Maps of Macao
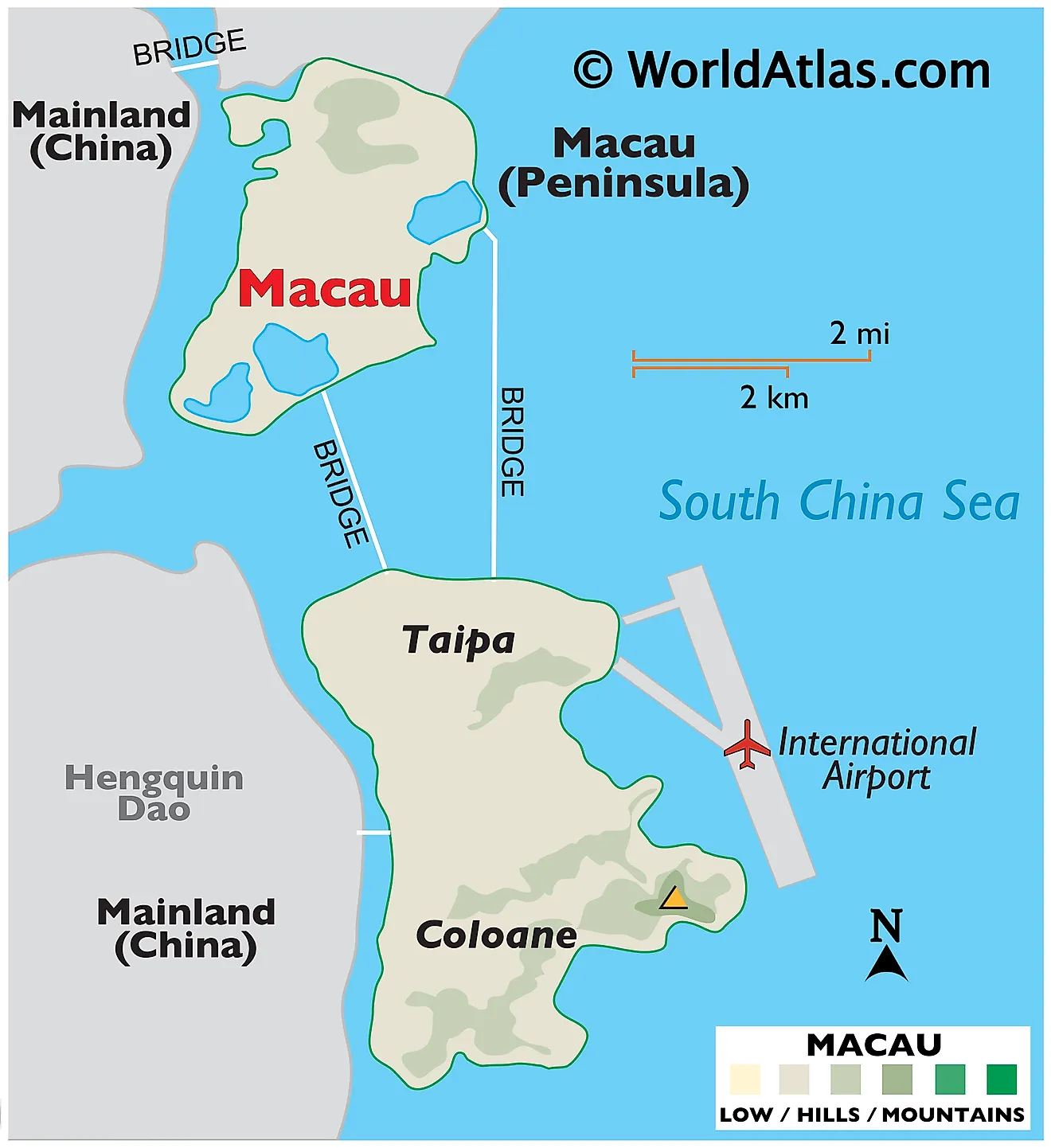
Macau is a Special Administrative Region of China with an area of 115.4 sq. km. As observed on the physical map of Maco, the region comprises of a peninsula attached to mainland Asia and the islands of Coloane and Taipa in the South China Sea.
Macao was formerly an island itself but was gradually connected to mainland by a growing sandbar. In more recent times, land reclamation has converted it into a peninsula. Constant land reclamation in the region has helped increase the area of Macau over the years.
The Macau Peninsula is mostly flat, but there are a few elevated spots.
Some steep, rolling hills are located on the island of Coloane, and along the southern coastline of the island of Taipa.
The highest point is Coloane Alto at 567 ft. (173 m). It has been marked on the map by a yellow upright trianble.
There are no major rivers or lakes in Macau.
Parishes of Macao Map
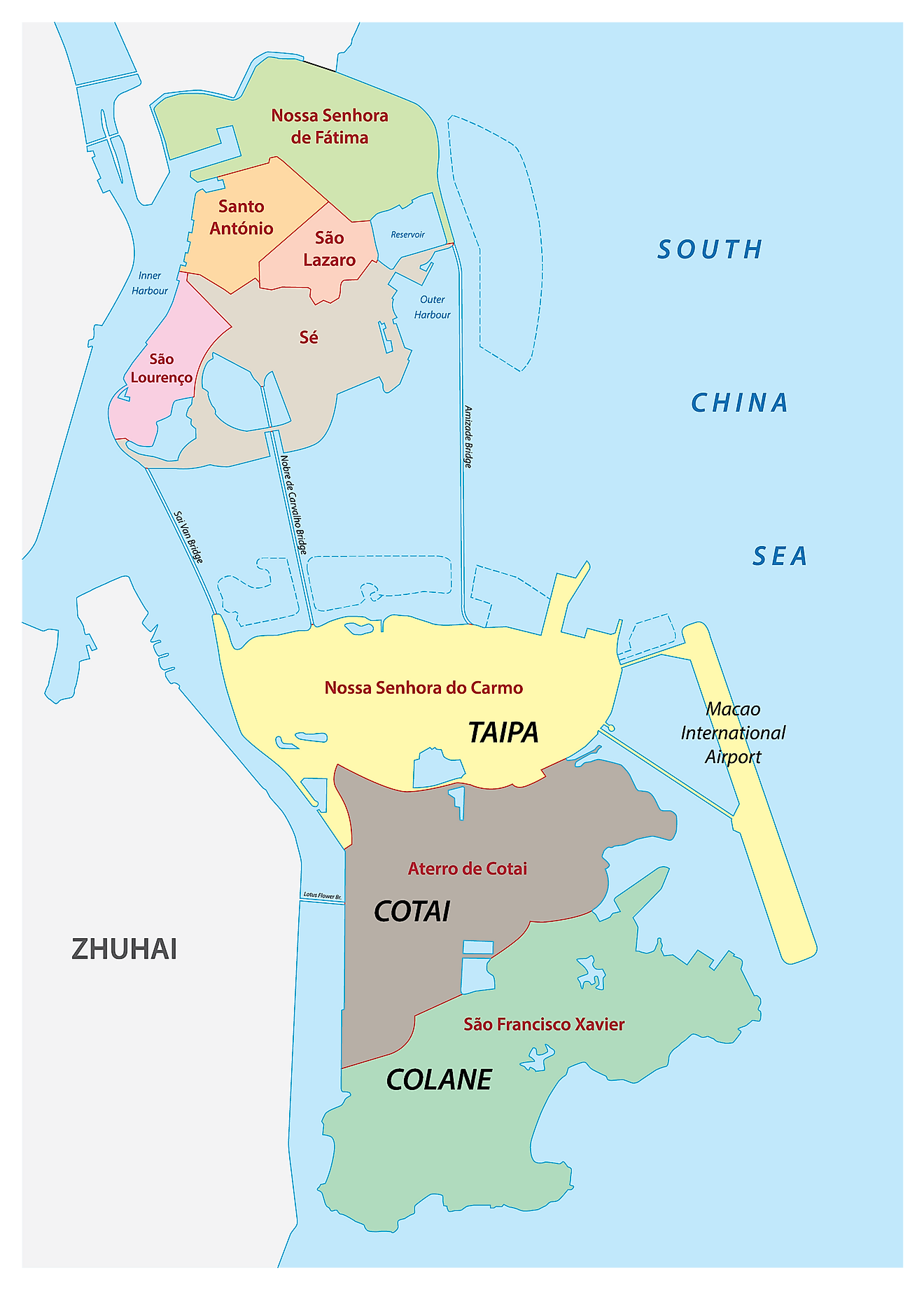
Macau is a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China. It has seven parishes for symbolic reasons only. These are: Nossa Senhora de Fátima, Santo António, São Lázaro, Sé, São Lourenço, Nossa Senhora do Carmo, and São Francisco Xavier.
The Aterror de Cotai is a special territory of Macao that is not part of any of the parishes.
Where is Macao?
Macao, formally known as the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China, is the world's most densely populated region. It is located on the western Pearl River Delta along the coast of the South China Sea in Southeast Asia. Hong Kong is located to the east of Macao. The South China Sea bounds it to the south and east while the Zhuhai city of Guandong, China, borders Macao to the north and west.
Regional Maps: Map of Asia
Outline Map of Macao
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Macau Special Administrative Region |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Total Area | 28.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 28.00 km2 |
| Water Area | N/A |
| Population | 640,445 |
| Largest City |
Macao (681,876) |
| Currency | Patacas (MOP) |
| GDP | $53.86 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $84,096.40 |
This page was last updated on February 24, 2021