Maps of The Philippines
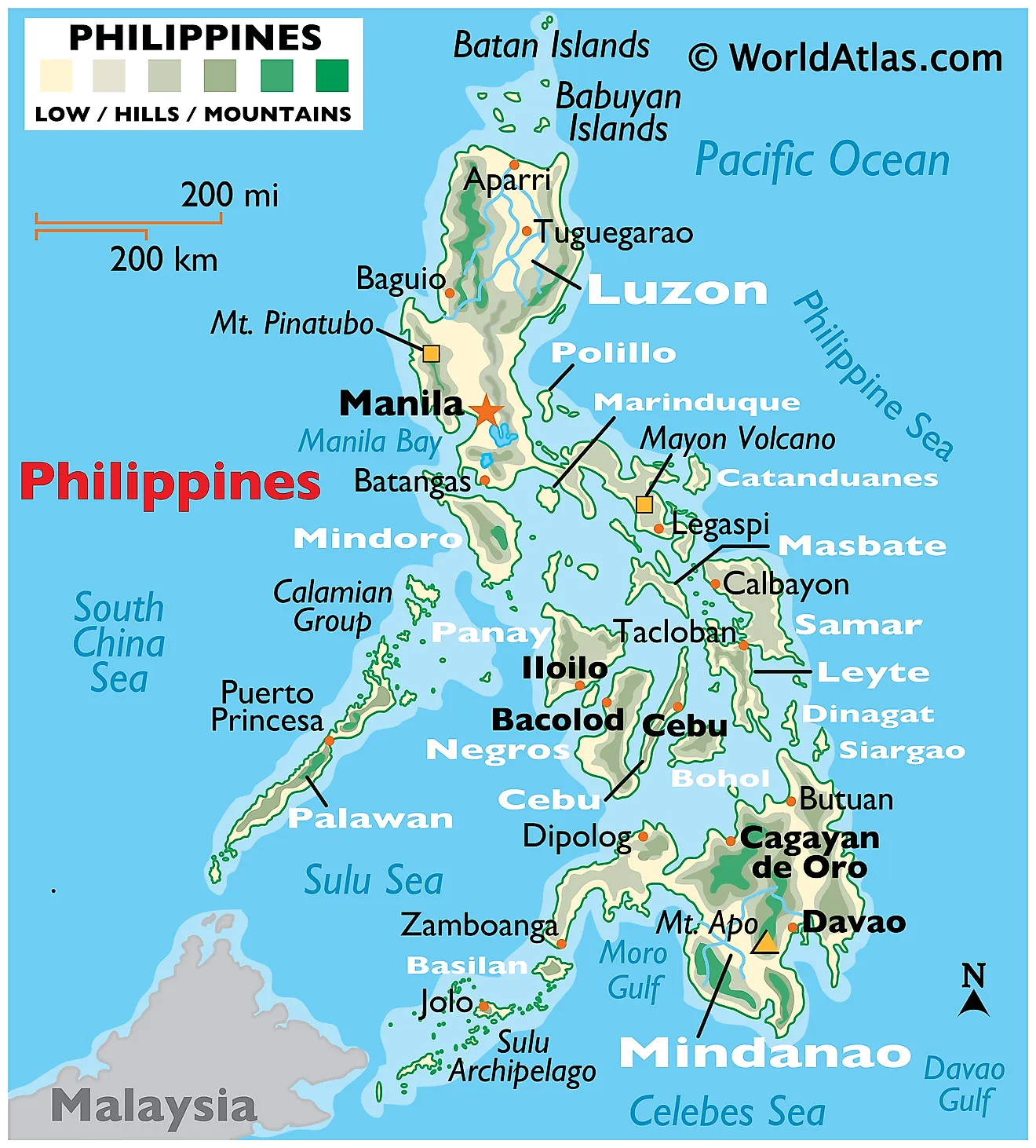
The Philippines, an archipelago in Southeast Asia, situates itself in the western Pacific Ocean. It shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the west, Taiwan to the north, Palau to the east, and Malaysia and Indonesia to the south. The archipelago encompasses a total area of approximately 300,000 km2 (about 115,830 mi2). The geographical profile of the Philippines is broadly divisible into three regions: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao.
Luzon, the largest and most populous island in the Philippines, rests in the northern part of the country. The northern part of Luzon features a rugged topography dominated by the Cordillera Central mountain range, including Mount Pulag, the second highest peak in the country. The Sierra Madre mountain range stretches along Luzon's eastern coast, providing a natural barrier against typhoons from the Pacific Ocean. Luzon's central area, known as the Central Plains, contains fertile agricultural land and numerous rivers, including the country's longest, the Cagayan River. The Bicol Peninsula to the southeast exhibits a mixture of flatlands and mountainous regions, notably hosting Mayon Volcano, one of the most active in the country.
Visayas, the central region of the Philippines, consists of several islands surrounded by the Philippine Sea to the east, the Sulu Sea to the west, and the Visayan Sea in the middle. The region comprises three main island groups: Western Visayas, Central Visayas, and Eastern Visayas. It exhibits a combination of mountainous terrain, coastal lowlands, and rolling hills. Panay Island in Western Visayas is notable for its central mountain range and fertile plains. Central Visayas includes Cebu, the country’s most densely populated island, and Bohol, known for its Chocolate Hills—a geological formation of over a thousand hills. Eastern Visayas, home to Samar and Leyte, presents a landscape dominated by extensive mountain ranges, narrow coastal plains, and low, rolling hills.
Mindanao, the second-largest island in the Philippines, anchors the southern region of the country. It features a broad range of landscapes from mountainous regions, such as the Diwata Range in the east and the Kitanglad Range in the north, to fertile valleys, such as the Bukidnon-Lanao Plateau and Cotabato Valley. The region also includes the country’s highest peak, Mount Apo. The island is almost equally divided into coastal lowlands and interior highlands, with the former being conducive to agricultural activities.
Bodies of Water: The Philippine Sea, a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean, lies to the east and north of the archipelago. On the western side, the South China Sea provides a natural maritime boundary. Internally, the country contains Laguna de Bay, the largest lake, located in Luzon, and Lake Lanao in Mindanao, the second-largest. Both lakes serve vital roles in providing hydroelectric power, irrigation, and drinking water.
The archipelago possesses an extensive river system. The Cagayan River in Luzon, the country's longest, starts from the Caraballo Mountains and drains into the Babuyan Channel. The Pasig River, which flows through the capital city of Manila, connects Laguna de Bay to Manila Bay. In Mindanao, the Rio Grande de Mindanao and the Agusan River are major river systems, vital for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
Islands: Comprising over 7,600 islands, the Philippines' two largest islands are Luzon and Mindanao. In the Visayas, notable islands include Cebu, Bohol, and Negros. The country also has several significant smaller islands, such as Palawan to the west of Visayas, known for its biodiversity, and Boracay, internationally recognized for its white-sand beaches. The Spratly Islands, a group of islets and reefs in the South China Sea, form part of the Philippines’ territorial disputes with several neighboring countries.
Administrative Map of The Philippines
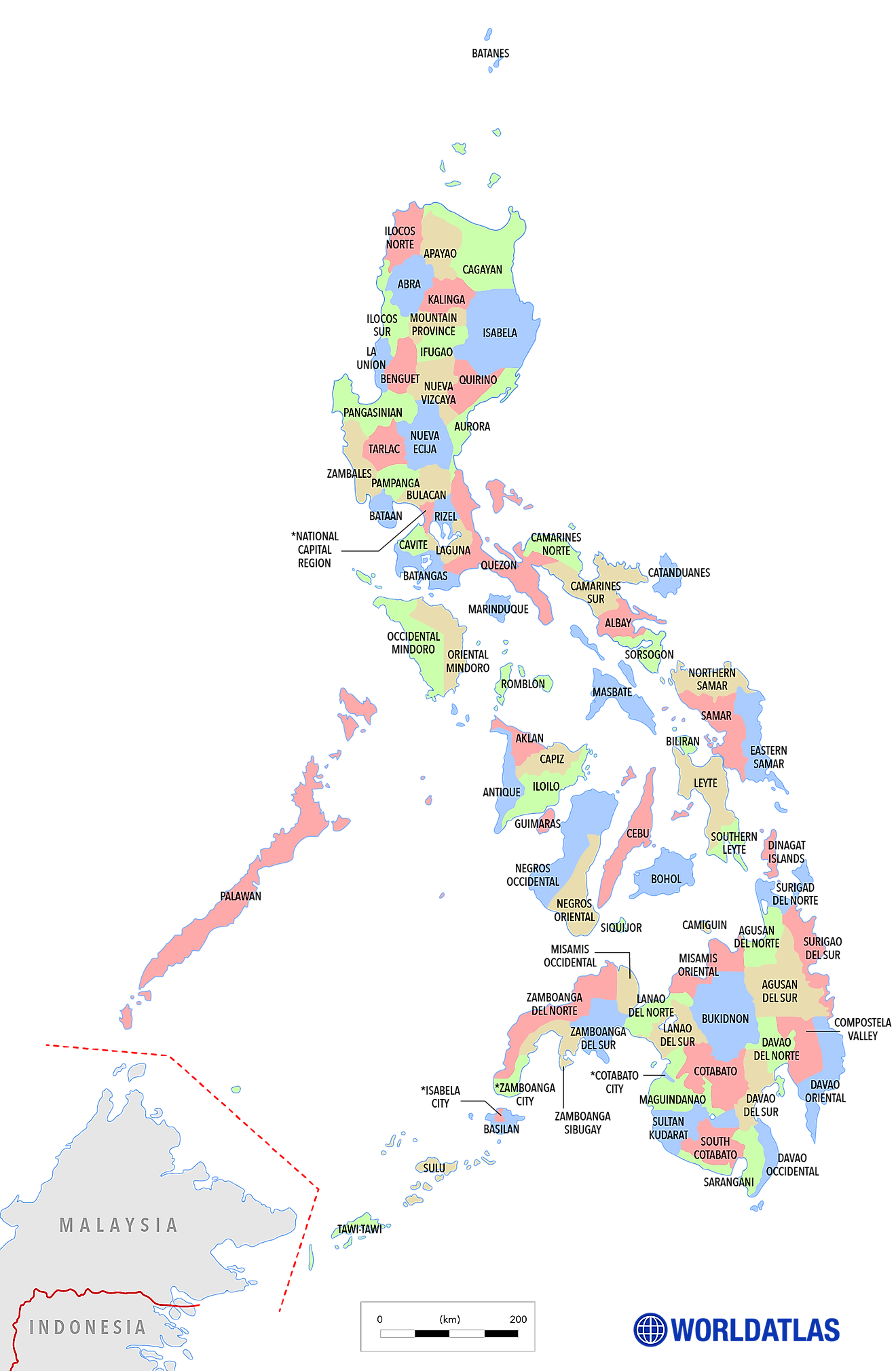
Philippines (officially, The Republic of Philippines) is administratively divided into 17 regions, 81 provinces, 146 cities, 1,488 municipalities, and 42,036 barangays.
The 81 provinces in alphabetical order are: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Basilan, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Biliran, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Compostela, Cotabato, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Occidental, Davao Oriental, Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, La Union, Leyte, Maguindanao, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar, Sarangani, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Tawi-Tawi, Zambales, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay;
Covering a total land area of 300,000 sq. km, the Philippines is an archipelagic nation located in Southeast Asia. Situated in the southwestern part of Luzon Island, along the eastern coast of Manila Bay is Manila – the capital city of the Philippines. It serves as the major administrative, political, social, cultural, and economic center of the country. Located at the heart of Luzon island, to the northeast of Manila is Quezon City – the largest and the most populous city of the Philippines. Both Manila and Quezon City are a part of Metro Manila, which is the National Capital Region of the Philippines. Metro Manila serves as the seat of the government of the Philippines.
Where is The Philippines?
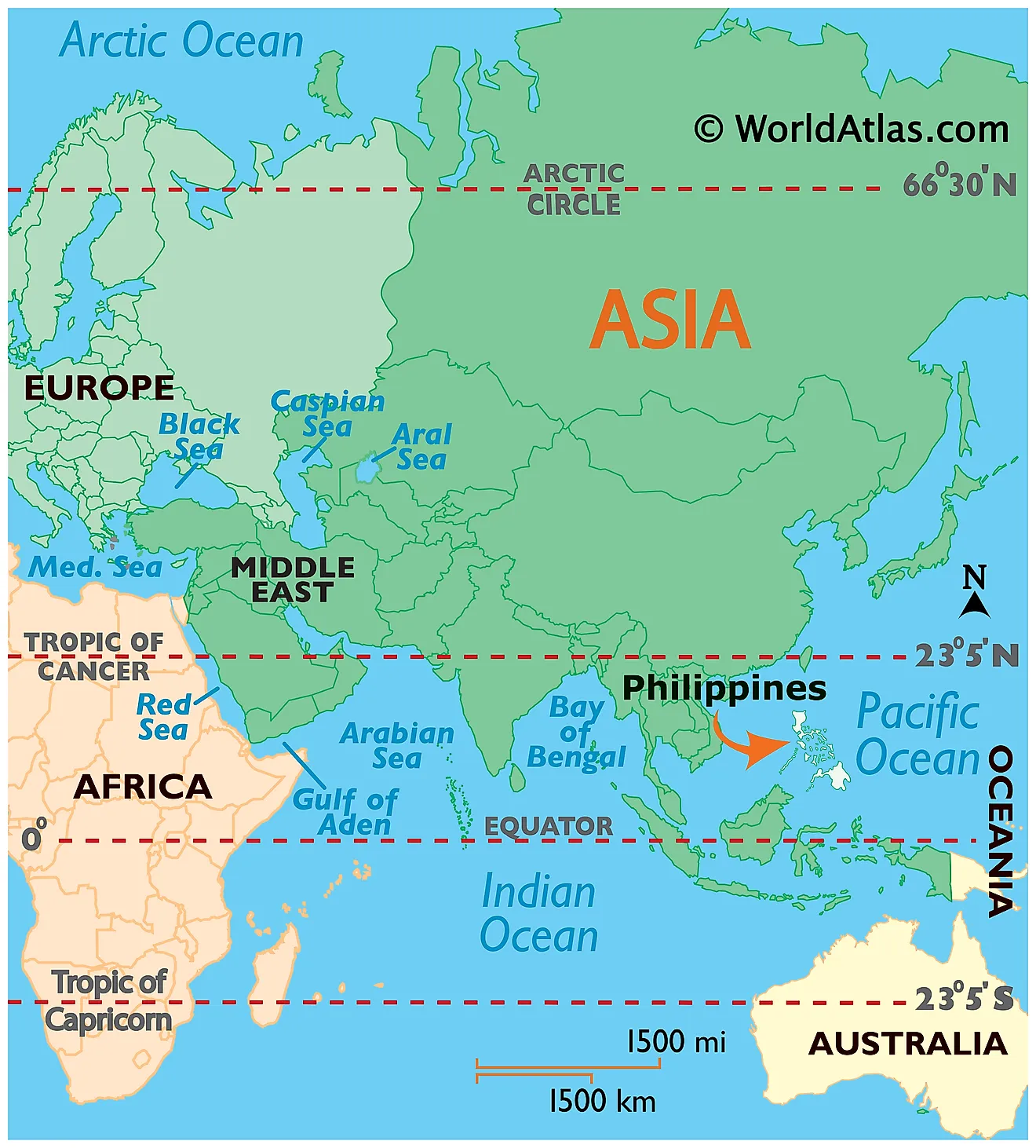
Positioned on the western edge of the Pacific Ocean, along the Ring of Fire, The Philippines is the 2nd largest archipelago in the world, with over 7,641 individual islands. It is geographically positioned both in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. The Philippines is surrounded by the South China Sea to the north and west; by the Philippine Sea to the east; by the Celebes Sea to the south; and by the Sulu Sea to the southwest. The Philippines shares its maritime border with Indonesia, China, Japan, Palau, Malaysia, Vietnam, and Taiwan.
Regional Maps: Map of Asia
Outline Map of The Philippines
The above blank map represents Philippines, an archipelagic nation located in Southeast Asia. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents Philippines, an archipelagic nation located in Southeast Asia.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of the Philippines |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Manila |
| 14 36 N, 120 58 E | |
| Total Area | 300,000.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 298,170.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 1,830.00 km2 |
| Population | 108,116,615 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | Philippine pesos (PHP) |
| GDP | $376.80 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $3,485.08 |
This page was last updated on July 17, 2023











