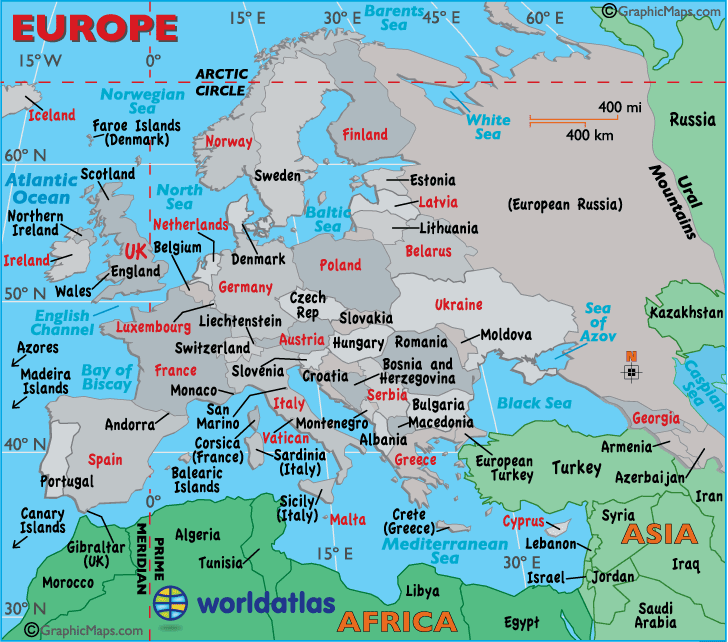
Europe Geography
Alps:
Located in south-central Europe, they extend for almost 700 miles from the coastline of southern France (near Monaco) into Switzerland, northern Italy and Austria, then southeast through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina as the (Dinaric Alps). Ending in Albania on the rugged coastline of the Adriatic Sea.
Known for stunning scenery, glaciers, lakes and valleys and the best skiing conditions on the planet, they're the source of many rivers and tributaries including the Danube, Po, Rhine and Rhone.
The highest point is Mont Blanc at 15,771 ft. (4,807 m)
Apennines:
The source of almost all rivers in Italy including the Arno, Tiber, and Volturno, the Apennines Mountains (Ital. Appennino) 830 miles (1,350 km) in length, form the backbone of the country, and run the entire length of the Italian Peninsula, ending on the island of Sicily.
The highest point is Mt. Corno at 9,560 ft. (2,914 m).
Atlantic Highlands:
Formed million of years ago during the Caledonian mountain-building periods as western lands were (forced) or pushed against the Scandinavian Shield. Significant mountain ranges here include the Kjolen in Norway and Sweden, and the Pennines that stretch through the central United Kingdom.
Balkan Mountains
These mountains extend from Yugoslavia across Bulgaria. Additional ranges run through Albania, Greece and Macedonia.
Its most famous mountain is Mt. Olympus, the highest and most awe-inspiring peak in all of Greece. In ancient times it was the mythical home of Zeus, and was declared the first national park in Greece in 1939. It stands at 9,568 ft. (2,918 m).
Carpathian Mountains
This mountain system located in eastern Europe is the source of the Dniester, Tisza and Vistula Rivers. They form the natural border between Slovakia and southern Poland, and then extend southward through Ukraine and into Romania.
There are major subdivisions, and the highest point is Mt. Gerlachovkain in northern Slovakia, standing at 8,711 ft. (2,655 m).
Caucasus Mountains
Stretching from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea, these volcanic mountains have many peaks above 15,000 ft. (4,572 m).
The highest point (and the highest point in Europe) is located here; Mt. Elbrus at 18,506 ft. (5,642 m).
Great Hungarian Plain
Located in southeastern Europe, and surrounded by mountains, the land features several small forests and large patches of grassland. It averages only 100 meters above sea level and often suffers from dry conditions, thus relying on winter snow run-off from the Alps and Carpathian Mountains.
Kjolen Mountains
This jagged mountain system runs along the border of eastern Norway and western Sweden. The highest point is Mt. Kebnekaise, standing at 6,965 ft. (2,123 m).
Massif Central
This mountainous plateau of southeastern France is the source of the Allier, Creuse and Loire. It's about 32,189 sq. miles (85, 001 sq. km) in size, and the highest point is Puy de Sancy at 6,186 ft. (1,885 m).
Mesata
The central plateau, or Mesata, covers nearly half of the entire country of Spain. This high plateau averages about 2,300 ft. (700 m) in the north, and 2,000 ft. (600 m) in the south.
It's surrounded by a series of mountain ranges including the Cantabrian, Sierra De Gata and Sierra Guadarrama in the north and central, and the Sierra Morena and Sierra Nevada in the south.
These mountains separate the Meseta from the Costa Verde, the Ebro valley, the Mediterranean and the valleys of Andalucia.
North European Plain
The fertile North European Plain slopes to the north-northeast from the Alps, extending to the Baltic Sea, and on into Denmark and southern Finland, Norway and Sweden. It continues east for almost 2,500 miles (4000 km), on into the Russian Federation.
The land is largely flat with smaller areas of hills, including the Central Russian Uplands. Farming is prevalent and agricultural communities dot the landscape.
Pyrenees
These mountains form the natural border between France and Spain and extend for about 270 miles from the Bay of Biscay to the Mediterranean Sea. The highest point is Pico de Aneto at 11,168 ft. (3,404 m)
Scandinavian Shield
An ancient area of rocky earth peppered with granite rock that was literally ground down by receding glacial ice sheets. It's a rolling area of land covered with thousands of lakes (mostly small), linked by rivers.
Ural Mountains
The Urals are 1,640 miles (2,640 km) in length and extend from the northern-edge of the Russian Federation down through Kazakhstan. They form a natural border between Asia and Europe.
The highest point is Mt. Narodnaya at 6,214 ft. (1,894 m).











