Top 10 Textile Importing Countries In The World
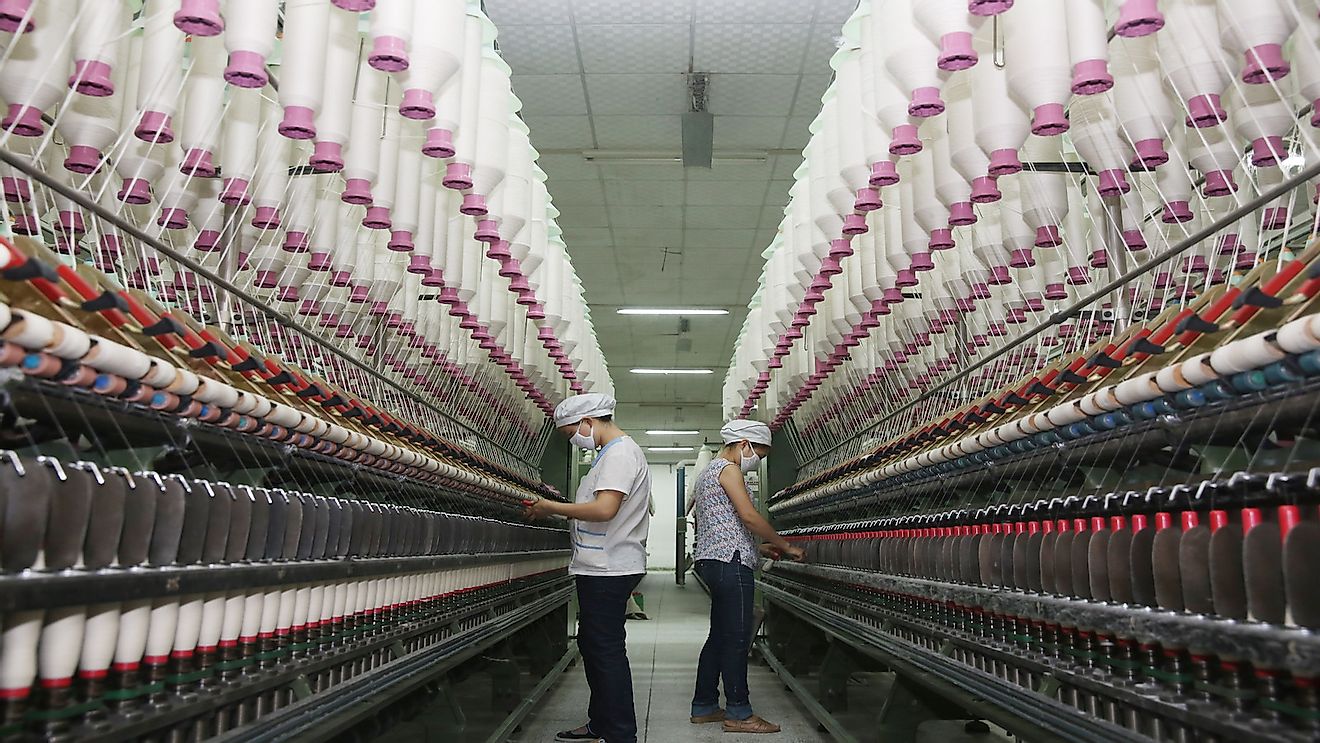

The international textile industry is one of the few sectors that impact almost everyone on earth. It is a $3 trillion industry that is concerned with refinement, distribution, and production of natural and synthetic fibers that are used in several other industries. Textile is the material that is made using either synthetic or natural fibers. The threads and fiber are worked on to produce yarn and then turned into cloth. The textile industry has employed about 60 million people on the planet. Jobs in the garment sector are crucial in the developing nations like Vietnam, Pakistan, and India. The industry accounts for about 2% of the world’s GDP and an even bigger portion of the GDP of the leading producers of textiles like China. China plays a key role in the global export and production of clothing and textile.
There are 2 types of fiber used in the textile industry (synthetic and natural). Synthetic fibers are manufactured by extruding polymers using spinnerets onto another medium where they harden. Natural fibers are either from plants (sisal, flax, and cotton) or from animals (silk-worm, rabbit, goat, and sheep). Vegetable fibers come from the leaf (sisal), the stem (jute, hemp, and flax), and seed (cotton). Cotton is the most crucial natural fiber on the planet. The global yield of 2007 was about 25 million tons from over 50 nations.
History Of The Textile Industry
There are numerous indications that the textile industry already existed during the Paleolithic era. A unique textile impression was discovered at Pavlov. Several Neolithic textiles were discovered in the pile-dwellings excavation sites in El-Fayum, Egypt, and Switzerland. The excavations site at El-Fayum dated back to around 5000 BC. During the Roman times, leather linen, and wool clothed the community, while silk, was an extravagant luxury. Silk was imported to Rome through the Silk Road. The use of linseed fiber to manufacture clothes in the northern parts of Europe dates back to the Neolithic era. People started importing cotton into Northern Europe during the late Middle Age. Cotton farming in the warmer parts of the Americas and Asia started in the late sixteenth century.
The primary steps in cloth production are producing the fiber and then converting it yarn and the cloth. The cloth is then sold to the garment manufacturers. The preparation process of fiber differs, depending on the type of fibers being used. Wool requires washing and carding, while flax requires retting and dressing. The weaving and spinning process is quite similar between wool and flex. The spinning process evolved from twisting of fiber by hands to using a spinning wheel and a drop spindle. Several spindles and parts of spindle have been excavated in various archaeological sites, and they are considered to be the first pieces of technology in this industry. The Spinning wheel was invented in the eleventh century in the Islam World.
The Switch From Natural To Synthetic Fibers
The wool and cotton producers dominated the textile industry until the twentieth century when other types of fibers were introduced in the market. Several chemical companies started manufacturing synthetic fibers for many uses. Nylon was created in 1935, while rayon was invented in 1910. Nylon and rayon were cheaper substitutes of silk, and they were used to produce a wide range of products, including military parachutes, toothbrushes, and women stockings. Spandex, polyester, and acrylic were invented in the 1950s, while Saran, metal fibers, modacrylic, and acetate were developed during the 1940s. Polyester became quite common in the apparel sector, and by the 1970s, more polyester was purchased in the U.S. than cotton.
The apparel sector was replaced as the biggest market in the textile industry by the home and industrial furnishings in the late 1980s. Global manufacturing and industry integration led to several small companies closing down in the U.S. in the 1970s and 1980s. 95% of the looms in Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina shut down. Several other textile companies were also closed in Virginia and Alabama.
The Top Importers Of Textile
European Union
According to the WTO, the European Union is the largest importer of textiles and apparel, accounting for over 23% of the global textile and apparel imports. The largest textile markets within the EU (Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, and the United Kingdom) were responsible for 72% of the European Union’s textile imports. The value of the textile imports to the EU has been increasing by 5.8% per annum. The largest product segment in the region is knitwear; however, the most attractive and fastest-growing product categories are active sportswear and fashion. The apparel market in the western parts of Europe is more developed and better than the eastern and central markets. The fastest-growing EU markets for textile imports are Romania, Hungary, Croatia, and Poland. Despite the rapid growth, these 4 nations accounted for only 6.7% of the region’s textile and apparel imports.
The United States
Other than being one of the world’s top exporters of textile products, the United States was the second-biggest textile importer in 2018. The value of the country’s imports increased by 7.2% from 2016 to 2017 ($25.7billion). The textile imports by the U.S. have grown by 77.8% from 2000 to 2017, while the apparel imports have decreased by 0.5% from 2016 to 2017. Since the U.S. is no longer a leading apparel manufacturer, but one of the world’s top consumers. Therefore, apparel accounted for 75.7% of the total American apparel and textile imports in 2017, followed by textile, yarns, and fabrics.
The Top Importer Of Textiles In Asia
The top textile importing countries in 2018 were China and Vietnam. Other than being the world’s biggest exporters of textiles, China is also the third-highest textile importing nation. China managed to import textiles worth $18billion in 2018 and export textiles worth $119billion in the same year. China was the top supplier of textile to the EU in 2017, with the EU’s textile imports from China doubling those of Bangladesh. The other top textile importer in Asia, Vietnam, managed to import textiles worth $18billion. Other top textiles importing Asian nations are Japan ($9billion), Bangladesh ($11billion), Hong Kong ($7billion), and Indonesia ($7billion).
Top 10 Textile Importing Countries In The World
| Rank | Country | Import value in billion USD |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | European Union | 77 |
| 2 | United States | 30 |
| 3 | China | 18 |
| 4 | Vietnam | 18 |
| 5 | Bangladesh | 11 |
| 6 | Japan | 9 |
| 7 | HongKong, China | 7 |
| 8 | Indonesia | 7 |
| 9 | Mexico | 7 |
| 10 | Turkey | 6 |