Flags, Symbols & Currency of Antigua and Barbuda

The National Flag of Antigua and Barbuda was officially adopted on February 27, 1967, when its status changed from a colony to an associated state of the United Kingdom. A ‘unique and easily recognizable flag’ designed by the renowned local artist and sculptor Sir Reginald Samuel was adopted as the flag of Antigua and Barbuda. The flag has a height to width proportion ratio of 2:3.
The national flag is designed as a horizontal rectangle and its background is segmented into three inverted triangles. Two of these triangles are red and are set from the hoist and fly side of the flag. The middle triangle has sides of equal length and is inverted, with its base on the top edge of the flag and is pointed towards the flag’s bottom. This triangle features three horizontal bands of black (top), light blue, and white, arranged horizontally, with the likeness of a yellow rising sun incorporated on the black band. The light-blue band is half the width of the red and white bands.
The red band represents the energy, tenacity, and dynamic nature of the nation’s people in forging their destinies. The colors red, yellow, blue, and white when combined represent the sun, the Caribbean Sea, and the beaches of the island nation. The rising sun symbolizes the dawning of a new era (a belief that was most profound after the country gained independence). The light-blue band also represents the hopes and aspirations of the people of the country. Even the V-shape made by the dissection of the isosceles triangle is symbolic and is said to represent victory. The black represents the African heritage of most of the population. It also symbolizes the fertile soils of the island nation.
History of the Flag of Antigua and Barbuda
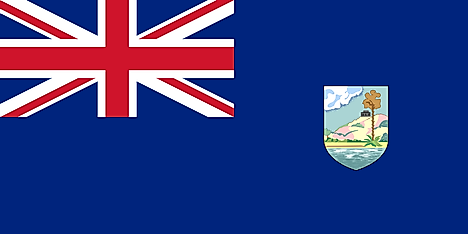
The first flag of Antigua and Barbuda had a simple design that followed the same pattern as most of the other colonial flags of the British Empire. The flag had a solid blue background which featured the Union Jack in the canton and the colonial coat of arms in the fly side. The coat of arms featured a natural scene representing the natural beauty of the island nation. This colonial flag was replaced when Antigua and Barbuda gained independence from the United Kingdom. The flag design was chosen from over 600 competitors as a part of a national competition organized in 1966 and was formally adopted on February 27, 1967. Full independence from the UK occurred in November 1981, but the new nation decided to retain the flag introduced as an associated state in 1967.
Symbols of Antigua and Barbuda
National Coat of Arms of Antigua and Barbuda

Antigua and Barbuda’s coat of arms was designed by Gordon Christopher in 1966 and was officially adopted on February 16, 1967. At the top of the Coat of Arms is a pineapple representing the famous Antigua Black Pineapple. The red hibiscus flowers are symbolic of the many varieties that bloom in the Nation. The Century Plant (DAGGER POLE) along with its stem and white flowers represents a part of the historic emblem of Antigua and the Leeward Islands. The design on the shield shows a golden sun rising from a blue and white sea. The sun represents a new beginning, the black background represents the African origins of most of the population. Supporting the shield are a pair of deer symbolic of the only large animal within the Eastern Caribbean and that is unique to the island nation. At the bottom of the shield, in front of the sea, sits a central sugar mill tower. Along with the stem of sugarcane, this symbolizes the production of sugar, which was once the main industry of the country. At the bottom is a scroll containing the National Motto.
National Motto
"Each Endeavouring, all achieving." It was composed by Mr. James H. Carrot M.B.E.
National Anthem
- Anthem Title: “Fair Antigua, We Salute Thee”
- Composer: Walter Garnet Picart Chambers
- Lyricist: Novelle Hamilton Richards
- Year of Completion: 1967
- Date of Adoption: 1981
The national anthem of Antigua and Barbuda is “Fair Antigua, We Salute Thee”. The music has been composed by Walter Garnet Picart Chambers while Novelle Hamilton Richards is the lyricist. It was officially adopted as the national anthem upon Antigua and Barbados' independence in 1981. Being a part of the British Commonwealth, “God Save the Queen” also serves as the royal anthem.
Fair Antigua, We Salute Thee (English)
Fair Antigua and Barbuda!
We thy sons and daughters stand
Strong and firm in peace or danger
To safeguard our native land
We commit ourselves to building
A true nation, brave and free;
Ever striving, ever seeking,
Dwell in love and unity
Raise the standard! Raise it boldly!
Answer now to duty’s call
To the service of thy country,
Sparing nothing giving all;
Gird your loins and join the battle
’Gainst fear, hate and poverty,
Each endeavouring, all achieving,
Live in peace where man is free.
God of nations, let Thy blessings
Fall upon this land ours;
Rain and sunshine ever sending,
Fill her fields with crops and flowers;
We her children do implore Thee,
Give us strength, faith, loyalty,
Never failing, all enduring
To defend her liberty.
The Currency of Antigua and Barbuda is the East Caribbean dollar
The current official currency of Antigua and Barbuda is the East Caribbean dollar ($, XCD). The East Caribbean dollar is also recognized as the official currency in all countries belonging to the organization of the Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). The East Caribbean dollar was first brought into circulation in 1965 replacing the British West Indies dollar.
Coins
Coins of the currency were circulating in 1, 2, 5, 10, and 25 cents denominations, and the 1 dollar was introduced at the beginning of 1981. Some of the coins have changed shape over the years, and they are composed of cupro-nickel and aluminum. The Ian Rank-Bradley design for Queen Elizabeth II’s portrait was adopted in 2002. The circulation of 1 and 2 cent coins was withdrawn in July 2015.
Banknotes
The Eastern Caribbean Currency Authority released notes of 1, 5, 20, and 100 dollars in 1965. Printed on the notes was the portrait of Queen Elizabeth done by Pietro Annigoni in 1956. The Eastern Caribbean Central Bank added the 10 dollars note in 1985 and the 50 dollars note in 1993. The institution also omitted the 1 dollar note. Banknotes issued by the Bank from April 1, 2008, excluded the country code letters and the barcode. Starting in 2012, the Bank rolled out a series of banknotes featuring Braille in the 10, 20, 50, and 100-dollar varieties.
Historical Currencies of Antigua and Barbuda
The gold standard was introduced in the British West Indies in 1704 through the proclamation of Queen Anne. The British introduced 1/4, 1/8, as well as 1/16 fractional ‘Anchor dollars' to be used in the British West Indies and Mauritius. Subsequently, copper fractional dollars were issued to circulate in Sierra Leone and Mauritius as well as in the British West Indies. Efforts to get the British sterling silver coinage in circulation in the colonies began in 1825 with an imperial order-in-council. Accounts in the region were kept in both sterling and dollars going into the 19th century. British Guiana, the Leeward Islands, Barbados, the Windward Islands, and Trinidad and Tobago participated in the West Indian Currency Conference in 1946 when they committed themselves to the creation of a common decimal currency system that was based on the West Indian dollar in replacement of the three Boards of Commissioners of currency that existed at the time. The British administration introduced the British West Indies dollar in 1949 in the Eastern Caribbean territories as well as in British Guiana. The new currency began circulating in 1950 when the Caribbean Currency Board (BCCB) was created in Trinidad. The British Virgin Islands together with Trinidad and Tobago subsequently withdrew their commitment from the new currency. The Eastern Caribbean dollar replaced the British West Indies dollar while the Eastern Caribbean Currency Authority was founded to replace the BCCB in 1965.