Where Is The Near East?

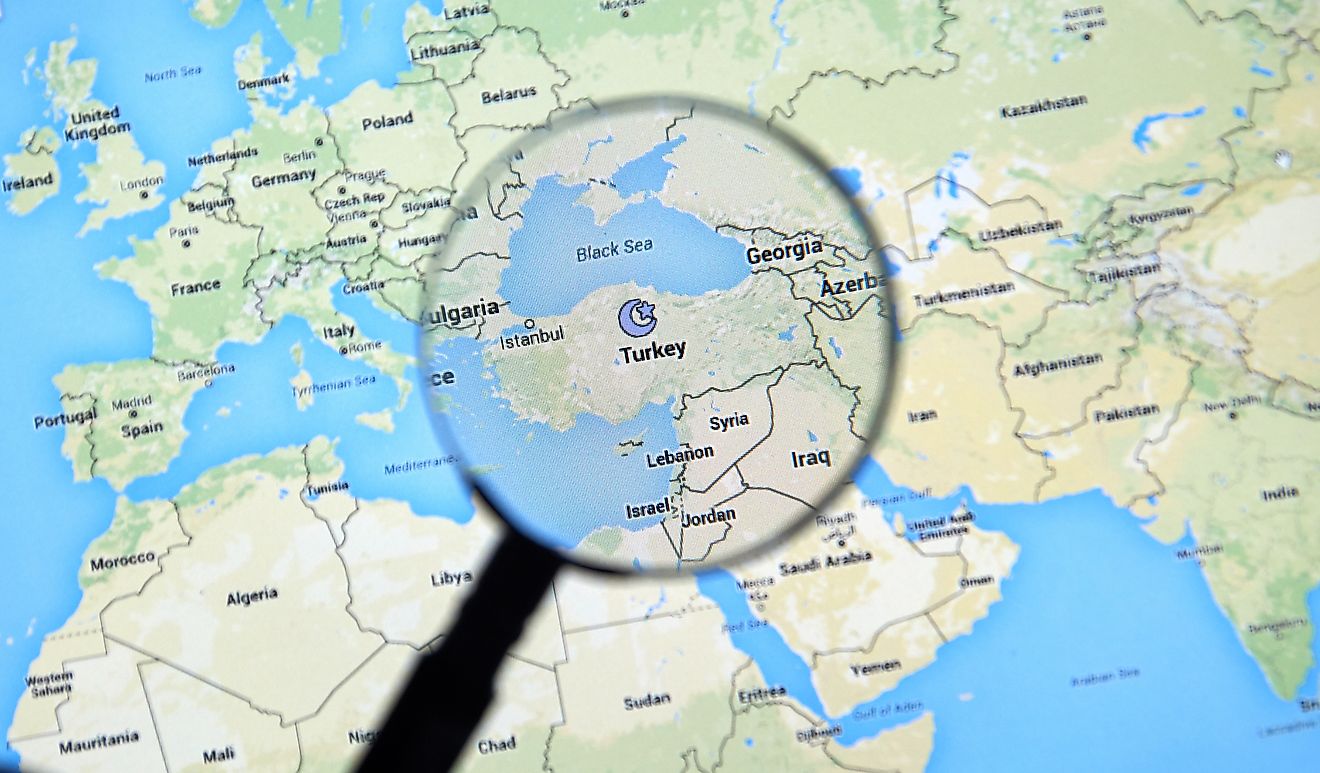
The Near East is the geographical region corresponding to western Asia. In modern times, the term is used interchangeably with the more common "Middle East". Sometimes, the Middle East and the Near East may include the same or different territories due to lack of a standard definition. The use of the term Near East began in the 19th century where areas to the east of Europe were defined by their closeness to Europe. In that case, the Near East was closest, followed by the Middle East and the Far East. Regions included in the Near East section were the Ottoman Empire and the Balkan plateau. The Arabian Peninsula, Egypt, Cyprus, Iraq, Iran, Jordan, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey and Palestinian territories make up the Near East region. Some sources such as the Food and Agriculture Organisation exclude North African countries and Palestinian territories and include Afghanistan. North African countries of the Near East region include Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt.
Ancient Near East
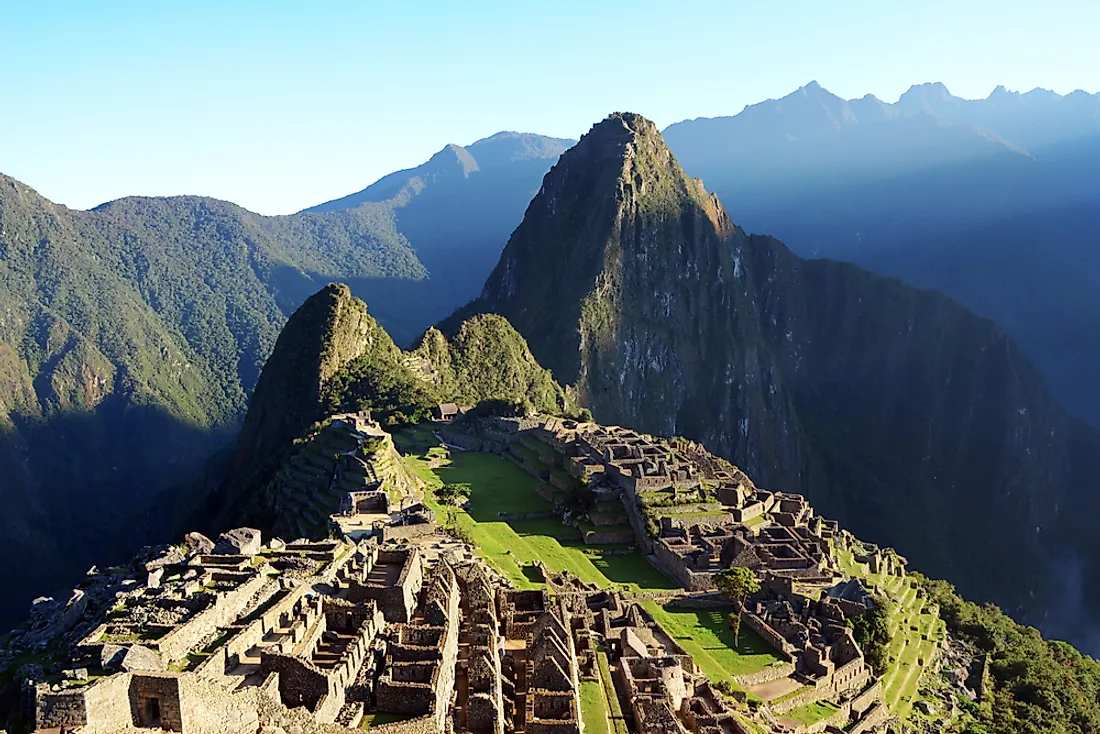
While the use of the term Near East has declined significantly and in its place the Middle East is used instead, archaeologists and historians often refer to the Near East and the ancient Near East in their scholarly studies and research. Ancient Near East is considered as one of the earliest homes to human civilizations with archaeological findings revealing artifacts of various ages and periods of civilization. Ancient Near East encompassed the modern day Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest and north-western Iran, north-eastern Syria, Asia Minor, the Armenian highlands, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, Cyprus, and the Arabian Peninsula. The modern use of the term Near East in archaeology, however, does not affect the fact that the ancient Near East represents regions of the Fertile Crescent.
The Eastern Question
In the 19th century diplomatic relations, the eastern question referred to the positions of the major European powers during the decline of the Ottoman Empire. The term Eastern question came about due to the location of the Ottoman Empire to the east of Europe. The near East played a significant role in the economic and political standing of these powers. For instance, British trade ties with the Ottoman Empire stood to lose should the Ottoman Empire fall. The near east region was also important for the Europeans in gaining access to other areas within the interior ofAsia such as Iran and the shores of southern and western Mediterranean (which were under the Ottoman rule). During this period, different authors from various regions defined the near east section, variously including or excluding some territories.
Middle East
The 20th century saw the increased reference of the Near East as the Middle East. With the fall of the colonial empire as well as the Ottoman Empire, diplomats and international agencies had to come up with a more descriptive term for the geographical region covered by the Near East. These agencies needed a more descriptive way to define their services and activities within the region. Some agencies and academic institutions still use the Near East in their reports or scholarly documents. The Middle East covers southwestern Asia as well as countries in North Africa (also referred to as MENA- Middle East and North Africa).