Are Whales Mammals?

- Whales are mammals, and not fish.
- Whales are warm blooded, breath air, and give birth to live young, all key signifiers of mammals
- Whales would not be considered fish as they are not cold blooded, don't breath through gills, and don't lay eggs.
Yes, whales are mammals. Whales, like many other large sea creatures, are classified as marine mammals, and certain species of whales are actually some of the largest mammals on earth. There can be some confusion concerning sea creatures regarding which are mammals and which are not. There are a few tips and rules which will help decipher which animals belong in which categories.
Types Of Whales
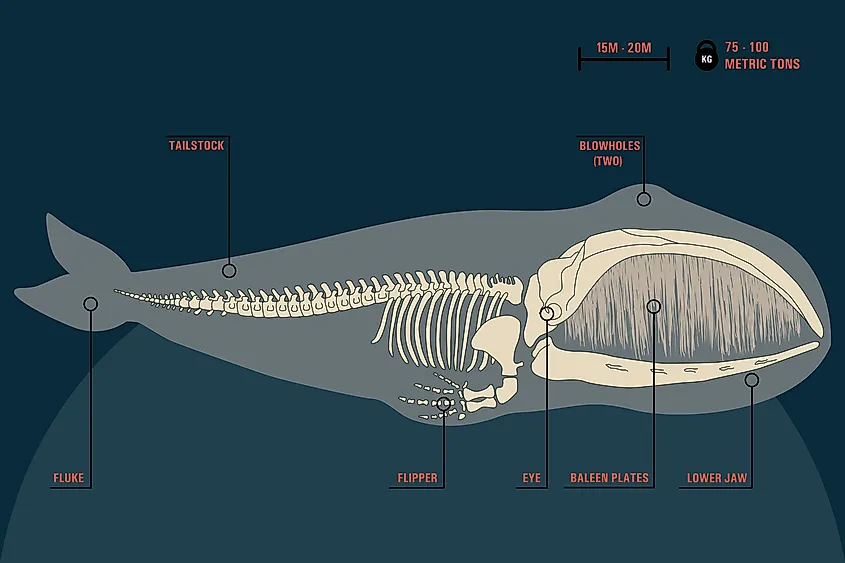
Whales, come in a variety of sizes and shapes depending on their species, but all are considered mammals. From the smallest whale, the 600 pound dwarf sperm, all the way up to the blue whale – the largest mammal on earth – all are classified as mammals. Whales are known as cetacean mammals, but also fall into one of two categories within this mammal distinction. The two categories are baleen, or Mysticeti, and toothed, or Odontoceti. Baleen whales eat plankton by way of baleen plates, a bony shelf in the front of their mouths, which filters tiny prey. Generally, baleen whales are the larger of the two suborders, and include species such as humpback whales and rorquals.
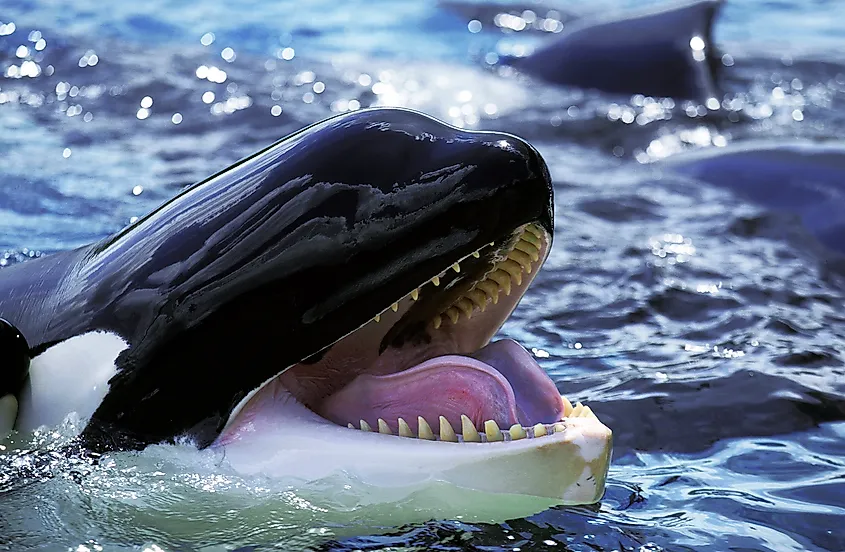

Toothed whales have more conventional teeth, which they use to eat larger prey such as penguins or fish or seals. Toothed whales are the small suborder, but still include a range of species from killer whales, or orcas, to narwhals and porpoises.
Why Are Whales Mammals?
Whales are warm-blooded or endothermic
Like all mammals, whales are warm blooded. When animals are warm blooded, or endothermic, it means that they can self regulate their body temperatures, and do not rely on external sources to warm or cool them. Their internal body temperature does not change based on their surroundings, but instead maintains a relatively constant state as they are able to regulate their metabolic rates.
Whales breath air through lungs
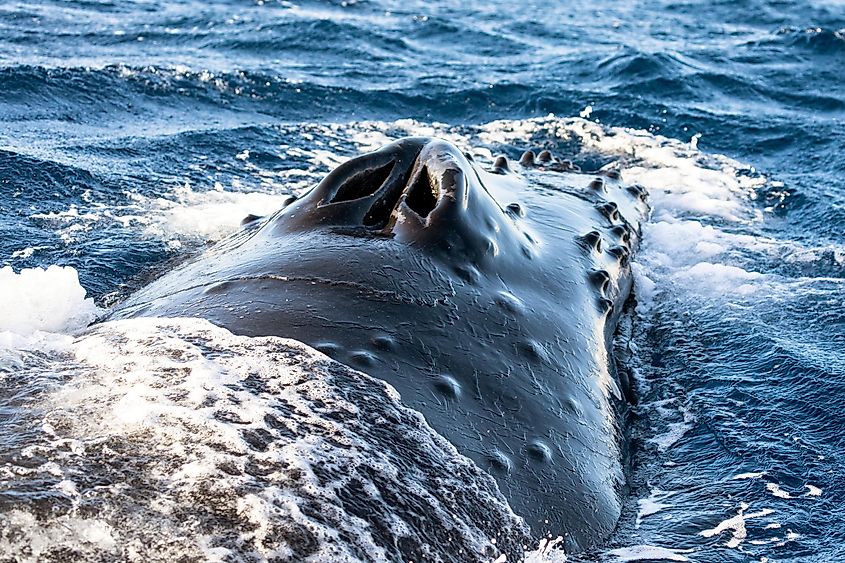

Another major indicator that whales are mammals is that they breath air from the surface, and do not – like fish – take oxygen from the water. Because whales spend their whole lives underwater, they must intermittently rise to the surface and take in oxygen through their blowholes. While whales do breath oxygen, and process it in their bodies through lungs, they do not breath air through their mouths, like most other mammals. Instead, most maritime mammals are equipped with a blow hole on the top of their head, or back. This blowhole is connected directly to the whale’s trachea, and air is taken in from here to the lungs.
This hole allows them to rise to the surface of the water to take in oxygen, without fully lifting themselves out of the water. The whale will shoot a burst of air out of the blowhole to clear away any water on the surface of the skin, ensuring water does not get in to the breathing ducts. Air and oxygen can then be taken in safely. The hole also has a strong suctioned airtight seal, which ensures water stays out when the whale is back underwater. Some whales have only one blowhole, while others have two. Generally, baleen whales have two blowholes, while toothed whales only have one. Whales are known to be able to hold their breath for a very long time, minimizing their need to rise to the surface. Some whales can only hold their breath for a few minutes, but others can last up to 90 minutes in between breaths.
Whales give birth to live young ones
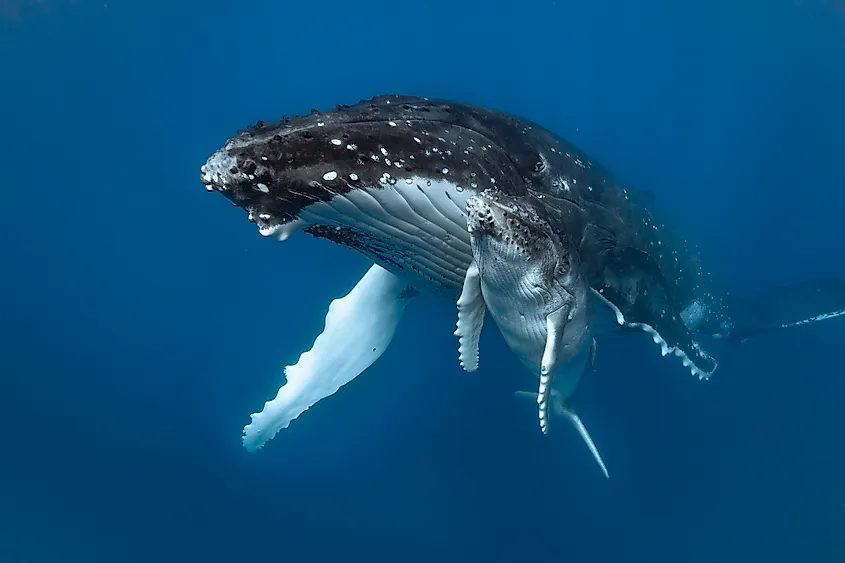

One of the defining traits of mammals is that in almost all cases, they give birth to live young. This means that whale babies are conceived and grow within the mother whale, and are born live and developed. Baby whales are known as calves. Most whales have a gestation period of ten to sixteen months, and most species of whale reproduce roughly every two to three years. As whales also only have one baby at a time, their reproduction rate is slower than a lot of other mammals. Whales are almost always born tail and fins first, and are born during the migration period. This means that whales are born ready to swim, and travel along with their pod during migrations.
Whales have mammary glands
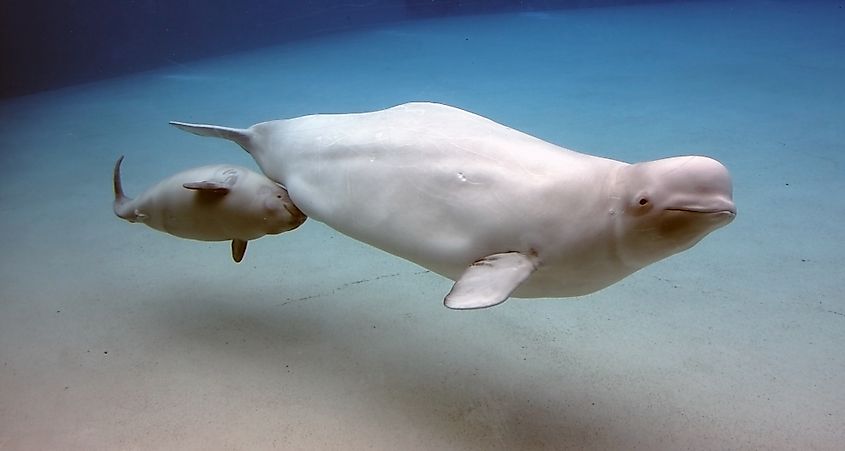

The word mammal actually comes from the word mammary, as in mammary gland. All mammals have mammary glands, and these glands are used to nurse their young. As whale calves are born live, they are then nursed by their mothers. A mother whale produces milk for her young from these mammary glands, and the young claves nurse underwater. Whales have only one calf at a time, and a baby will usually nurse for a full year.
Why Are Whales Not Fish?
There are several characteristics which can help indicate which animals are mammals. Similarly, there are indicators which can disqualify a marine animal from being a fish. Here are several reasons why whales cannot be considered fish.
Whales do not have gills
Because whales breath through blowholes and lungs, they do not have gills. Gills are a distinguishing characteristic of all fish, and they use these to filter oxygen out of the water around them. Whales do not have gills for breathing, and must instead surface in order to breath air above sea level.
Whales have hair when young
One of the classic ways to identify mammals in comparison to non mammals, is to determine whether or not they have hair on them. In most cases, mammals have hair or fur, while fish never do. Fish almost always have scales, although sharks do not. Even in cases of whales, or dolphins, which are smooth skinned marine mammals, the young do have vestigial hairs at some point. Most species of cetaceans lose their hair before they or born or shortly after birth however some whales continue to have hairs on their heads or around their mouths later in life. This is distinctly different from fish which do not have hair at any point in their lives.
Whales do not lay eggs
Similarly, most fish lay eggs. Whales do not lay eggs, and as such cannot be classified as fish.
Whales are cold-blooded
Fish are cold blooded. This means they do not possess the ability to regulate their internal body temperature. Instead, they are greatly effected by the temperature of the water around them, and are highly susceptible to changes in temperature and surrounding. Since whales are warm blooded, they are no fish.
Whales have horizontal tail orientation
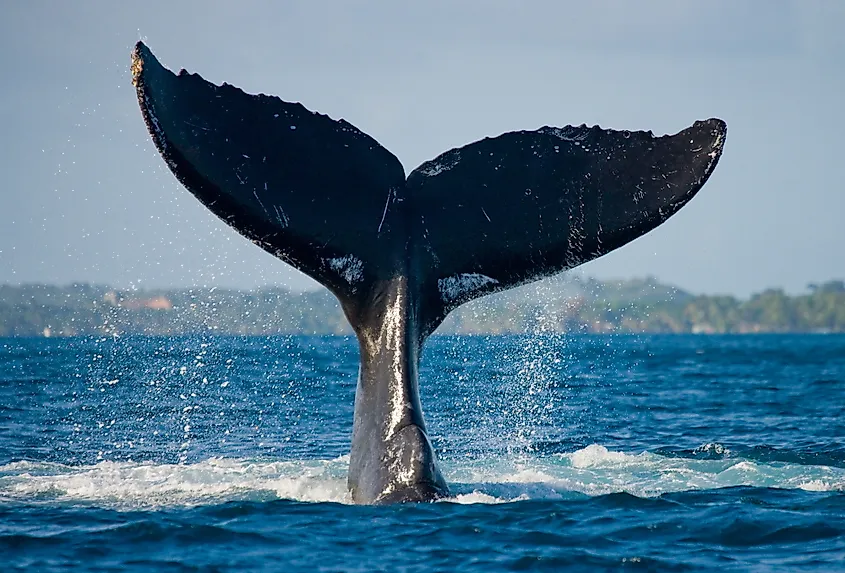

Fin orientation: Fish have tail fins which are oriented vertically. This means that they move their tail in a slashing, side to side motion in order to swim. This is in contrast to whales, and other marine mammals like dolphins and seals, which have horizontally oriented tail fins. This is why whales swim in a rolling up and down motion as they move forward, as they beat their tail up and down to move, rather than sideways.
By examining the distinguishing factors of mammals, fish, and whales more specifically, it is clear to see why whales are considered mammals and not fish.











