Gulf Of Finland
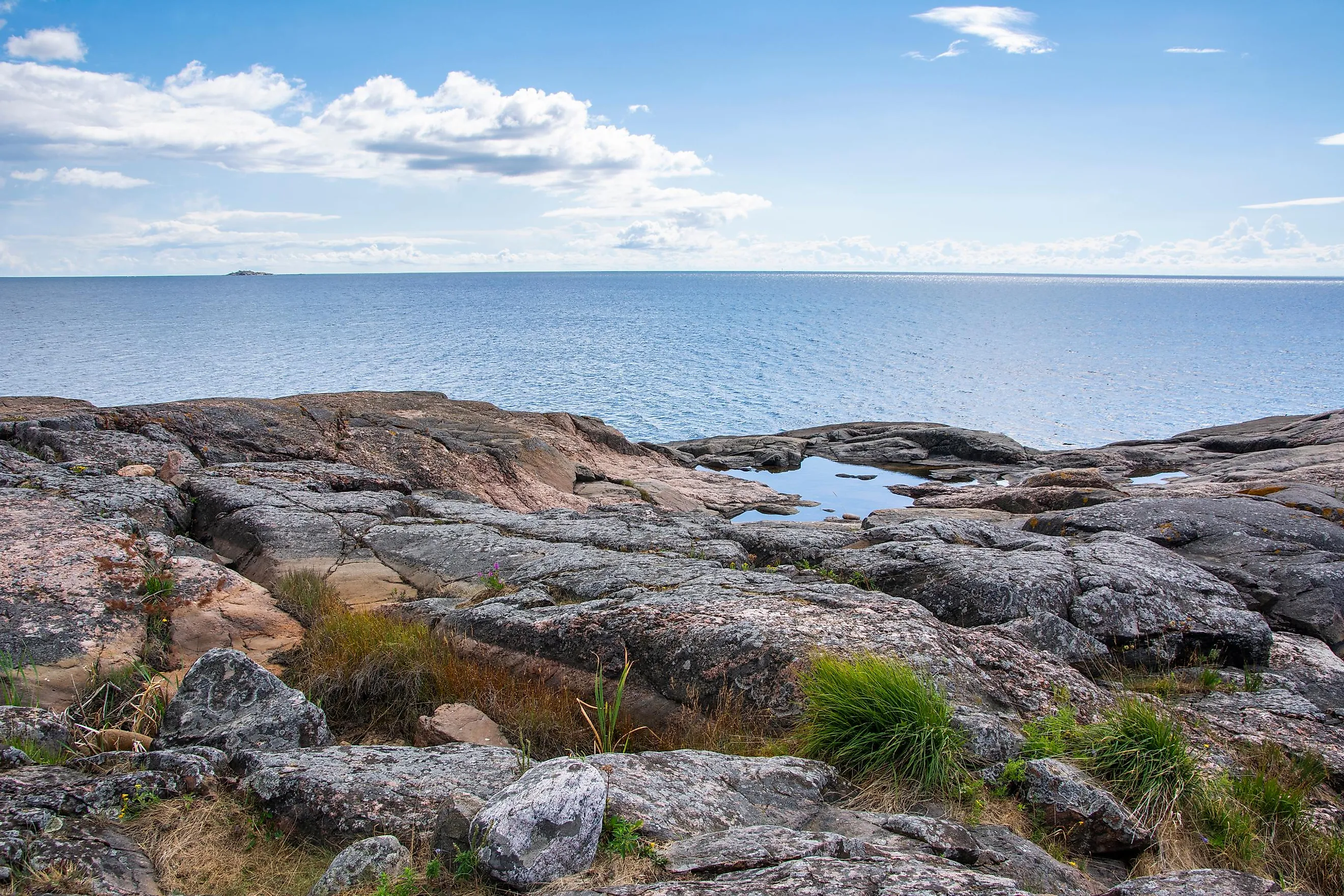
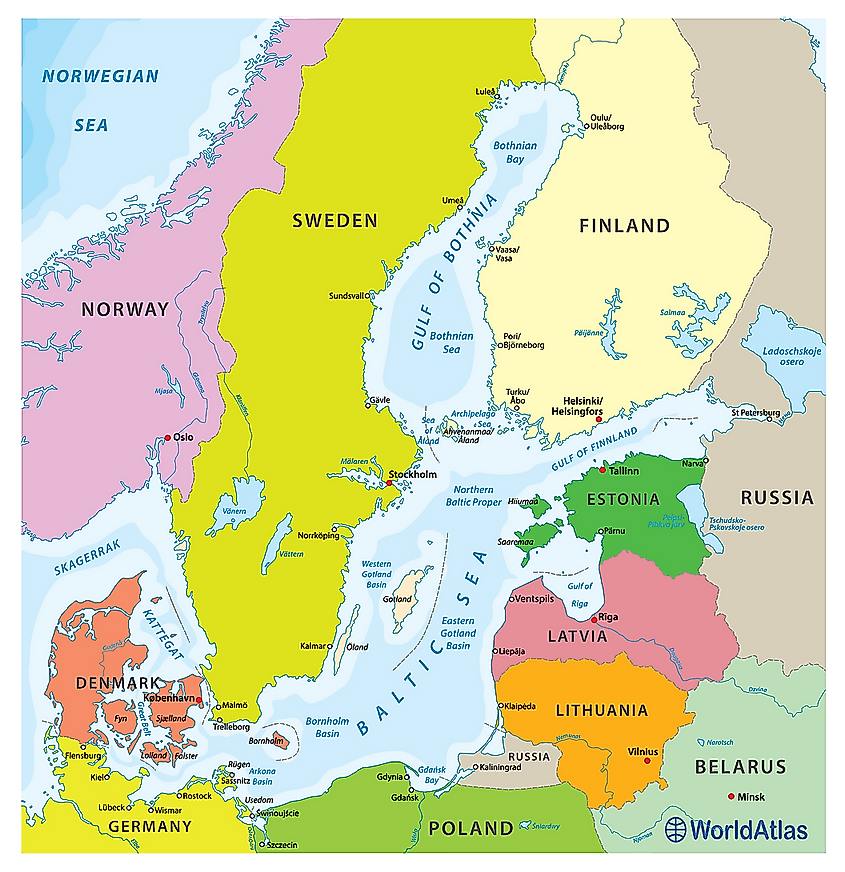
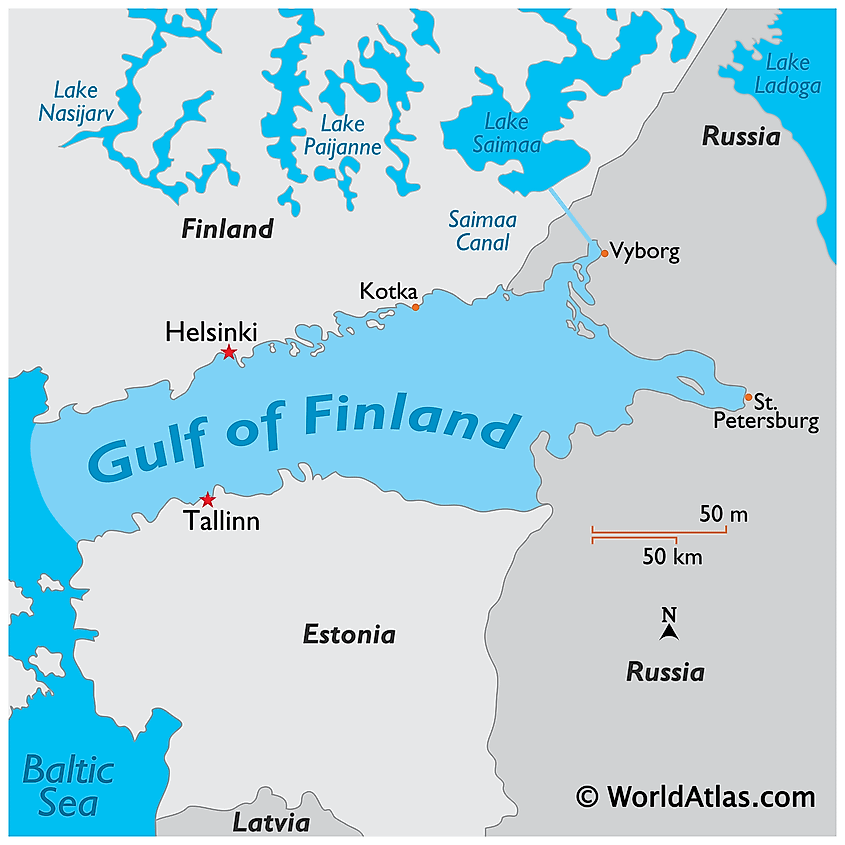
Covering an area of 30,000 km2, the Gulf of Finland is the easternmost extension of the Baltic Sea located in Northern Europe. It is bordered by Finland in the north, Russia in the east and Estonia in the south. The Gulf of Finland's southern coast was designated a Ramsar Wetland on September 13, 1994.
Geography
The Gulf of Finland extends for about 400 km from Saint Petersburg in the east to the Hanko Peninsula in the west. It has a maximum width of 130 km at its widest point. The gulf is relatively shallow with a maximum depth of 115 m and an estimated average depth of 38 m. It has been observed that the western part of the gulf is much deeper, while its eastern part is shallower. Numerous large and small rivers drain into the Gulf of Finland including the Jägala, Kymi, Keila, Kovashi, Kunda, Luga, Neva, Narva, Pirita, Porvoo, Sestra, Sista, and Vanta. The gulf is also connected to the Saimaa Lake via the Saimaa Canal. The huge amount of freshwater inflow from these rivers accounts for the extremely low salinity of the Gulf of Finland.
The highly curved northern coastline of the gulf consists of many rocky islets and small and large bays like Vyborg Bay and the Porkkalanniemi and Hanko Peninsulas. The southern coastline of the gulf is comparatively smooth and shallow. It also features the Baltic Klint, a 1,200 km-long limestone escarpment that stretches along the entire southern coastline of the gulf.
According to the Köppen climate classification, the Gulf of Finland region faces a humid continental climate with hot summers and relatively harsh winters. The average water temperature ranges from 0 °C in the winter to 17 °C in summer. The gulf freezes during the winter season from December to late April. Strong western winds are quite frequent in this region and cause floods, higher waves, and water surges.
Islands
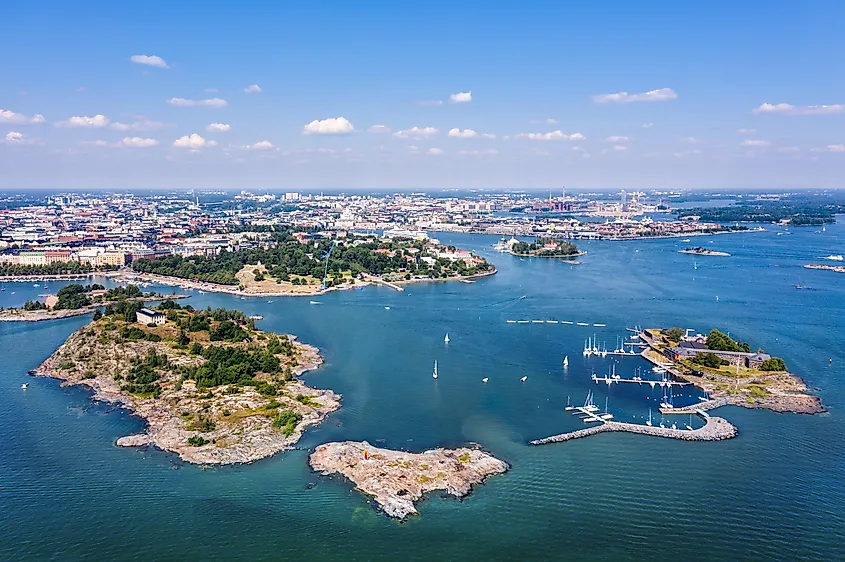

The Gulf of Finland contains several islands including the Beryozovye Islands, Bolshoy Tyuters, Gogland, Kotlin Island, Kimitoön, Kökar, Lisiy, Moshtchny, Maly Vysotsky Island, Naissaar, Pakri Islands, Seskar, and Sommers Island. The Pakri Island group comprises the two Estonian islands of Väike-Pakri and Suur-Pakri and are administered under the Harju County of Estonia. There are about 15 islands in the Beryozovye Island group among which the Bolshoy Beryozovy is the largest. All the islands of the Beryozovye Island group are protected as sanctuaries for seabirds.
About 19 artificial islands with forts have been constructed by the Russians in the Gulf of Finland. Some of these forts include Fort Alexander, Ino, Krasnaya Gorka, Kronshlot, and Totleben.
Wildlife

Hundreds of species of higher vascular plants are found in the coastal areas of the Gulf of Finland. The shallow waters of the gulf contain many aquatic plants like the spiny naiad and the ditch grass. The eastern part of the gulf features areas of wetland vegetation (marshes) that mainly consist of common reeds, bulrush, and several aquatic plants like acute sedge, and yellow and white water lilies. The forest vegetation of the coast and islands of the gulf are dominated by a mixture of pine and spruce forests as well as deciduous forests of birch, willow, aspen, black and grey alder, etc.
Several important species of fish including the Atlantic salmon, European chub, European smelt, common minnow, crucian carp, brown trout, stickleback, perch, lamprey, Atlantic cod, European eel, and Baltic herring are found in the Gulf of Finland. Grey seals are also found here.
Brief History

Humans first inhabited the areas surrounding the gulf after the complete melting of ice-age glaciers. Archaeologists have discovered several ancient sites that are more than 9,000 years old and some Neolithic settlements have also been found in the Sestra River region of Russia’s Leningrad Oblast. The indigenous tribal groups of Finno-Ugric, Eesti, Votes, Izhorians, and Korela tribes inhabited several areas along the gulf coasts. In the 8th and 9th centuries, the Gulf of Finland and the bank of the Neva River was occupied by the East Slavs, particularly the llmen and Krivichs Slavs. For many years beginning in the Middle Ages, the islands and the coastal areas of the gulf were a part of the Kingdom of Sweden.
After the Russo-Swedish War, the areas along the Gulf of Finland and the Neva River were handed over to Russia by Sweden. Many shipwrecks have been discovered in the Gulf of Finland, due to which the gulf’s bottom is regarded as one of the largest ship cemeteries in the world.
The Gulf of Finland functions as an important shipping corridor for Russia, Finland, and Estonia. Some of the major ports in the gulf include the Russian ports of St. Petersburg and Kronshtadt; the Finnish ports of Helsinki, Porkkala, and Kotka; and the Estonian port of Tallinn. The Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant is located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland. Fishing is also a major economic activity in the gulf region. However, the Gulf of Finland has been severely affected by pollution due to the contamination of the gulf waters by copper, mercury, phenols, organochlorine pesticides, petroleum products, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.