India's National Parks
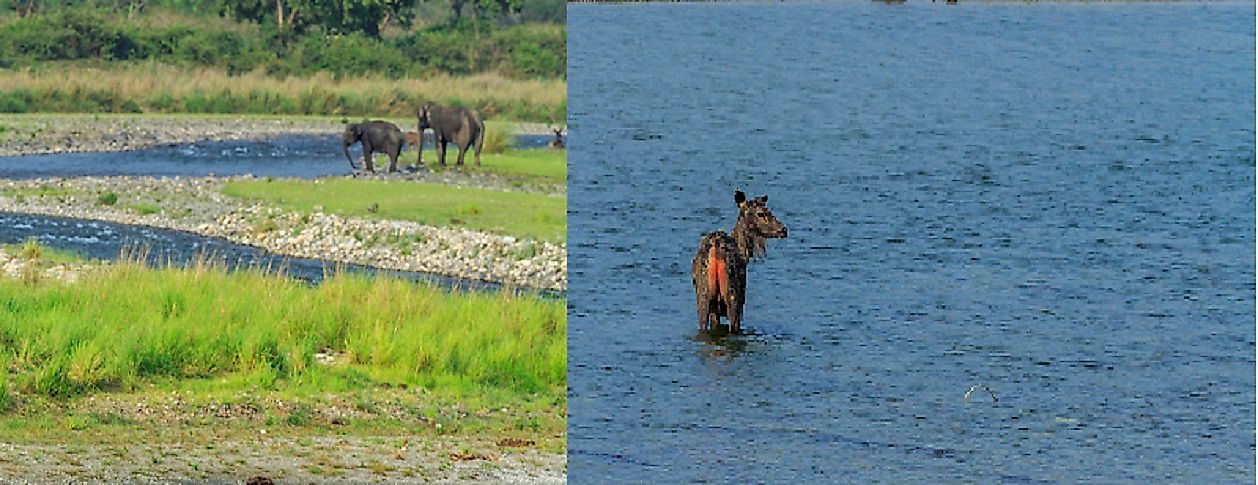
India is a South Asian nation that has been endowed with a wide range of beautiful terrains and ecosystems. The country’s landscape stretches from the Himalayan Mountains to the Indian Ocean coastlines. India is on the list of the 17 mega-diverse countries of the world. Due to its rich natural heritage, India established more than 100 national parks and protected zones to preserve the wealth. Notable national parks in India include Jim Corbett National Park and Hemis National Park, the country's oldest and largest, respectively.
Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park was India’s first national park. It was established in 1936 as a reserve area for the Bengal Tiger. The park covers an area of 509 square miles of which 200 square miles is the core area, and the rest 309 square miles is the buffer zone. Its terrain is comprised of rivers, deciduous forests, lakes, grasslands, hills, and valleys. Jim Corbett National Park experiences subtropical and highland climate. The park is home to more than 580 bird species, 480 plant species, 50 mammal species and 25 reptile species. The Crested serpent eagle, red jungle fowl, and blossom-headed parakeet are a few of the birds found in the park. The park has suffered from excess tourist visits that have exerted pressure on the park resources. The increasing population of the local communities has led to encroachment into the park. The Indian authorities have proposed the construction of a wall on the park’s border to keep out the invaders.
Hemis National Park
Hemis National Park is India’s largest park, covering an area of 1,700 square miles. It is located in a high altitude region. The park is famous for its population of the rare snow leopard. River Indus flows along the northern border of the park. The park hosts a variety of animal species including the endangered brown bear, Asiatic Ibex, Tibetan wolf, mountain weasel and the Himalayan marmot. It is also an ideal site for bird watching with birds such as Robin Accentor, streaked rose finch, chukar and red-billed chough inhabiting the park. Hemis National Park accommodates 15 endangered plant species that have medicinal value. There are approximately 1,600 people who live within the park. The people largely practice pastoralism which poses a threat to the park’s resources. The park is managed by the Department of Wildlife Protection of the Jammu and Kashmir government.
Desert National Park
Desert National Park is one of India’s most unique national parks, and is located in the northwestern region of the country. It is among India’s largest parks covering an area of 1,220 square miles. The park lies in the Thar Desert. Its landscape consists of craggy rocks, sand dunes, and sparse vegetation. The park is a popular site for migratory birds including kestrels, harriers, buzzards, eagles, falcons, and vultures. The main attraction to the park is the great Indian Bustard, an endangered bird found only in India. Animals such as desert fox, wild cats, and wolves are found in the park. The vegetation consists of grasslands and shrubs.
Valley of Flowers National Park
Valley of Flowers National Park is a scenic park in the West Himalayas region of India. The park is endowed with beautiful alpine flowers most of which are endemic to the area. It covers an area of 34 square miles and forms part of UNESCO biosphere reserve. The park is popular with mountaineers, botanists, and site seers. It also holds religious significance for the yogis who visit the area for meditation. The park is managed by the Forestry department of Uttarakhand. There are no settlers in the park and grazing in the area was banned in 1983.
Role of National Parks in India
India is rich in terms of the wildlife and natural scenes it houses. The country hosts unique plants and animals that attract tourists from far and wide. The national parks have helped preserve the endangered plant and animal species. They also provide an avenue for eco-tourism in the country.
India's National Parks
| India's National Parks | Square Miles of Area |
| Anamudi Shola National Park | 3 |
| Anshi National Park | 161 |
| Balphakram National Park | 85 |
| Bandhavgarh National Park | 172 |
| Bandipur National Park | 338 |
| Bannerghatta National Park and Biological Park | 40 |
| Bhitarkanika National Park | 56 |
| Bison (Rajbari) National Park | 12 |
| Blackbuck National Park | 13 |
| Buxa Tiger Reserve | 293 |
| Campbell Bay National Park | 165 |
| Chandoli National Park | 123 |
| Clouded Leopard National Park | 2 |
| Dachigam National Park | 54 |
| Desert National Park | 1,221 |
| Dibru-Saikhowa National Park | 131 |
| Dudhwa National Park | 189 |
| Eravikulam National Park | 37 |
| Galathea National Park | 42 |
| Gangotri National Park | 923 |
| Gir Forest National Park | 545 |
| Gorumara National Park | 31 |
| Govind Pashu Vihar Wildlife Sanctuary | 182 |
| Great Himalayan National Park | 291 |
| Gugamal National Park | 139 |
| Guindy National Park | 1 |
| Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park | 2 |
| Guru Ghasidas Sanjay National Park | 556 |
| Hemis National Park | 1,699 |
| Hazaribagh National Park | 71 |
| Inderkilla National Park | 40 |
| Indira Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park | 45 |
| Indravati National Park | 486 |
| Jaldapara National Park | 83 |
| Jim Corbett National Park | 509 |
| Kalesar National Park | 39 |
| Kanha National Park | 363 |
| Kanger Ghati National Park | 77 |
| Kasu Brahmananda Reddy National Park | 1 |
| Kaziranga National Park | 332 |
| Keibul Lamjao National Park | 15 |
| Keoladeo National Park | 11 |
| Khangchendzonga National Park | 689 |
| Khirganga National Park | 274 |
| Kishtwar National Park | 154 |
| Kudremukh National Park | 232 |
| Madhav National Park | 145 |
| Mahatma Gandhi Marine National Park | 109 |
| Mahavir Harina Vanasthali National Park | 6 |
| Manas National Park | 193 |
| Mandla Plant Fossils National Park | <1 |
| Marine National Park, Gulf of Kutch | 63 |
| Mathikettan Shola National Park | 5 |
| Middle Button Island National Park | <1 |
| Mollem National Park | 41 |
| Mouling National Park | 186 |
| Mount Abu Wildlife Sanctuary | 112 |
| Mount Harriet National Park | 18 |
| Mrugavani National Park | 1 |
| Mudumalai National Park | 124 |
| Mukundra Hills National Park | 77 |
| Mukurthi National Park | 30 |
| Murlen National Park | 39 |
| Namdapha National Park | 767 |
| Nameri National Park | 53 |
| Nanda Devi National Park | 243 |
| Navegaon National Park | 52 |
| Neora Valley National Park | 34 |
| Nokrek National Park | 18 |
| North Button Island National Park | <1 |
| Ntangki National Park | 78 |
| Omkareshwar National Park | 113 |
| Orang National Park | 30 |
| Pambadum Shola National Park | 1 |
| Panna National Park | 210 |
| Papikonda National Park | 391 |
| Pench National Park | 293 |
| Periyar National Park | 118 |
| Phawngpui Blue Mountain National Park | 19 |
| Pin Valley National Park | 312 |
| Rajaji National Park | 317 |
| Nagarhole National Park | 248 |
| Rajiv Gandhi Rameswaram National Park | 1 |
| Rani Jhansi Marine National Park | 99 |
| Ranthambore National Park | 151 |
| Saddle Peak National Park | 13 |
| Salim Ali National Park | 4 |
| Sanjay National Park | 180 |
| Sanjay Gandhi National Park | 40 |
| Sariska Tiger Reserve | 334 |
| Satpura National Park | 202 |
| Silent Valley National Park | 92 |
| Simbalbara National Park | 11 |
| Sirohi National Park | 16 |
| Simlipal National Park | 327 |
| Singalila National Park | 30 |
| South Button Island National Park | <1 |
| Sri Venkateswara National Park | 136 |
| Sultanpur National Park | 1 |
| Sundarbans National Park | 514 |
| Tadoba National Park | 241 |
| Valley of Flowers National Park | 34 |
| Valmiki National Park | 347 |
| Vansda National Park | 9 |
| Van Vihar National Park | 2 |











