Where is Quinoa Grown?
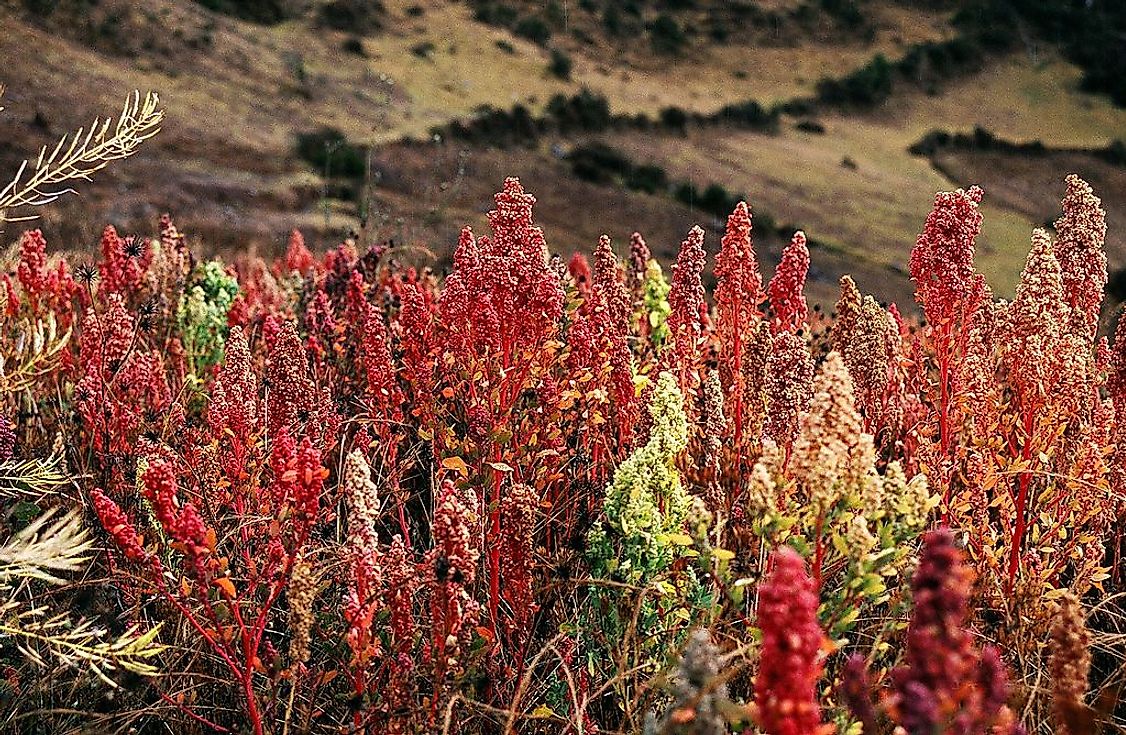

What Is Quinoa?
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) is a plant of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae. A pseudocereal, it is mainly grown as a grain crop for its seeds.
History Of Cultivation
The Quinoa plant is a native of the Andean region of South America. It was domesticated about 3,000 to 4,000 years back from weed or wild populations of the same species. The people living in the Lake Titicaca basin of Bolivia and Peru would grow this crop for consumption.
Description Of The Plant
The quinoa is a dicotyledonous annual plant that is about 1 to 2 meters tall. It possesses broad leaves that are hairy, powdery, and lobed. The central stem is woody in nature and may or may not be branched. This feature varies between varieties of the plant. The stem is red, purple or green in color. The flowers are green and hypogynous. They are self-fertilizing in nature. The fruits are about 2 mm in size and have varying colors from red to white to black. The seeds of this plant have a coating of saponin that is unpalatable and hence is removed during processing of the seeds. The saponin layer is, however, useful for cultivation purposes as it deters pests and birds from the crop, protecting it from damage.
How Is Quinoa Cultivated?
The quinoa plant’s optimum cultivation conditions vary with the varieties of the plant. In general, the plant is altitude-hardy and requires less attention and care than many other crop plants. The quinoa plant is grown from lowland coastal areas to elevations as high as 13,000 feet in the Andes. The plants grow best in a cool climate where temperatures vary between −4 °C at night to 35 °C during the day. Light frosts do not affect the growth of the plant except for when it is flowering. 300 to 1,000 mm of rainfall during the growing season is within the acceptable limit of rainfall for the growth of the quinoa plant.
Production Of Quinoa
In 2014, 192.5 thousands of tons of quinoa was produced in the world. Three South American countries were the top producers of the crop in the same year. With a production of 114.3 thousand tons, Peru was the largest quinoa producer. The second leading quinoa producer was Bolivia with a production of 77.4 thousand tons. Ecuador ranked third by producing 0.8 thousand tons of quinoa in 2014.
Uses Of Quinoa
Quinoa in the raw, uncooked form contains 64% carbohydrates, 14% protein, 13% water, and 6% fat. Quinoa is a rich source of dietary fiber, protein, B vitamins, and dietary minerals like phosphorus, manganese, iron, magnesium, and zinc. The product is gluten free and hence easy to digest.
After harvesting, the quinoa seeds are processed to remove the saponin-containing outer coating. Then, the seeds are cooked in a way similar to rice and used to prepare a variety of dishes. The leaves of the plant are consumed as a leaf vegetable.
The Top Quinoa Producing Countries In The World
| Rank | Country | Production in thousand metric tons, 2014 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Peru | 114.3 |
| 2 | Bolivia | 77.4 |
| 3 | Ecuador | 0.8 |
| 4 | Total | 192.5 |