Emerald Triangle
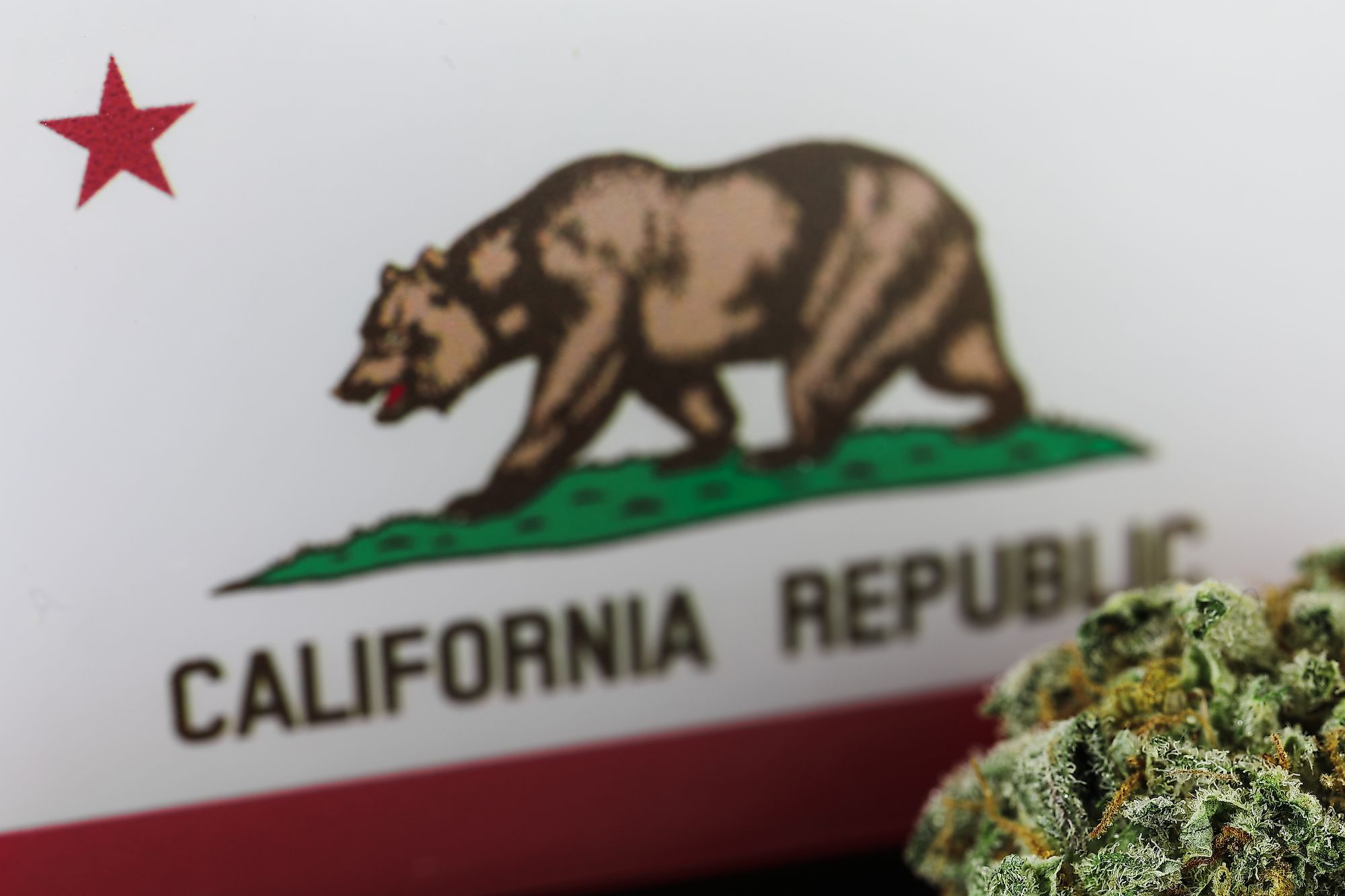
The Emerald Triangle is a region located in Northern California in the United States of America. It earned that name for being the largest cannabis-producing region in the country. The Emerald Triangle includes Humboldt, Trinity, and Mendocino counties in an upside-down triangular configuration. Collectively, the trio of counties produces more cannabis than any other place in the country.
Cannabis plants have been cultivated in the region since the 1960s, during San Francisco’s Summer Love. The majority of the residents in this region are either directly or indirectly reliant on the cannabis industry, which boomed after the passage of California Proposition 215, which legalized the use of cannabis for medical purposes in the state.
Geography Of Emerald Triangle
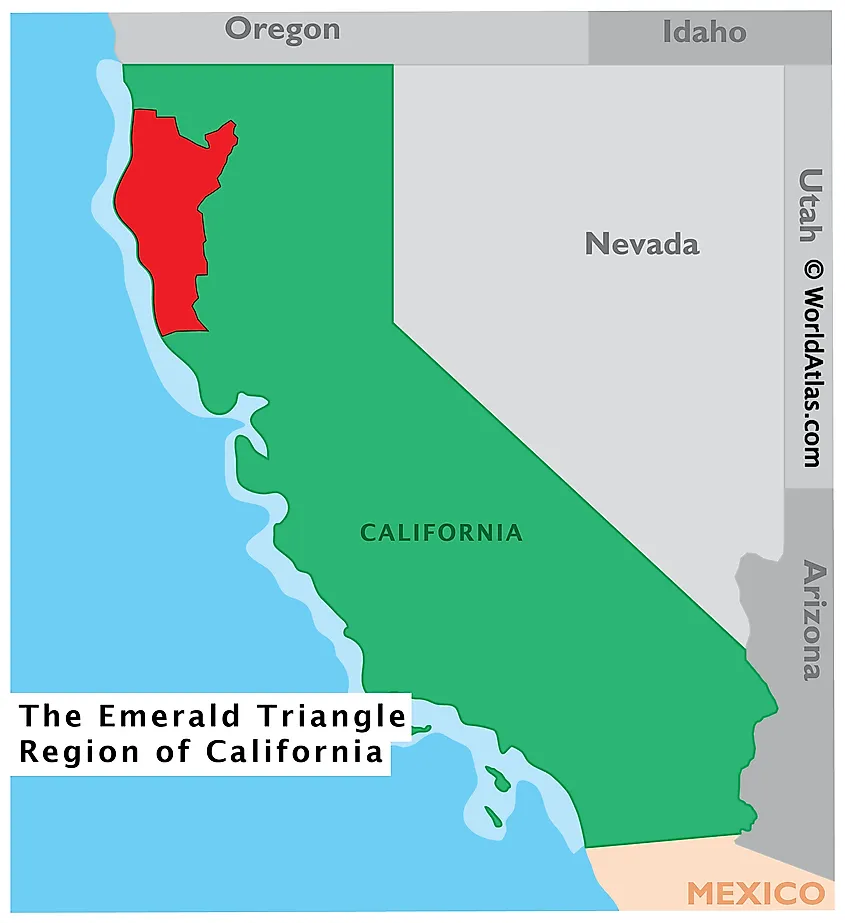
With an area that spans over 26,000 sq. km, the Emerald Triangle is composed of Mendocino, Humboldt, and Trinity counties. The region covers rural farmland, valleys, mountains, and the coast.
Humboldt County
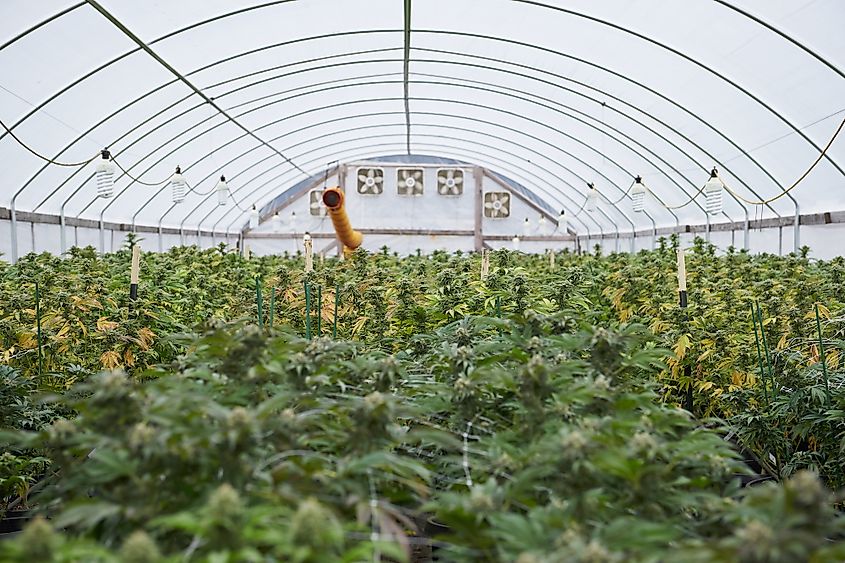

Humboldt County is home to over 135,000 people and has Eureka, the largest town in the Emerald Triangle. The county stretches north up to Del Norte County, the northmost county of California that borders Oregon. The fine production of cannabis that takes place in Humboldt has made the “Humboldt-grown” stamp on packaging desirable among consumers who consider the stamp a sign for top-quality products. In addition to the popularity of cannabis production, Humboldt is also famous for its stunning nature and state parks such as Humboldt Redwoods State Park and Redwood National Park. The county also has the famous Avenue of the Giants, a stretch of narrow highway surrounded by towering Redwoods.
Mendocino County

Mendocino County is bounded by Humboldt and Trinity counties on the north, Tehama County on the northeast, Glenn and Lake counties on the east, and Sonoma County on the south. The county stretches from the Pacific Ocean east into the Mendocino National Forest and from Cloverdale in the south up to the North Eel River that makes the borders of Mendocino and Humboldt. Mendocino has 10,040 sq. km with lots of farmlands and countless apple orchards, craft breweries, small-production wineries, and cannabis plantations. It is rich with national and state parks such as Admiral William Standley State Recreation Area, Henry Wood State Park, and Manchester State Park. In addition, about 9.6% of the county’s total area is water made of rivers, including Big River, Eel River, and beaches like Glass Beach.
Trinity County
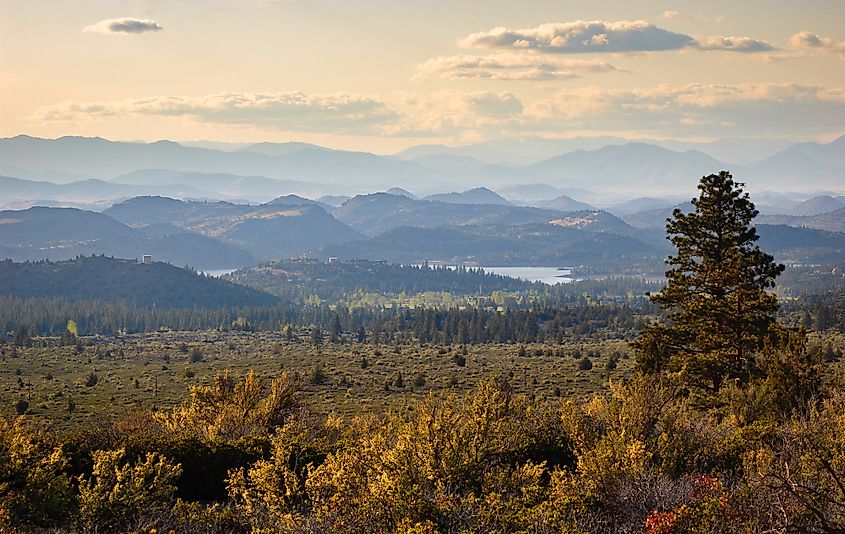

Trinity County is the smallest of the three counties in the Emerald Triable, both in size and population. Siskiyou County bounds the county on the north, Shasta County on the east, Tehama County on the southeast, Mendocino County on the south, and Humboldt County on the west. With an area of 8,310 sq. km, Trinity County is home to several national protected areas, including Shasta-Trinity National Forest, Six Rivers National Forest, and Mendocino National Forest.
History Of Emerald Triangle
The story of the Emerald Triangle begins with San Francisco’s Summer of Love in 1967. This social phenomenon movement was countercultural back-to-the-land and exploded in the Haight-Ashbury neighborhood of San Francisco. More than 100,000 “hippies” gathered in the Golden City to protest the Vietnam War, enjoy lots of weed, spread love, and promote art in the same year. The movement consisted of many progressive individuals, sometimes called flower children, who created a foundation for cannabis culture to thrive.
The U.S. President Richard Nixon’s DEA was looking to destroy the movement by going after the hippies, associating its members with marijuana and “blacks” with heroin, and heavily criminalizing both. The attempt was to disrupt the communities and drive them out of Haight and cities into rural America. The hippies established farms and agricultural communes from the Canadian border all the way to the deep south, but mostly in what is now called The Emerald Triangle. The hippies grew vegetables, fruits, and weed. Cannabis cultivation in California went through the roof as the movement members from Haight became weed farmers in the Emerald Triangle.
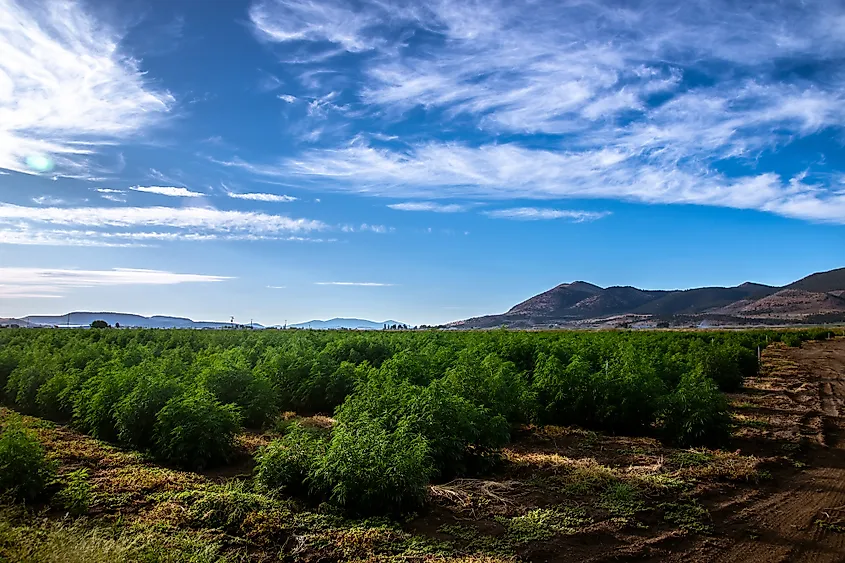

Thirty years later, in 1996, California passed Proposition 215, which legalized the use of cannabis for medical purposes. Although opponents greeted this law with controversy, the area was already ripe for marijuana cultivators to reap their harvest in California. Furthermore, the passage of California Proposition 64 in 2016 legalized the general sale and distribution of cannabis in the state.
Environmental Concerns
The Mediterranean climate and volcanic soil found in Emerald Triangle made the region ideal for growing weed. Many cultivators use sustainable practices to grow cannabis without pesticides or other chemicals. However, some growers don’t adopt organic marijuana cultivation and don’t employ sustainable farming practices. Environmentalists had concerns about illegal damming, pesticide runoff, and the worsening of water shortages that have plagued California for years. Moreover, some parts of the Emerald Triangle have experienced other pitfalls of unsustainable agriculture, such as landslides and the loss of animal habitats.











