Countries Without a Railway Network

The railway network is the oldest form of transportation in the world, in fact, the history of railway network started in ancient Greece in the 6th century BCE. Previously it was used in mines, but with the introduction of steam engines, commercial railways were introduced and they helped people move from one place to the other. Although the railway network is used in hundreds of countries in the world, there are some countries without railway transportation.
Countries Without a Railway Network
Andorra
Andorra is the 11th smallest nation by population and the 16th tiniest by land. Other than the French railway line connecting Toulouse and Latour-de-Carol which runs approximately 1.2 miles into this country’s border, Andorra has never had a railway network. The nearest railway station is the one in France which is connected to the nation by a bus service to Andorra-la-Vella.
Bhutan
Bhutan is one of the smallest land-locked nations located in South Asia. Bhutan has no railway network, but there are plans to link the southern parts of Bhutan to the vast Indian railway network. India plans to construct an 11 mile long network linking Toribari in Nepal to Hashimara in western Bengal.
Cyprus
Currently, Cyprus has no operational railway network, but the country had a railway network which operated from 1905 to 1951. The train was 76 miles long with 39 stations but it closed down due to financial reasons. Another extension was constructed to serve the Cyprus-mines Corporation which shut down in 1974.
East Timor
East Timor has poor communication networks and transportation infrastructure. East Timor has never had a railway network, and the primary transportation system in the nation is via the roads which are in poor condition. There is a proposal to construct a 310.7 miles extended electrified single-track network running from Los Palos to Bobonaro.
Guinea-Bissau
Located in West Africa, Guinea-Bissau is one of the few African nations which have never had a railway network. The primary transportation method used in the country is via the tarmacked roads in the capital and the unpaved roads in the other towns. Guinea Bissau signed an agreement in 1998 with Portugal for the construction of a railway network in the country.
Iceland
Although there have been three railway networks in Iceland, the country has never had a public railway network. Iceland has no public railway network, and this is because of stiff competition from the automobile traffic, a small population, and harsh environmental conditions. There have been abandoned proposals for a railway network since the early 1900s. New plans were introduced in the 2000s to construct a railway in the capital city.
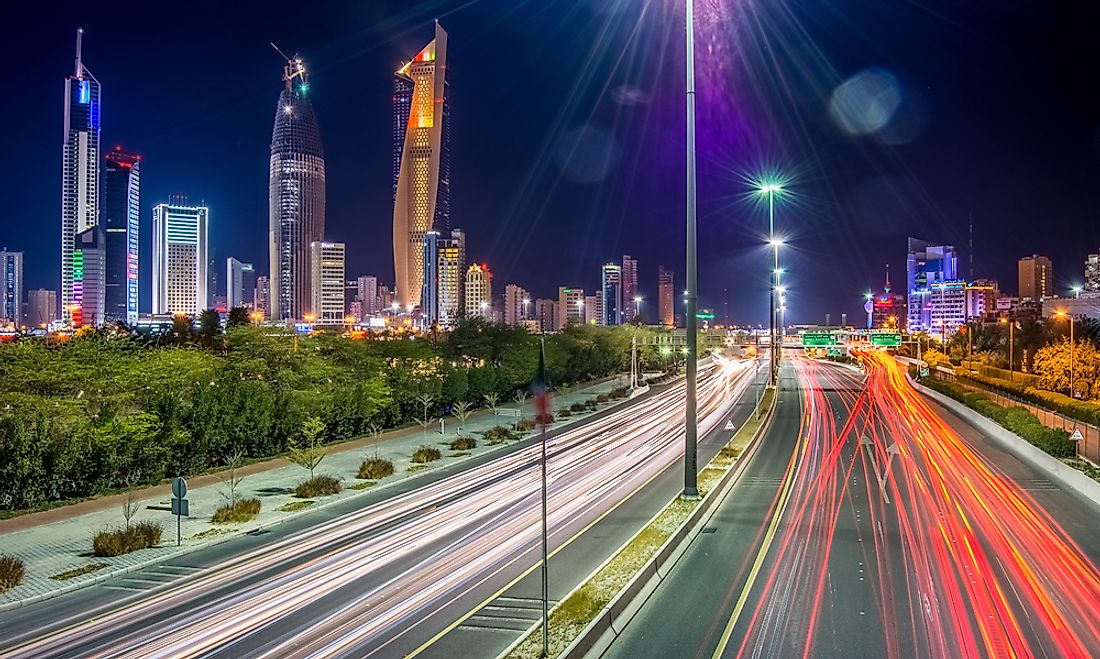
Kuwait
Kuwait is an oil-wealthy nation whose transport system is highly dominated by roads. Currently, Kuwait has no railway, but several railway network projects are being planned. The country plans to construct a 1,200 mile Gulf Railway network which will run from Kuwait city to Oman.
Libya
With all the previous railway lines dismantled, Libya has not had an operational railway network since 1965. Libya has numerous railway networks projects under construction. In fact, the construction of the line connecting Ras Ajdir and Sirte began in 2001. The development of the line from Ras Ajdir to Tripoli began in 2008 and 2009.
Why Do These Countries Lack Railway Networks?
The main reason why these nations do not have a railway network is due to lack of funds for construction. The primary challenge affecting the construction of railways in countries like Iceland is a poor environment. In the oil-rich nations like Kuwait, transportation is dominated by roads, so the government did not see the need for constructing a railway line, but congestion on the streets caused by an increased number of vehicles is forcing them to start building railway networks.
Countries Without a Railway Network
| Rank | List of Countries Without a Railway Network |
|---|---|
| 1 | Andorra |
| 2 | Bhutan |
| 3 | Cyprus |
| 4 | East Timor |
| 5 | Guinea-Bissau |
| 6 | Iceland |
| 7 | Kuwait |
| 8 | Kibya |
| 9 | Macau |
| 10 | Malta |
| 11 | Marshall Islands |
| 12 | Mauritius |
| 13 | Micronesia |
| 14 | Niger |
| 15 | Oman |
| 16 | Papua New Guinea |
| 17 | Qatar |
| 18 | Rwanda |
| 19 | San Marino |
| 20 | Solomon Islands |
| 21 | Somalia |
| 22 | Suriname |
| 23 | Tonga |
| 24 | Trinidad and Tobago |
| 25 | Tuvalu |
| 26 | Vanuatu |
| 27 | Yemen |