What And Where Are Coastal Deserts?
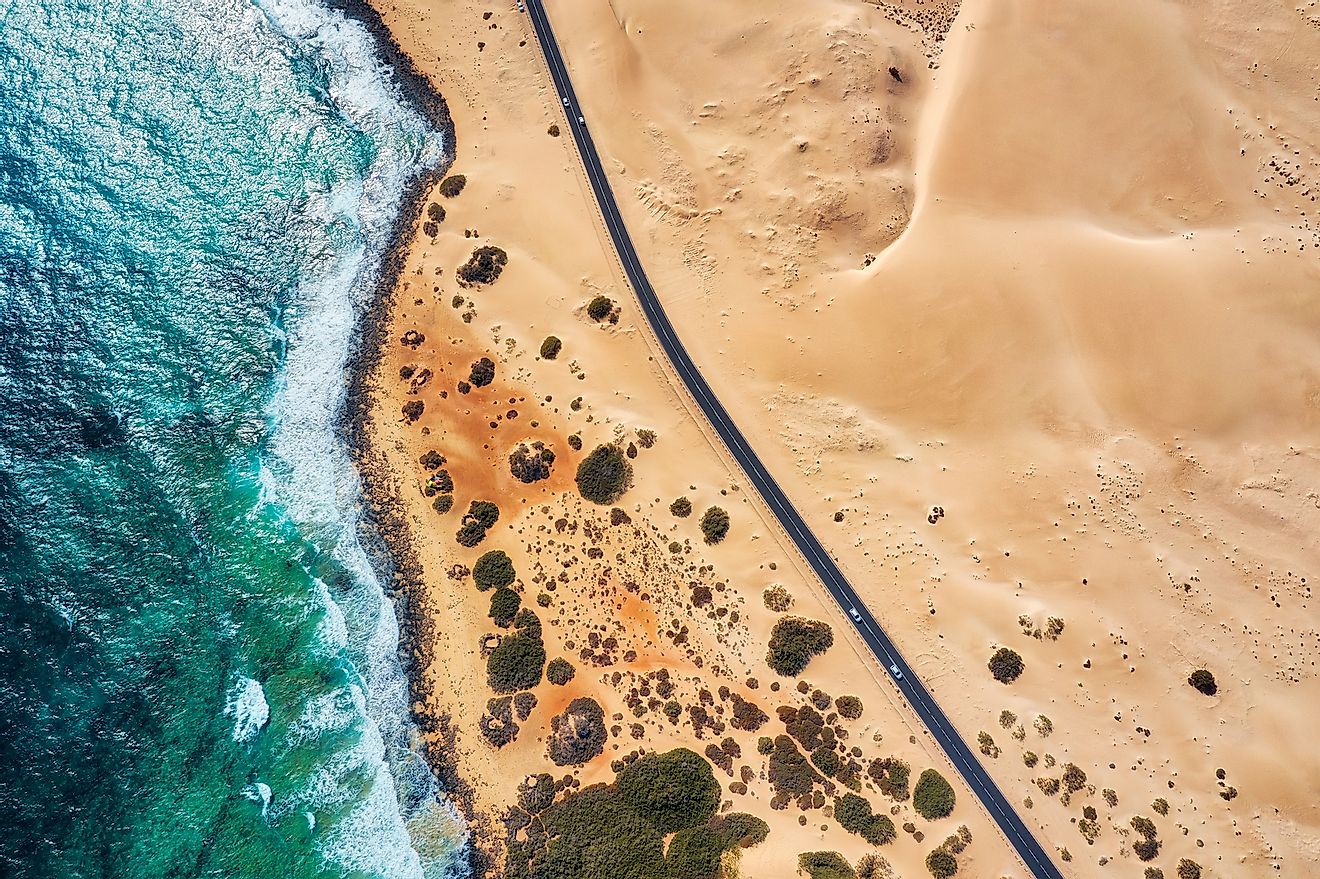

- Coastal deserts are one of the four major types of deserts.
- Such deserts are usually found on the western edges of continents with cold ocean currents running parallel to the coast.
- The Namib Desert of Africa and Atacama Desert of South America are examples of coastal deserts.
What Are Coastal Deserts?
As the name implies, coastal deserts are deserts stretching along the sea coast. They are one of the four major types of deserts. Their nearness to the sea gives them unique properties not found in deserts elsewhere. Such deserts are usually found on the western edges of continents with cold ocean currents running parallel to the coast. As the cold currents cool the air above, the air is unable to hold moisture and most of it falls as rain on the sea before it reaches land. Thus, the land alongside the coast with cold ocean currents receives little or no precipitation and turns into a desert.
Characteristics Of Coastal Deserts
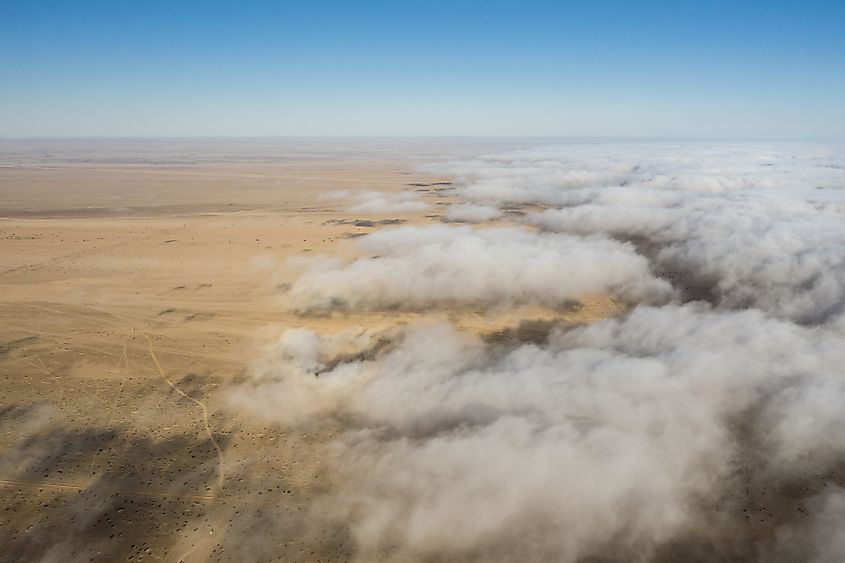

Coastal deserts have moderately brief winter seasons whose temperatures are 5°C and below, with the lowest recorded temperature being -4°C. The summer temperatures range from 13°C to 24°C, with 35°C being the highest ever experienced in the coastal deserts. An average of 13cm of rainfall is known to occur annually. Despite being near water sources, these deserts remain notably dry because most precipitation occurs in the ocean with negligible amounts of moisture reaching land. These deserts have more porous soils characterized by a moderate texture and salt content. Another unique feature of coastal deserts is the formation of heavy fogs in winter. Upwelling cold currents lead to the formation of such fogs often blanketing the desert and blocking solar rays from reaching the sands.
Plants And Animals Of Coastal Deserts
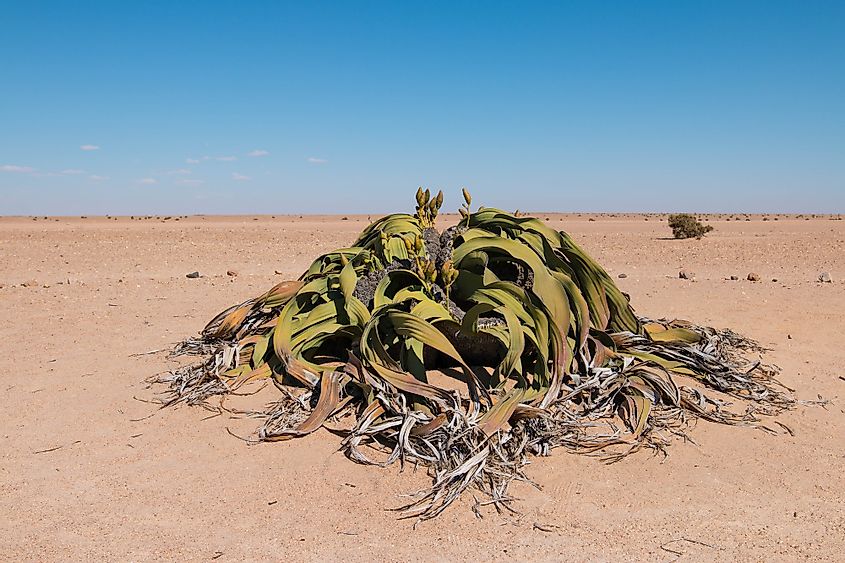

The plants growing in coastal deserts have thick fleshy leaves and stems for storing nutrients and extensive root systems for tapping whatever moisture is available. These adaptations help the plants survive the harsh coastal desert climate. Black sage, salt bushes, and rice grass are some of the plants growing in coastal deserts.
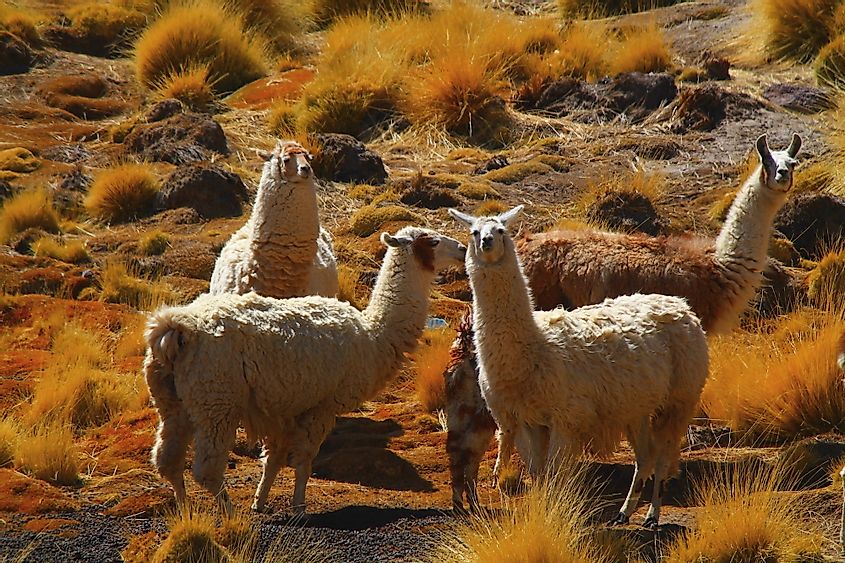

Coastal deserts support mammals like coyotes, gemsbok, Grant's golden mole, etc. Many species of reptiles and lizards are found including venomous snakes like Peringuey's adder. It also hosts birds like golden eagles, Karoo bustard, great horned owls, and others. Amphibians and invertebrate species also live in these deserts. The fauna of coastal deserts exhibit several adaptations to survive in the relatively harsher desert conditions. For example, several species of birds and reptiles living here lay eggs that remain dormant until conditions are more bearable.
Examples Of Coastal Deserts
Namib Desert
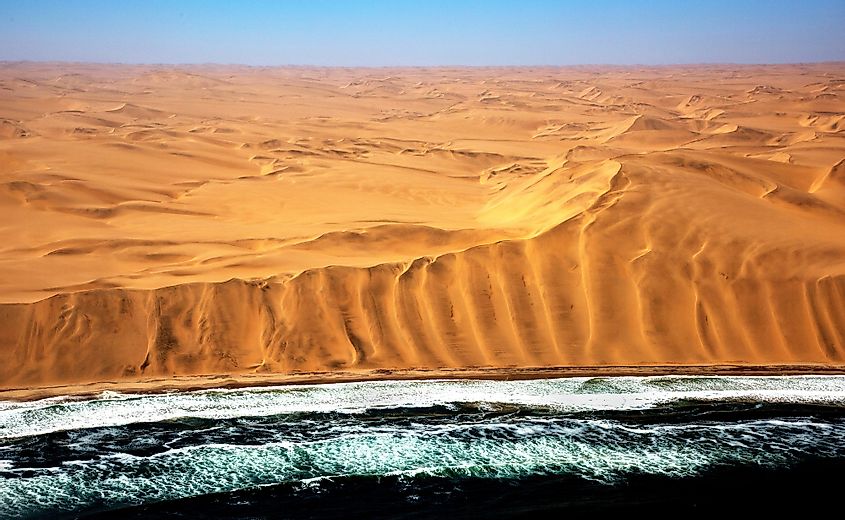

The Namib Desert is southern Africa is a coastal desert. It stretches for over 2,000 km along the Atlantic Ocean coast of Angola, Namibia, and South Africa. Annual precipitation here ranges from 0.079 in to 7.9 in. The Namib is regarded as the world's oldest desert as it has experienced arid to semi-arid conditions for around 55 to 80 million years.
Atacama Desert
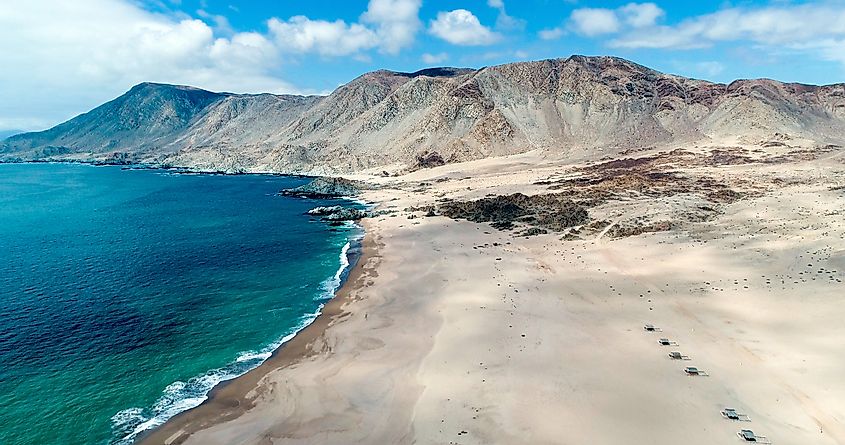

Another example of a coastal desert, the Atacama Desert extends for around 1,600 km along the Pacific Ocean coast in South America to the west of the Andes Mountains. After the polar deserts, it is the driest desert in the world. Due to its extreme habitat, the Atacama has served as an important site for experimentations for Mars expedition simulations. The desert is mostly barren stony terrain with sand, salt lakes, and felsic lava flows.