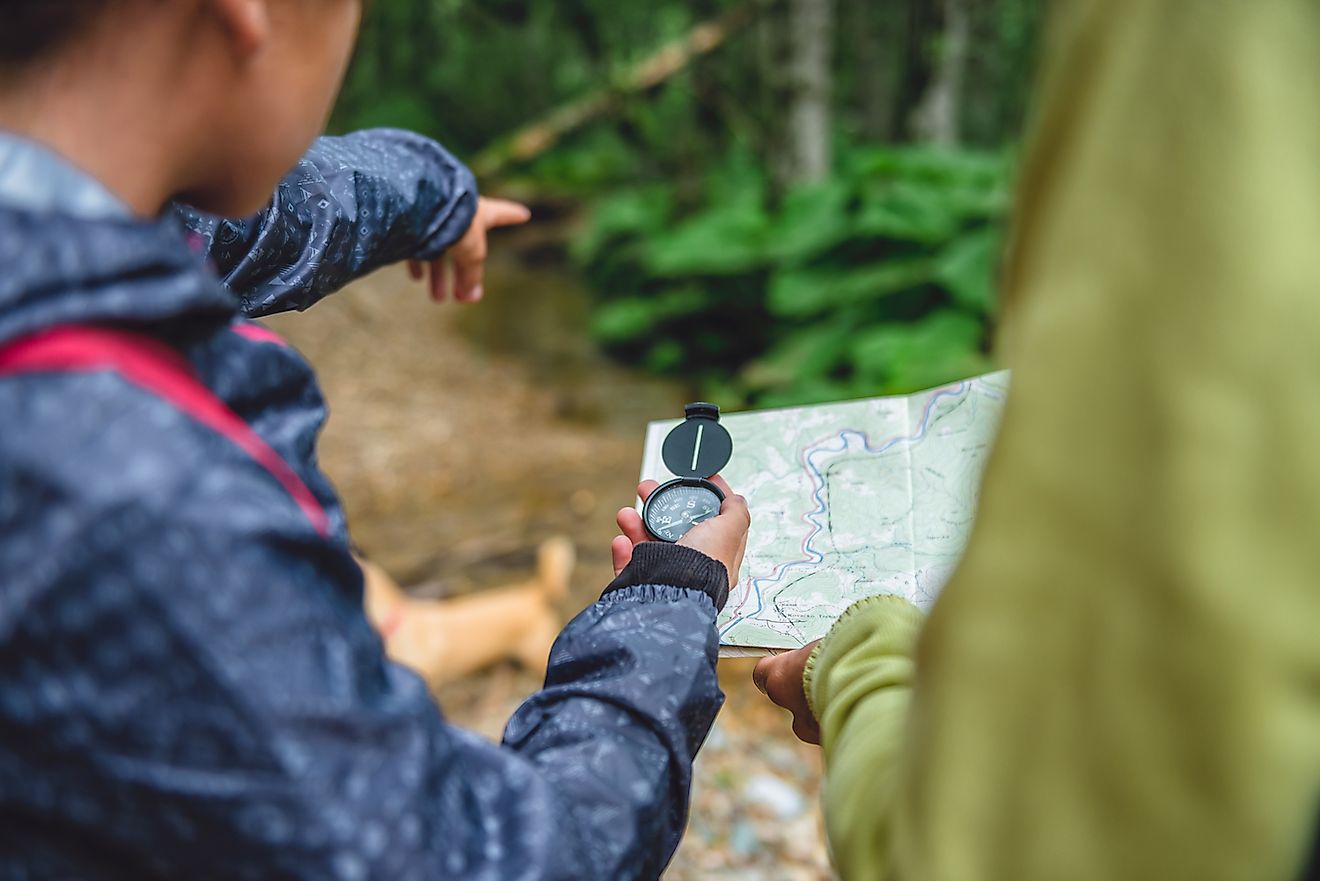

This is perhaps the most commonly-known function of our magnetic field. If you have ever used a compass to find your way, you know that the needle with an arrow always points towards North, whether you are in the northern hemisphere or the southern hemisphere. This happens because your compass has a magnet in it. This magnet is aligning with the Earth’s natural magnetic fields.
If you happen to find yourself at Earth’s magnetic North or South poles, however, something else will happen. Your compass needle will want to point straight down at the Earth. This is truly where magnetic North is sitting. It cannot though, as a needle can’t “stand up” in a compass. The needle in your compass will then float about aimlessly. The same effect will happen should you find yourself at the South pole.
6. It helps animals who migrate.
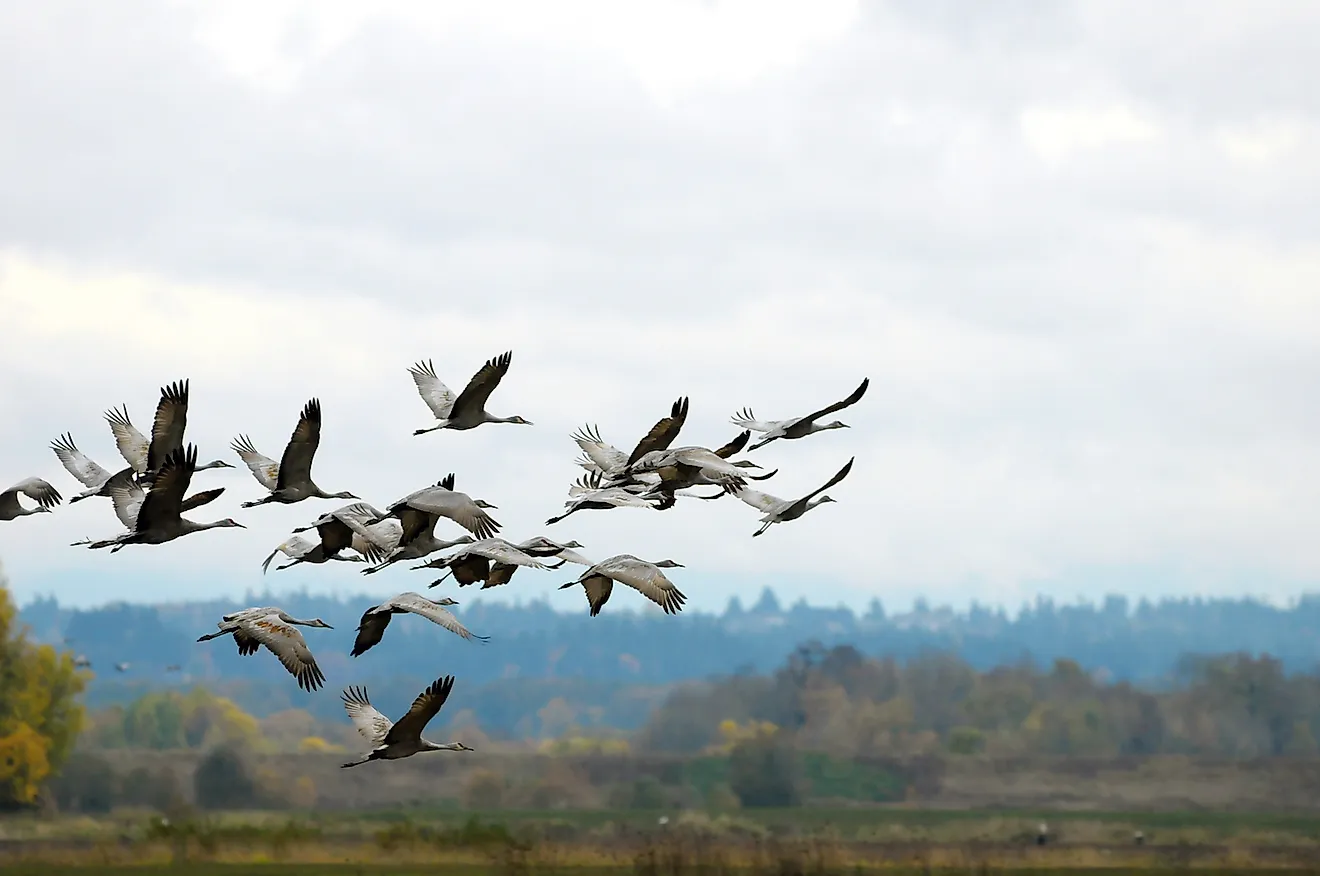

You may have always wondered how animals who migrate know where to go. Part of their success has to do with the fact that they can sense the magnetic poles. According to scientists, these animals have magnetoreception, which truly is a super power. Some animals such as zebra finches detect the Earth’s magnetic field by using an unusual eye protein called Cry4. This protein is a cryptochrome, meaning it allows the animals to see Earth’s magnetic field by being able to detect the blue wavelength of light. Certain molecules in this wavelength are thought to appear different to the migrating animals depending on how they are oriented to the magnetic field. This allows them to “see” which way is North, and which way to travel.
5. It can help military personnel locate submerged submarines and other objects.

Part of a military’s success sometimes lies in being able to detect things in their environment that do not belong . Militaries can use magnetic anomaly detectors to recognize things like submerged submarines on an ocean floor. Submarines are typically made of ferromagnetic materials, and when they sit deep in the ocean, they disrupt Earth’s magnetic field. When this can be detected, the presence of an enemy submarine may be revealed.
4. It helps companies detect things in geophysical prospecting.

Geophysical prospecting involves exploring Earth for minerals or mineral fuels, and examining rocks to determine if there is anything worth mining therein. Some companies use magnetic and electromagnetic surveying equipment to perform these investigations. These methods can help detect abandoned mine shafts, steel drums buried underground, contaminated soil sediments, lateral changes in geology, soil types, and more.
3. It might help predicting earthquakes.

Studying Earth’s geomagnetic field could even potentially help scientists predict earthquakes. Researchers from Tokyo have developed an efficient way of quickly analyzing the magnetic field by observing what is happening to the field at various locations.
When an earthquake strikes, a very large amount of accumulated stress is released along a fault. This has such a large impact on Earth that it actually results in local changes to the magnetic field. Researchers hope that if they can detect these changes rapidly enough, they can issue warnings to citizens and save lives. Earth’s geomagnetic field in many places is a fluctuating signal. The use of this type of system depends on being able to know what constitutes a “normal” geomagnetic field in a particular location and detecting any changes that may take place.
2. It allows us to study the deep ocean floor.

Sometimes people do not wish to study what might be sitting on the ocean floor, but they want to learn about the bottom of the ocean, itself. Magnetometers are devices that can detect tiny deviations in the Earth’s magnetic field. These instruments have been used to map the ocean floor. The ground of the ocean is made of magnetite, that is part of iron-rich volcanic rock. This rock has strong magnetic properties that allow us to see the history of Earth’s magnetic field. Work done in 2017 revealed that Earth’s magnetic field has not just flipped poles once, but many times in the last one thousand years.
1. It could help us predict rainfall in tropical locations.
The local weather reporter may not be about to start providing TV viewers with a daily analysis of the Earth’s magnetic field, but it is true that variations in it have been linked to changes in weather patterns. As stated at the beginning of this post, the magnetic field of our planet protects us against solar particles stripping our atmosphere bare and exposing us to too much ultraviolet light. The Earth’s magnetic field is constantly changing, however. Some atmospheric stripping does result from solar winds. This happens when the magnetic field’s strength varies, and it has been found to affect how much rain falls on Earth’s tropical areas. By constantly analyzing the magnetic field for variations, these changes could potentially be predicted.