What Are The Major Natural Resources Of Cyprus?

Cyprus is an island nation located in the Eastern region of the Mediterranean Sea, and it is the 3rd largest island in the region after the Islands of Sicily and Sardinia, both of which belongs to Italy. Cyprus is the 80th largest Island in the world spanning an area of 3,572 square miles. Cyprus was classified as a high-income country in 2001 by the World Bank, and the IMF listed the country as one of the advanced economies in the same period. In the 1990s the country experienced erratic growth rates indicating vulnerabilities in the country’s economy caused by political instability, swings in the arrival of tourists, and change in economic situations in Western Europe. The country adopted the Euro as its official currency in January 2008. Currently, the country is the world’s 118th largest exporting economy, and in 2016, its exports were worth $3.11 billion, and imports were valued at $7.63 billion. In the same year, the country’s GDP was $20 billion while its GDP per capita was about $32,700
Land
As of 2011, Cyprus had arable land which was about 9.6% of the total land area, and out of this only 3.54% was under permanent crops. When the country gained its independence in 1960, agriculture was the main backbone of the economy and was primarily comprised of subsistence farming and small-scale farms. Development of irrigation projects on the island made it possible to commercialize farming and the country was able to export fruit and vegetables. It was able also to substantially increase production of meat, dairy products, and wine to meet local demand and some for export. By the 1970s most farms were small-scale and contributed about 70% of all exports while employing about 95,000 people, which was equivalent to one-third of the country’s labor force. As the economy of Cyprus expanded, manufacturing and service sectors began playing a key role, and by the first half of 1970, the role of agriculture had declined significantly to account for only 18% of the GDP. After the division of the country following the Turkish occupation in 1974, the Turkish Cypriots in the North were in possession of agricultural resources which produced approximately four-fifths of cereal crops and citrus, all of the tobacco and about two-thirds of green fodder. The Southern Cypriots were in possession of agricultural land producing about three-fourths of potatoes, two-thirds of carob trees, two-thirds of livestock population, and half of land with olive trees. By the 1990s, significance of agriculture in the country’s economy declined much further as the service industry became even more dominant.
Mining and Quarrying
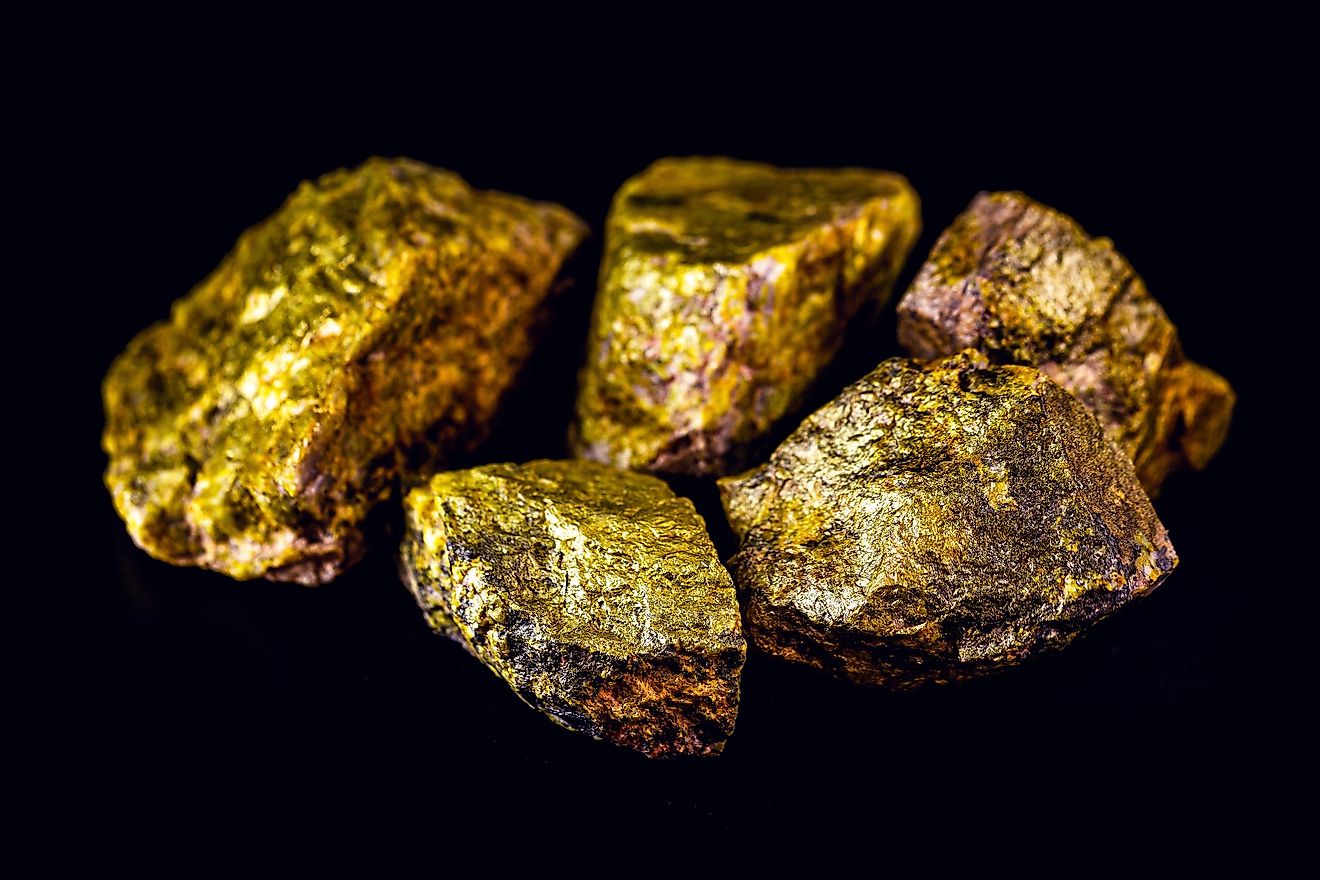
Mining in Cyprus has a long history and copper mining dates back to 2500 BC. Currently, mining in the country has been on the decline. Copper has been the dominant mineral in the country along with other minerals like gold, iron pyrite, cement, asbestos, and chromites. Although copper was the dominant mineral at one time, as of 2012 it did not contribute significantly to the country’s gross national product. There is huge quarrying in Cyprus, and there are about 220 quarries spread across the country producing gravel and sand, havara, ochre and umber, limestone, building stones, gypsum, clay, and bentonite. The country also produces hydrated lime, gypsum plasters, and other types of cement for export. According to the information from government, mining and quarrying in the country generated $105.3 million in 2011, which was a drop of $61.4 million from the previous year. The Skouriotissa Copper Mine is possibly the oldest operational mine in the world having started its operations in 1914 by the Cyprus Mines Corporation.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry in Cyprus is still undergoing development, and recent discoveries were made in the country’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and vast deposits of natural gas in the Zohr gas field near the Egyptian waters. Presently, there are eight concession licenses given to different companies. The first license to be granted was for Block 12 known as Aphrodite, which was granted in October 2008 to Noble Energy, and in 2012 the company announced the discovery of natural gas field estimated to hold between 5 and 8 trillion cubic feet. In 2013, the reserves were revised to be in the tune of 3.6 to 6 trillion cubic feet, and 2014, it was revised upwards again by 12%. Other companies which have partnered with Nobel Energy include Royal Dutch Shell, and Delek and Avner of Israel among others.
Water Resources
The Island of Cyprus has had a shortage of water throughout its history and droughts are a common phenomenon. The country has no river with perennial flow. Groundwater was the main source of water for irrigation purposes until 1970, and it led to almost all aquifers being severely depleted. Water problem in Cyprus was recognized early enough and the government in conjunction with the international organizations engaged in designing long-term solutions to overcome the problem. Currently, Cyprus has 108 reservoirs and dams which have a combined holding capacity of 11,653,800,000 cubic feet. The dams in the country are now the main source of water for both domestic and agricultural use. The country has also constructed water desalination plants to deal with the prolonged droughts experienced lately. The largest dam in the country is Kouris which collects water from Kryos, Limnatis, and Kouris rivers. The dam also receives water from Diarizos River, which is diverted to the dam through a 9 mile long connecting tunnel. Other dams in the country include Asprokremmos, Evretou, Geçitköy, and Kannaviou among others.
Fascinating Landscape
The island nation of Cyprus has beautiful land and scenery, and therefore the country is popular with tourists. As a result, tourism plays a key role in the country’s economy and in 2006 it accounted for 10.7% of the GDP. In the same period, the tourism sector employed 113,000 Cypriots. The country receives about 3 million visitors every year making the country the 40th most popular destination globally. The tourism sector in the country has received numerous international honors. Similarly, the county’s beaches have also been awarded 57 blue flags. In 2013, the world economic forum ranked the country 29th in travel and tourism competitiveness index. The country was also ranked the first globally regarding tourism infrastructure.
Economic Growth
The first quarter of 2018, the economy of Cyprus grew by 0.8%, which was similar to the growth in the previous period. From 1995 to 2018 the GDP growth rate has been about 0.59%. In the fourth quarter of 2012 GDP, it grew by -2%, which was the lowest, while the third quarter of 2001 was the highest at 2.4%. It is forecasted that the GDP growth will trend at about 0.4% in 2020 based on econometric models.