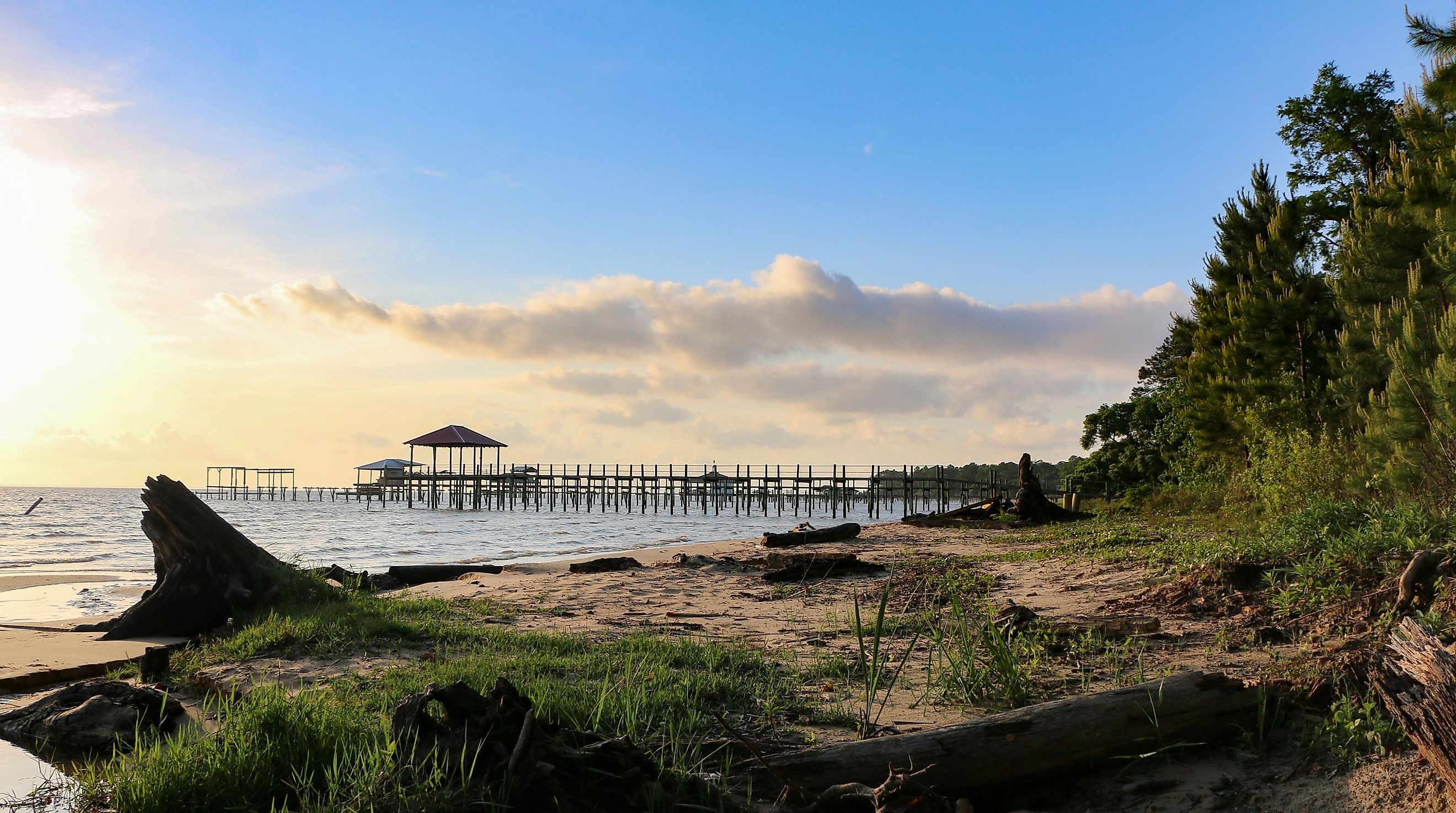
Mobile Bay
The Gulf of Mexico, bounded by the United States and Mexico, is popular for its white-sand pristine beaches, calm and warm water, islands, and bays. One of its major assets is Mobile Bay in Alabama, US. Mobile Bay is the US’ fourth-largest estuary (enclosed coastal water body). It is a popular spot in Alabama because of the “jubilee,” a natural phenomenon whereby crustaceans and fish swim to the bay's shores.
Where Is Mobile Bay?
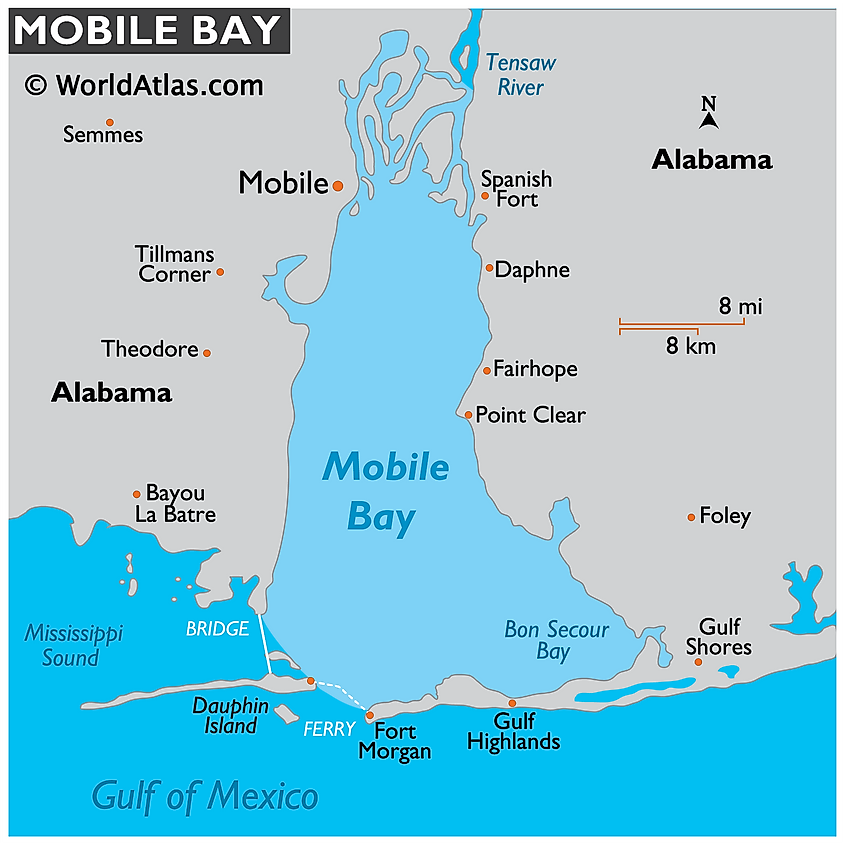
The Mobile Bay lies in southwest Alabama, near the western border with Mississippi and the eastern border with Florida. Dauphin Island in the west and Fort Morgan Peninsula in the east form the bay’s mouth. Mobile City is on the western shores, near the head of the bay. Several towns are located on the Eastern Shore, including Daphne, Point Clear, Spanish Fort, and Fairhope. Montgomery, Alabama’s capital, is approximately 270 km northeast of Mobile Bay.
Geography
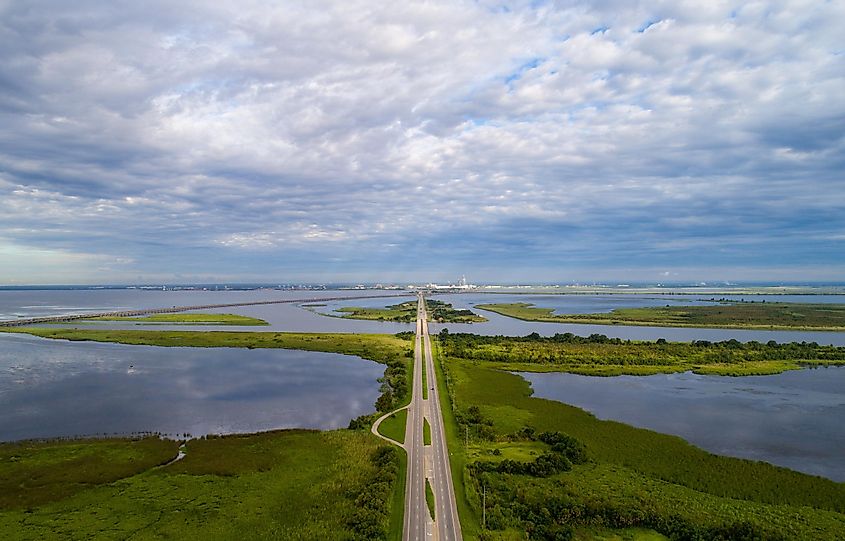

Mobile Bay extends 50 km north from the Gulf of Mexico’s outlet to the Mobile River’s mouth. The width varies from 13 km at its narrowest point to 39 km near the outlet into the Gulf of Mexico. The Bay covers an estimated area of 1,070 km2, with an average depth of 3 m. The deepest points, located in the shipping channel, exceed 23 m in depth. It has a significant discharge of 1,800 m3 per second. Several rivers empty into the Bay, including Tensaw River and Mobile River in the north, Fowl, Dog, and Deer Rivers in the west, and Fish River in the east.
Marine Life
Alabama has the fifth-highest species diversity in the US, thanks in no small part to Mobile Bay. The bay is home to 126 reptile and amphibian species, 49 mammals, 337 fish, and 355 birds. Endemic species within the bay include 110 aquatic snails, 33 mussels, and 40 fish. Some of the megafauna in the bay are crabs, shrimps, oysters, finfish, demersal fish, and crinoids. The plant species on the bay’s shores include spruce pine, saw palmetto, and cherry bark oak.
Brief History

The areas near Mobile Bay were long occupied by the Indigenous peoples of the area, such as the Mississippians. Years later, Spanish explorers sailed into the region and named the bay Bahia del Espiritu Santo, meaning “the Holy Spirit Bay.” Between 1516 and 1519, the area was extensively explored by Alonso Pineda and Diego Miruelo. In 1540, Hernando de Soto explored the Mobile Bay area and discovered the Indigenous people inhabiting the area. He destroyed the fortified town of Maubila, from where the name “Mobile” is derived.
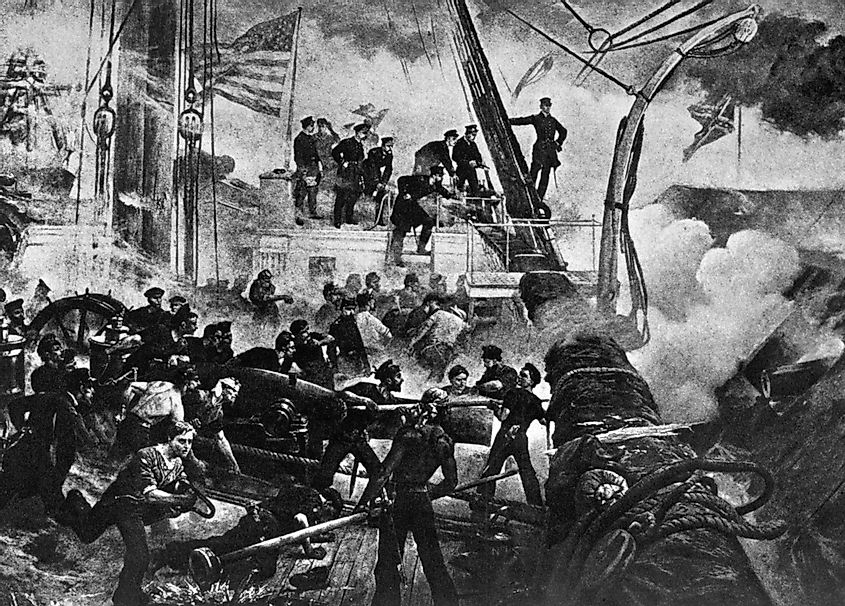
Mobile Bay was a major port for steamships that brought supplies during the American Civil War. During the 1864 Battle of Mobile Bay, the Union forces completely sealed off the bay’s southern port. Several ship wreckages of the Civil War era were on the Bay. The areas near Mobile Bay have experienced several natural disasters. In 1979 and 2005, Hurricane Frederic and Hurricane Katrina devastated the area, destroying Dauphin Island, beach houses, and boats.